
Concept explainers
Have you ever wondered whether soccer players suffer adverse effects from hitting “headers”? The authors of the article “No Evidence of Impaired Neurocognitive Performance in Collegiate Soccer Players” (Amer. J. of Sports Med., 2002: 157–162) investigated this issue from several perspectives.
a. The paper reported that 45 of the 91 soccer players in their sample had suffered at least one concussion, 28 of 96 nonsoccer athletes had suffered at least one concussion, and only 8 of 53 student controls had suffered at least one concussion. Analyze this data and draw appropriate conclusions.
b. For the soccer players, the sample
c. Here is summary information on scores on a controlled oral word-association test for the soccer and nonsoccer athletes:
Analyze this data and draw appropriate conclusions.
d. Considering the number of prior nonsoccer concussions, the values of
a.
Analyze the given data and draw conclusions.
Answer to Problem 47SE
There is sufficient evidence to conclude that there is a difference in the proportion of concussion with respect to three groups.
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
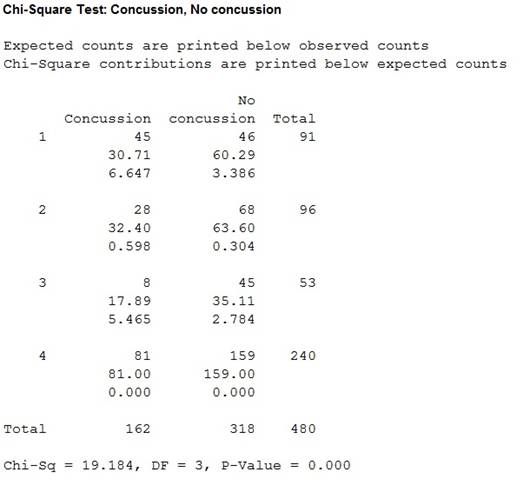
The report says that 45 out of 91 soccer players had suffered at least one concussion, 28 of 96 non-soccer athletes suffered at least one concussion and 8 of 53 students had at least one concussion.
Calculation:
From the given data the following can be observed,
| Group | Concussion | No concussion | Total |
| Soccer | 45 | 46 | 91 |
| Non soccer | 28 | 68 | 96 |
| student | 8 | 45 | 53 |
| Total | 81 | 159 | 240 |
The claim is to test whether there is any homogeneity among the proportion of concussions with respect to the three groups. If the claim is rejected, then there is no homogeneity among the proportion of concussions with respect to the three groups.
Null hypothesis:
That is, the proportion of concussions is homogenous with respect to the three groups.
Alternative hypothesis:
Test statistic:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to find the chi-square test statistic using MINITAB is given below:
- Choose Stat > Tables > Chi-Square Test (Two-Way Table in Worksheet).
- In Columns containing the table, enter the columns of Concussion and Nonconcussion.
- Click OK.
Output obtained from MINITAB is given below:
Decision rule:
If
If
Conclusion:
The P-value is 0.000 and the least level of significance is 0.001.
The P-value is lesser than the level of significance.
That is,
Thus, the null hypothesis isrejected.
Hence, there is sufficient evidence to conclude that there is a difference in the proportion of concussion with respect to three groups.
b.
Interpret the given results.
Answer to Problem 47SE
There is no sufficient evidence to conclude that there exists a negative correlation or association in the population at 1% level of significance.
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
The sample correlation coefficient for the soccer players group is calculated by using the soccer exposure x and the score on an immediate memory recall test y and it is –0.220.
Calculation:
Testing the significance of correlation:
Null hypothesis:
That is, there is no correlation between x and y.
Alternative hypothesis:
That is, there is a negative correlation between x and y.
Test statistic:
Where,
r represents the correlation coefficient value.
n represents the total sample size.
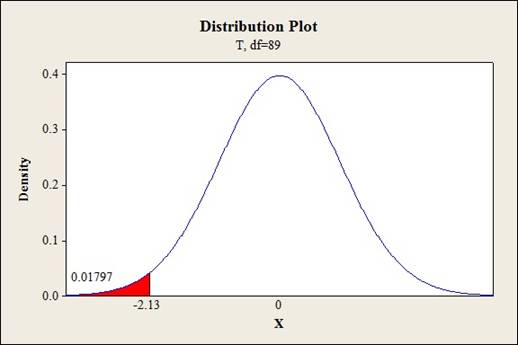
Substitute r as –0.220 and n as 91.
Thus, the test statistic is –2.13.
P-value:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the P-value is given below:
- Click on Graph, select View Probability and click OK.
- Select t, enter 89 in degrees of freedom..
- Under Shaded Area Tab select X value under Define Shaded Area By and select left tail.
- Choose X value as –2.13.
- Click OK.
Output obtained from MINITAB is given below:
Conclusion:
The P-valueis 0.018 and the level of significance is 0.01.
The P-valueis lesser than the level of significance.
That is,
Thus, the null hypothesis is not rejected.
Hence, there is no sufficient evidence to conclude that there exists a negative correlation or association in the population at 1% level of significance.
c.
Analyze the given data and draw conclusions.
Answer to Problem 47SE
There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the average scores of two groups are the same.
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
An oral test was conducted for soccer and non-soccer athletes. The summary statistics are given below:
Calculation:
Testing the hypothesis:
Null hypothesis:
That is, the average test score is same for the two groups.
Alternative hypothesis:
That is, the average test score is not the same for the two groups.
Test statistic:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the test statistic using MINITAB is given below:
- Choose Stat > Basic Statistics > 2-Sample t.
- Choose Summarized data.
- In first, enter Sample size as 26, Mean as 37.50, Standard deviation as 9.13.
- In second, enter Sample size as56, Mean as 39.63, Standard deviation as 10.19.
- Select Assume equal variances.
- Choose Options.
- In Confidence level, enter 95.
- Choose not equal in Alternative.
- Click OK.
Output obtained from MINITAB is given below:

Conclusion:
The P-value is 0.366 and the level of significance is 0.10.
The P-value is greater than the level of significance.
That is,
Thus, the null hypothesis is not rejected.
Hence, there is sufficient evidence to conclude that the average scores of two groups are the same.
d.
Analyze the given data and draw conclusions.
Answer to Problem 47SE
There is sufficient evidence to conclude that there is a difference in the average number of prior non-soccer concussion between the three groups.
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
The mean plus or standard deviation for the three groups with respect to the number of prior non-soccer concussions are
Calculation:
Testing the hypothesis:
Null hypothesis:
That is, there is no difference in the average number of prior non-soccer concussion between the three groups.
Alternative hypothesis:
That is, there is a difference in the average number of prior non-soccer concussion between the three groups.
Test statistic:
Where,
MSE represents the mean sum of squares due to error.
Sum of squares with respect to the three groups is calculated as follows:
Where,
Mean sum of squares due to treatment:
Sum of squares due to error:
Mean sum of squares due to error:
Thus, the F-statistic is calculated as follows:
Critical value:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the P-value is given below:
- Click on Graph, select View Probability and click OK.
- Select F, enter 2 in numerator df and 236 in denominator df.
- Under Shaded Area Tab select X value under Define Shaded Area By and select right tail.
- Choose Probability as 0.05.
- Click OK.
Output obtained from MINITAB is given below:
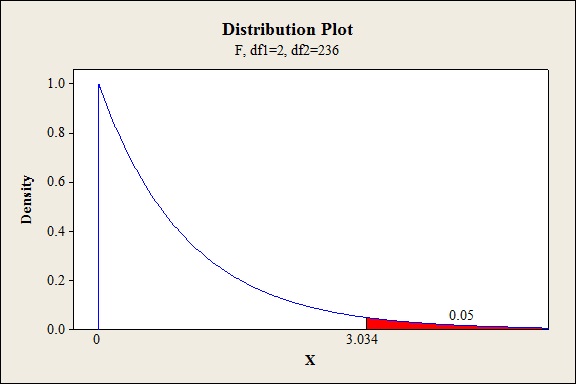
Thus, the critical value is 3.034.
Conclusion:
The test statisticis 3.319and the critical value is 3.034.
The test statisticis lesser than the critical value.
That is,
Thus, the null hypothesis is rejected.
Hence, there is sufficient evidence to conclude that there is a difference in the average number of prior non-soccer concussion between the three groups.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
EBK PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS FOR ENGI
- Obtain the linear equation for trend for time series with St² = 140, Ey = 16.91 and Σty= 62.02, m n = 7arrow_forwardA quality characteristic of a product is normally distributed with mean μ and standard deviation σ = 1. Speci- fications on the characteristic are 6≤x≤8. A unit that falls within specifications on this quality characteristic results in a profit of Co. However, if x 8, the profit is -C2. Find the value ofμ that maximizes the expected profit.arrow_forwardA) The output voltage of a power supply is normally distributed with mean 5 V and standard deviation 0.02 V. If the lower and upper specifications for voltage are 4.95 V and 5.05 V, respectively, what is the probability that a power supply selected at random conform to the specifications on voltage? B) Continuation of A. Reconsider the power supply manufacturing process in A. Suppose We wanted to improve the process. Can shifting the mean reduce the number of nonconforming units produced? How much would the process variability need to be reduced in order to have all but one out of 1000 units conform to the specifications?arrow_forward
- der to complete the Case X T Civil Service Numerical Test Sec X T Casework Skills Practice Test Maseline Vaseline x + euauthoring.panpowered.com/DeliveryWeb/Civil Service Main/84589a48-6934-4b6e-a6e1-a5d75f559df9?transferToken-News NGSSON The table below shows the best price available for various items from 4 uniform suppliers. The prices do not include VAT (charged at 20%). Item Waterproof boots A1-Uniforms (£)Best Trade (£)Clothing Tech (£)Dress Right (£) 59.99 39.99 59.99 49.99 Trousers 9.89 9.98 9.99 11.99 Shirts 14.99 15.99 16.99 12.99 Hi-Vis vest 4.49 4.50 4.00 4.00 20.00 25.00 19.50 19.99 Hard hats A company needs to buy a set of 12 uniforms which includes 1 of each item. If the special offers are included which supplier is cheapest? OOO A1-Uniforms Best Trade Clothing Tech Q Search + ** 109 8 CO* F10 Home F11 F12 6arrow_forwardto complete the Case × T Civil Service Numerical Test Sec x T Casework Skills Practice Test + Vaseline euauthoring.panpowered.com/DeliveryWeb/Civil Service Main/84589a48-b934-4b6e-a6e1-a5d75f559df9?transferToken=MxNewOS NGFSPSZSMOMzuz The table below shows the best price available for various items from 4 uniform suppliers. The prices do not include VAT (charged at 20%). Item A1-Uniforms (£)Best Trade (£)Clothing Tech (£)Dress Right (£) Waterproof boots 59.99 39.99 59.99 49.99 Trousers 9.89 9.98 9.99 11.99 Shirts 14.99 15.99 16.99 12.99 Hi-Vis vest 4.49 4.50 4.00 4.00 20.00 25.00 19.50 19.99 Hard hats A company needs to buy a set of 12 uniforms which includes 1 of each item. If the special offers are included, which supplier is cheapest? O O O O A1-Uniforms Best Trade Clothing Tech Dress Right Q Search ENG L UK +0 F6 四吧 6 78 ㄓ F10 9% * CO 1 F12 34 Oarrow_forwardCritics review films out of 5 based on three attributes: the story, the special effects and the acting. The ratings of four critics for a film are collected in the table below.CriticSpecialStory rating Effects rating Acting rating Critic 14.44.34.5Critic 24.14.23.9Critic 33.943.4Critic 44.24.14.2Critic 1 also gave the film a rating for the Director's ability. If the average of Critic 1's ratings was 4.3 what rating did they give to the Director's ability?3.94.04.14.24.3arrow_forward
- Two measurements are made of some quantity. For the first measurement, the average is 74.4528, the RMS error is 6.7441, and the uncertainty of the mean is 0.9264. For the second one, the average is 76.8415, the standard deviation is 8.3348, and the uncertainty of the mean is 1.1448. The expected value is exactly 75. 13. Express the first measurement in public notation. 14. Is there a significant difference between the two measurements? 1 15. How does the first measurement compare with the expected value? 16. How does the second measurement compare with the expected value?arrow_forwardA hat contains slips of paper numbered 1 through 6. You draw two slips of paper at random from the hat,without replacing the first slip into the hat.(a) (5 points) Write out the sample space S for this experiment.(b) (5 points) Express the event E : {the sum of the numbers on the slips of paper is 4} as a subset of S.(c) (5 points) Find P(E)(d) (5 points) Let F = {the larger minus the smaller number is 0}. What is P(F )?(e) (5 points) Are E and F disjoint? Why or why not?(f) (5 points) Find P(E ∪ F )arrow_forwardIn addition to the in-school milk supplement program, the nurse would like to increase the use of daily vitamin supplements for the children by visiting homes and educating about the merits of vitamins. She believes that currently, about 50% of families with school-age children give the children a daily megavitamin. She would like to increase this to 70%. She plans a two-group study, where one group serves as a control and the other group receives her visits. How many families should she expect to visit to have 80% power of detecting this difference? Assume that drop-out rate is 5%.arrow_forward
- A recent survey of 400 americans asked whether or not parents do too much for their young adult children. The results of the survey are shown in the data file. a) Construct the frequency and relative frequency distributions. How many respondents felt that parents do too much for their adult children? What proportion of respondents felt that parents do too little for their adult children? b) Construct a pie chart. Summarize the findingsarrow_forwardThe average number of minutes Americans commute to work is 27.7 minutes (Sterling's Best Places, April 13, 2012). The average commute time in minutes for 48 cities are as follows: Click on the datafile logo to reference the data. DATA file Albuquerque 23.3 Jacksonville 26.2 Phoenix 28.3 Atlanta 28.3 Kansas City 23.4 Pittsburgh 25.0 Austin 24.6 Las Vegas 28.4 Portland 26.4 Baltimore 32.1 Little Rock 20.1 Providence 23.6 Boston 31.7 Los Angeles 32.2 Richmond 23.4 Charlotte 25.8 Louisville 21.4 Sacramento 25.8 Chicago 38.1 Memphis 23.8 Salt Lake City 20.2 Cincinnati 24.9 Miami 30.7 San Antonio 26.1 Cleveland 26.8 Milwaukee 24.8 San Diego 24.8 Columbus 23.4 Minneapolis 23.6 San Francisco 32.6 Dallas 28.5 Nashville 25.3 San Jose 28.5 Denver 28.1 New Orleans 31.7 Seattle 27.3 Detroit 29.3 New York 43.8 St. Louis 26.8 El Paso 24.4 Oklahoma City 22.0 Tucson 24.0 Fresno 23.0 Orlando 27.1 Tulsa 20.1 Indianapolis 24.8 Philadelphia 34.2 Washington, D.C. 32.8 a. What is the mean commute time for…arrow_forwardMorningstar tracks the total return for a large number of mutual funds. The following table shows the total return and the number of funds for four categories of mutual funds. Click on the datafile logo to reference the data. DATA file Type of Fund Domestic Equity Number of Funds Total Return (%) 9191 4.65 International Equity 2621 18.15 Hybrid 1419 2900 11.36 6.75 Specialty Stock a. Using the number of funds as weights, compute the weighted average total return for these mutual funds. (to 2 decimals) % b. Is there any difficulty associated with using the "number of funds" as the weights in computing the weighted average total return in part (a)? Discuss. What else might be used for weights? The input in the box below will not be graded, but may be reviewed and considered by your instructor. c. Suppose you invested $10,000 in this group of mutual funds and diversified the investment by placing $2000 in Domestic Equity funds, $4000 in International Equity funds, $3000 in Specialty Stock…arrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt




