
Computing Divisional Income: Incomplete Information and Financial Ratios
As a part of an employment interview, you are given the partial income statement and selected financial ratios shown for Sneaky Pete’s, a chain of western stores. Sneaky Pete’s is organized into two divisions: Mountain and Valley. You are told that corporate
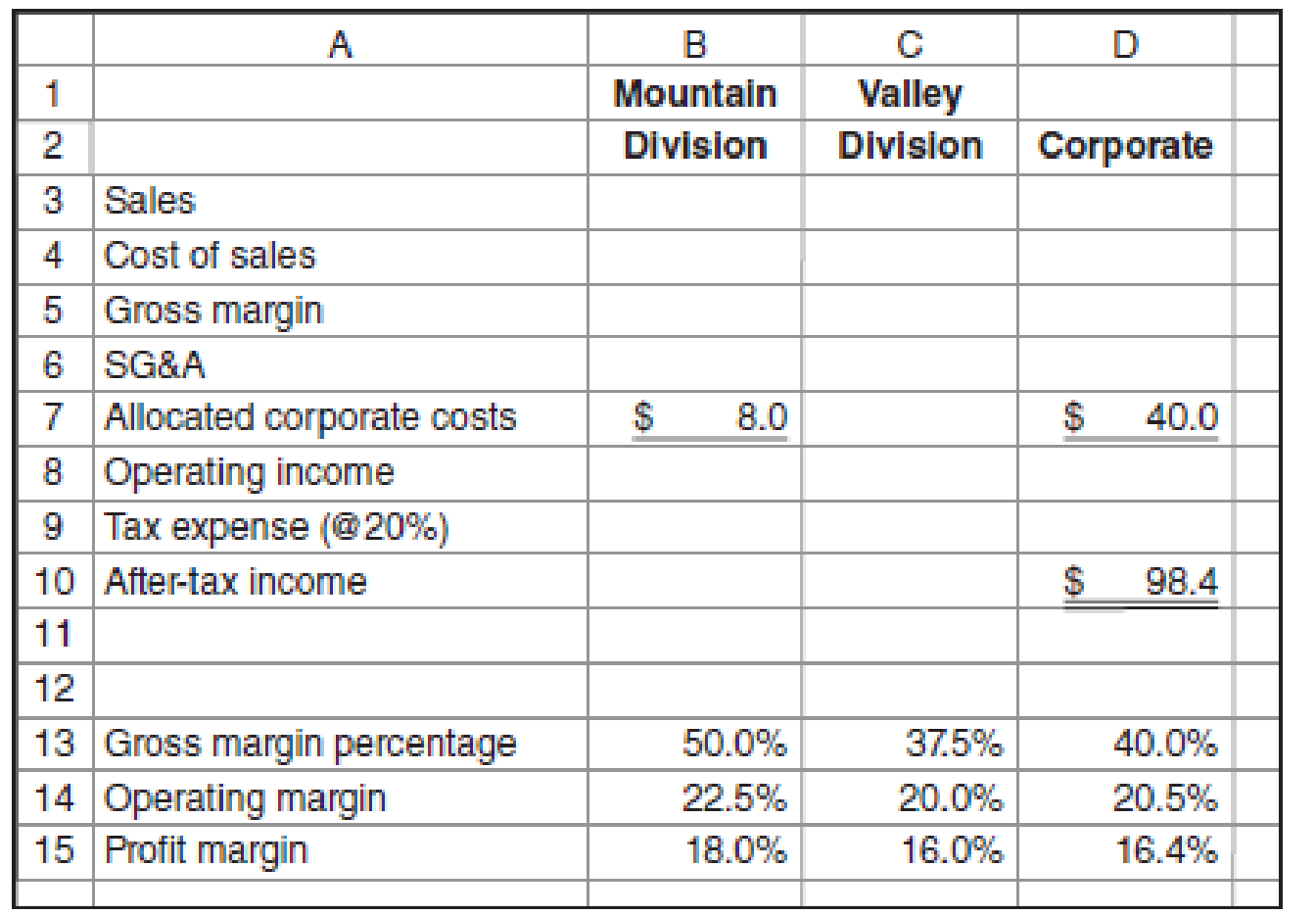
Required
- a. Complete the income statements for both divisions and the corporation as a whole.
- b. What recommendation(s) would you make about computing divisional income for divisional performance measurement at Sneaky Pete’s?
a.
Complete the income statements for both divisions along with the corporation as a whole.
Explanation of Solution
Divisional income statement:
The divisional income statement shows the income of various divisions of the business. It calculates the operating profit of the division by subtracting the expenses of the business from the sales of the division.
Calculate the divisional income statement for mountain division, valley division and corporate:
|
Company S Divisional Income Statement | |||
| Particulars | Mountain division | Valley division | Corporate |
| Sales | $120.00(6) | $480.00(7) | $600.00(1) |
| Cost of sales | $60.00(10) | $300.00(10) | $360.00(4) |
| Gross margin | $60.00(8) | $180.00(8) | $240.00(3) |
| SG&A | $25.00(9) | $52.00(5) | $77.00(5) |
| Allocated corporate costs | $8.00 | $32.00(11) | $40.00 |
| Operating income(a) | $27.00(8) | $96.00(8) | $123.00(2) |
| Tax expenses | $5.40 | $19.20 | $24.60 |
| After tax profit | $21.60 | $76.80 | $98.40 |
Table: (1)
Working note 1:
Calculate the overall corporate sales:

Working note 2:
Calculate the operating income:

Working note 3:
Calculate the gross margin:
Working note 4:
Calculate the cost of sales:
Working note 5:
Calculate the SG&A:
Working note 6:
Calculate the sales for mountain division:
The allocated corporate costs are allocated on the basis of sales. The sales level is $600 on the costs of $40, and it will be computed as follows for the costs of $8:
Working note 7:
Calculate the sales for valley division:
Working note 8:
Calculate the gross and operating income for both the divisions:
| Particulars |
Sales (a) |
Gross margin (b) |
Operating margin (c) |
Gross margin |
Operating profit |
| Mountain division | $120 | 50% | 23% | $60 | $27 |
| Valley division | $480 | 38% | 20% | $180 | $96 |
Table: (2)
Working note 9:
Calculate the SG&A:
Working note 10:
Calculate the cost of sales:
| Particulars | Sales | Gross margin | Cost of sales |
| Mountain division | 120 | 50% | $60 |
| Valley division | 480 | 38% | $298 |
Table: (3)
Working note 11:
Calculate the allocated corporate costs:
b.
Provide recommendations to Company S.
Explanation of Solution
Recommendations to company S:
Company S should not allocate the corporate cost to the divisions. It is not a division specific cost so it should not be allocated on the basis of the revenue of the unit.
Thus, Company S should not allocate the corporate cost to the mountain division and valley division.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Fundamentals of Cost Accounting
- Help me in this general account tutorarrow_forwardABC Company sold a machine for $56,000 that originally cost $306,000. The balance of the Accumulated Depreciation account related to this equipment was $240,000. The entry to record the gain or loss on the disposal of this machine would include: a. A debit to gain in the amount of $10,000 b. A debit to loss in the amount of 10,000 c. A credit to loss in the amount of $10,000 d. A credit to gain in the amount of $10,000arrow_forwardProvide answer general accountingarrow_forward
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning





