
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The statement “Hexanoic acid has a lower melting point than hexanal” has to be predicted as true or false. If the statement is false, the reason for the false statement has to be described.
(a)
Answer to Problem 2MCP
The given statement is false because hexanoic acid has a higher melting point than hexanal due to exclusive intermolecular hydrogen bonding and strong dipole-dipole attractions.
Explanation of Solution
Hexanoic acid is a
Carboxylic acids have high melting point when compared to alcohols,
Therefore, hexanoic acid has a higher melting point than hexanal. This higher melting point of hexanoic acid is due to intermolecular hydrogen bonding and strong dipole-dipole attractions.
Hence, the statement “Hexanoic acid has a lower melting point than hexanal” is false.
(b)
Interpretation:
The statement “Hexanoic acid has a higher boiling point than hexanol” has to be predicted as true or false. If the statement is false, the reason for the false statement has to be described.
(b)
Answer to Problem 2MCP
The given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
Hexanoic acid is a carboxylic acid and hexanol is an alcohol.
Carboxylic acids have strong intermolecular hydrogen bonding with each other and strong dipole-dipole attractions.
The presence of polar carboxyl group and intermolecular hydrogen bonding makes these acids have higher boiling points. The presence of dimers increases the strength of the van der Waals dispersion forces, which makes them have high boiling points.
Therefore, hexanoic acid has a boiling point than hexanol. This higher boiling point of hexanoic acid is due to intermolecular hydrogen bonding and strong dipole-dipole attractions.
Hence, the statement “Hexanoic acid has a higher boiling point than hexanol” is true.
(c)
Interpretation:
The statement “Hexanoic acid is not soluble in water” has to be predicted as true or false. If the statement is false, the reason for the false statement has to be described.
(c)
Answer to Problem 2MCP
The given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
Hexanoic acid is a saturated fatty acid with a medium chain length of six carbons. The carboxylate group
Therefore, hexanoic acid is barely soluble in water or insoluble in water. Hence, the statement “hexanoic acid is not soluble in water” is true.
(d)
Interpretation:
The statement “Hexanoic acid is polar” has to be predicted as true or false. If the statement is false, the reason for the false statement has to be described.
Concept Introduction:
Carboxylic acid consists of carboxyl group. A carboxyl group is a
(d)
Answer to Problem 2MCP
The given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
The functional group present in carboxylic acids is carboxyl group
Carboxylic acids are polar in nature. This is due to the presence of the carboxyl group that comprises of two polar functional groups namely, carbonyl group and hydroxyl group. The carbonyl group is polar due to the presence of oxygen, which is more electronegative than carbon. This produces a dipole in which oxygen carries a partial negative charge and carbon carries a partial positive charge. This allows intermolecular dipole-dipole attractions. The hydroxyl group is polar because oxygen is higher electronegativity than hydrogen and oxygen atom has two unpaired electrons. This results in the formation of polar bond in which oxygen carries a partial negative charge and hydrogen carries a partial positive charge. This results in the formation of hydrogen bonding.
Therefore, hexanoic acid is polar in nature due to presence of polar carbonyl and hydroxyl groups. Hence, the statement “Hexanoic acid is polar” is true.
(e)
Interpretation:
The line formula of hexanoic acid has to be predicted as true or false. If the statement is false, the reason for the false statement has to be described.
(e)
Answer to Problem 2MCP
The given line formula of hexanoic acid is false because it represents hexanal.
Explanation of Solution
The given line formula is,
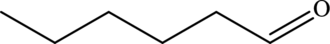
The above line formula represents hexanal.
Hence, the given line formula is false because it represents hexanal.
The line formula of hexanoic acid is,
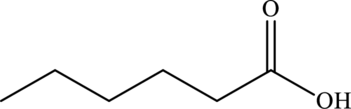
(f)
Interpretation:
The statement “Hexanoic acid is solid at room temperature” has to be predicted as true or false. If the statement is false, the reason for the false statement has to be described.
(f)
Answer to Problem 2MCP
The given statement is false because it appears as an oily liquid at room temperature.
Explanation of Solution
Hexanoic acid appears as a colorless oily liquid with an odor that is fatty, cheesy and waxy. It is found naturally in various animal fats and oils.
It has chemical formula
The common name of hexanoic acid is caproic acid. It is a saturated medium-chain fatty acid with six-carbon backbone.
Hence, the statement “Hexanoic acid is solid at room temperature” is false because it is an oily liquid in room temperature.
(g)
Interpretation:
The statement “Oxidation of hexanoic acid would produce a primary alcohol” has to be predicted as true or false. If the statement is false, the reason for the false statement has to be described.
(g)
Answer to Problem 2MCP
The given statement is false because the oxidation of primary alcohol (hexanol) would produce hexanoic acid.
Explanation of Solution
Hexanoic acid can be produced by the oxidation of hexanol that is primary alcohol. The equation is,
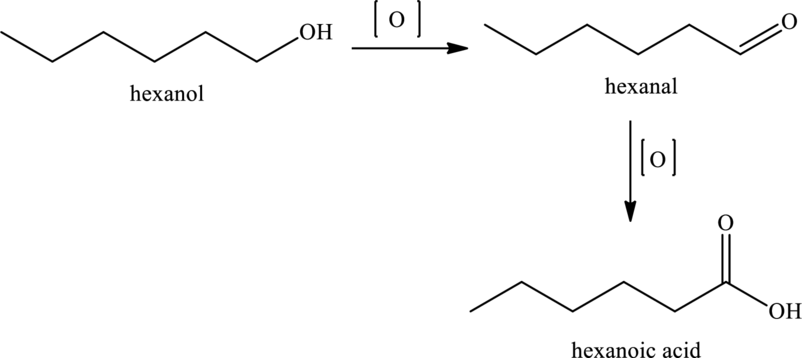
Therefore, the statement “Oxidation of hexanoic acid would produce a primary alcohol” is false because primary alcohols undergo oxidation to form hexanoic acid and not the vice-versa.
(h)
Interpretation:
The statement “Hexanoic acid is more oxidized than hexanal” has to be predicted as true or false. If the statement is false, the reason for the false statement has to be described.
(h)
Answer to Problem 2MCP
The given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
The presence of hydrogen bonding capabilities and the presence of two oxygen atoms makes them more oxidized than hexanal.
Hence, the statement “Hexanoic acid is more oxidized than hexanal” is true.
(i)
Interpretation:
The statement “The reaction of hexanoic acid with an ethanol molecule would produce an acetal” has to be predicted as true or false. If the statement is false, the reason for the false statement has to be described.
(i)
Answer to Problem 2MCP
The given statement is false because an ester is produced when hexanoic acid is reacted with ethanol.
Explanation of Solution
The addition of an ethanol molecule to hexanoic acid results in the formation of ethyl hexanoate, an ester. The reaction is,
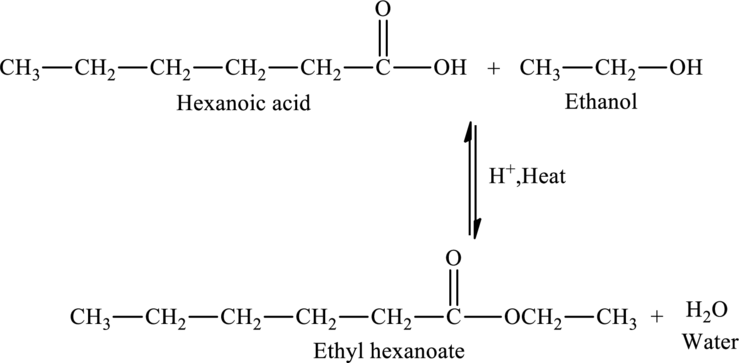
The statement “Hexanoic acid reaction with an ethanol would produce an acetal” is false because an ester called ethyl hexanoate is produced when an ethanol molecule is added to hexanoic acid.
(j)
Interpretation:
The statement “The reaction of hexanoic acid with sodium hydroxide would produce sodium hexanoate” has to be predicted as true or false. If the statement is false, the reason for the false statement has to be described.
(j)
Answer to Problem 2MCP
The given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of hexanoic acid with sodium hydroxide would produce sodium hexanoate and water.
The
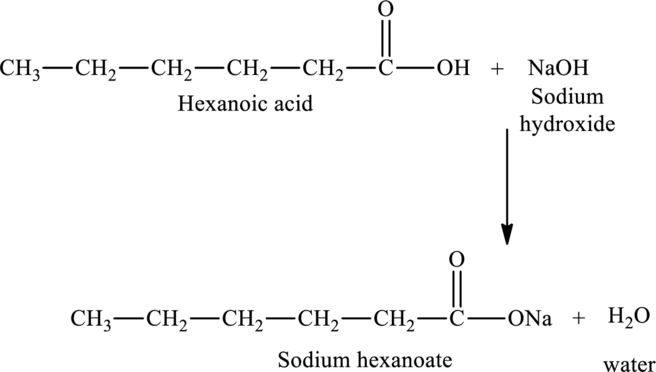
Hence, the statement “The reaction of hexanoic acid with sodium hydroxide would produce sodium hexanoate” is true.
(k)
Interpretation:
The statement “The reaction of hexanoic acid with methanol would produce hexyl methanoate” has to be predicted as true or false. If the statement is false, the reason for the false statement has to be described.
(k)
Answer to Problem 2MCP
The given statement is false because an ester named methyl hexanoate is produced when hexanoic acid is reacted with methanol.
Explanation of Solution
The addition of methanol to hexanoic acid results in the formation of methyl hexanoate, an ester. The reaction is,
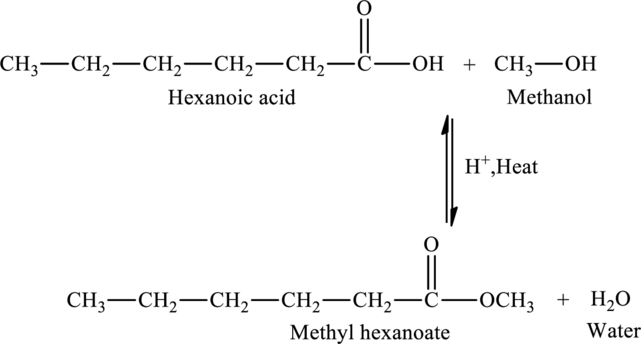
The statement “The reaction of hexanoic acid with methanol would produce hexyl methanoate” is false because an ester named methyl hexanoate is produced when hexanoic acid is reacted with methanol.
(l)
Interpretation:
The statement “Hexanoic acid could be produced by the oxidation of
(l)
Explanation of Solution
The oxidation of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
GENERAL,ORGANIC+BIOCHEM (LOOSELEAF)
- Done 18:25 www-awu.aleks.com .III LTE Chapter 12 HW Question 29 of 39 (6 points) | Question Attempt: 1 of Unlimi... Oli 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Consider this structure. CH2 CH2CH2 CH2CH2CH₂ C -C. -CH2CH3 H CH Part: 0 / 3 Part 1 of 3 Give the IUPAC name of this structure. Skip Part < Check ☑ Save For Later © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility ....................arrow_forwardCalculate Ecell at 25.0 oC using the following line notation. Zn(s)|Zn+2(aq, 0.900 M)||Cu+2(aq, 0.000200 M)|Cu(s)arrow_forwardPredict the product of this organic reaction: O OH + H + OH A P + H2O Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of P. If there isn't any P because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X G ☐ :arrow_forward
- 0.0994 g of oxalic acid dihydrate is titrated with 10.2 mL of potassium permanganate. Calculate the potassium permanganate concentration. Group of answer choices 0.0433 M 0.135 M 0.0309 M 0.193 Marrow_forwardExperts...can any one help me solve these problems?arrow_forwardAccording to standard reduction potential data in Lecture 4-1, which of the following species is the most difficult to reduce? Group of answer choices Zn2+ AgCl(s) Al3+ Ce4+arrow_forward
- Which Group 1 metal reacts with O2(g) to form a metal peroxide (M2O2)? Group of answer choices Li K Rb Naarrow_forwardWhich of the following statements is true regarding the reaction between Group 1 metals and water? Group of answer choices These reactions result in a basic solution. The metals do not actually react easily with water due to the metals' lack of conductivity. These reaction result in an acidic solution. The metals need their outer coatings of metal oxides to react.arrow_forwardWhich element cannot interact with hydrogen through hydrogen bonds? Group of answer choices O S Br Narrow_forward
- Which of the following statements is false regarding hydrogen gas production? Group of answer choices Steam reforming requires a catalyst. Methanol (CH3OH) can react with water using a ZnO catalyst to form H2(g). Methanol (CH3OH) can react with O2(g) using a Pd catalyst to form H2(g). The reaction between CH4(g) and H2O to form H2(g) requires a temperature of at least 700 oCarrow_forwardWhich of the following forms of hydrogen is the least stable? Group of answer choices H H2 H− H+arrow_forwardConsider the following reduction half reactions and standard reduction potentials: Fe3+ + e− → Fe2+ Eo = +0.77 V Fe2+ + e− → Fe(s) Eo = -0.44 V Which of the following statements is true? Group of answer choices The Fe2+ reduction to Fe(s) is spontaneous. Fe2+ can disproportionate into Fe3+ and Fe(s) The Fe3+ reduction to Fe2+ is not spontaneous. Fe3+ and Fe(s) can undergo a comproportionation reaction to form Fe2+arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





