
Concept explainers
A = 2300 mm2, I = 9.5(106) mm4.
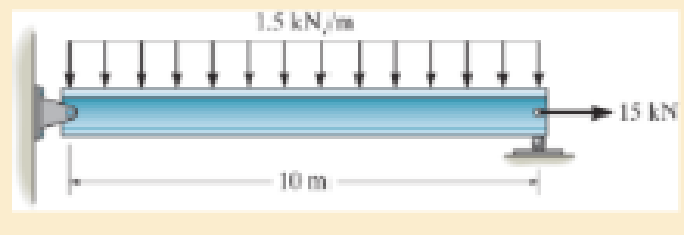
R14–1
Answer to Problem 1RP
The total axial and bending strain energy in the A992 steel beam is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The cross-sectional area of the beam is
Moment of inertia of the beam is
Assumption:
The modulus of elasticity or Young’s modulus of theA992 steelis
Explanation:
Determine the reactions:
Entire beam:
Show the free body diagram of the entire beam as in Figure 1.
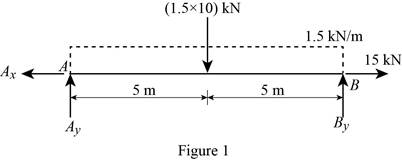
Moment about the point A:
Determine the vertical reaction at point B by taking moment about point A.
Along the vertical direction:
Determine the vertical reaction at point B by resolving the vertical component of forces.
Along the horizontal direction:
Determine the horizontal reaction at point A by resolving the horizontal component of force.
Show the calculation of reaction as follows:
Solve Equation (1).
Substitute 7.5kN for
Solve Equation (3).
Region
Show the free-body diagram of the section as in Figure 2.
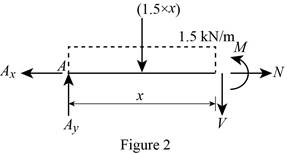
Moment about the section:
Determine the moment at section by taking moment about the section.
Along the horizontal direction:
Determine the normal axial force at the section by resolving the horizontal component of forces.
Show the calculation of values as follows:
Substitute 7.5kN for
Substitute 15 kN for
Strain energy due to axial load:
Determine the strain energy of a bar of constant cross-sectional area A and constant internal axial load N using the equation.
Here, N is the axial load, L is the length of beam, E is Young’s modulus or modulus of elasticity, and A is cross-sectional area of the beam.
Substitute 15 kN for N, 10 m for L,
Strain energy due to Bending:
Determine the strain energy in the beam due to bending using the equation.
Here, M is the moment in the beam and I is the moment of inertia of the beam.
Substitute 10 m for L,
Total strain energy:
Determine the total strain energy by adding the strain energy due to axial load and the strain energy due to bending.
Substitute 2.4456 J for
Thus, the total axial and bending strain energy in the A992 steel beam is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm (16th Edition)
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
BASIC BIOMECHANICS
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
- Homework#5arrow_forwardIf you have a spring mass damper system, given by m*x_double_dot + c*x_dot + kx = 0 where m, c, k (all positive scalars) are the mass, damper coefficient, and spring coefficient, respectively. x ∈ R represents the displacement of the mass. Using linear stability analysis, show that the system is asymptotically stable. Hint: stability of a linear system z_dot = Az is characterized by the eigenvalues of A.arrow_forwardWhat would the electropneumatic diagram of a circuit with the sequence a+b+c+(a-b-c-) look like?arrow_forward### What would the electropneumatic diagram of a circuit with the sequence a+b+c+(a-b-c-) look like, with a counter, in the fluidsim?arrow_forwardYou are asked to design a unit to condense ammonia. The required condensation rate is 0.09kg/s. Saturated ammonia at 30 o C is passed over a vertical plate (10 cm high and 25 cm wide).The properties of ammonia at the saturation temperature of 30°C are hfg = 1144 ́10^3 J/kg andrv = 9.055 kg/m 3 . Use the properties of liquid ammonia at the film temperature of 20°C (Ts =10 o C):Pr = 1.463 rho_l= 610.2 kf/m^3 liquid viscosity= 1.519*10^-4 kg/ ms kinematic viscosity= 2.489*10^-7 m^2/s Cpl= 4745 J/kg C kl=0.4927 W/m CCalculate the surface temperature required to achieve the desired condensation rate of 0.09 kg/s( should be 688 degrees C) a) Show that if you use a bigger vertical plate (2.5 m-wide and 0.8 m-height), the requiredsurface temperature would be now 20 o C. You may use all the properties given as an initialguess. No need to iterate to correct for Tf. b) What if you still want to use small plates because of the space constrains? One way to getaround this problem is to use small…arrow_forwardHomework#5arrow_forwardQuestion 1: Beam Analysis Two beams (ABC and CD) are connected using a pin immediately to the left of Point C. The pin acts as a moment release, i.e. no moments are transferred through this pinned connection. Shear forces can be transferred through the pinned connection. Beam ABC has a pinned support at point A and a roller support at Point C. Beam CD has a roller support at Point D. A concentrated load, P, is applied to the mid span of beam CD, and acts at an angle as shown below. Two concentrated moments, MB and Mc act in the directions shown at Point B and Point C respectively. The magnitude of these moments is PL. Moment Release A B с ° MB = PL Mc= = PL -L/2- -L/2- → P D Figure 1: Two beam arrangement for question 1. To analyse this structure, you will: a) Construct the free body diagrams for the structure shown above. When constructing your FBD's you must make section cuts at point B and C. You can represent the structure as three separate beams. Following this, construct the…arrow_forwardA differential element on the bracket is subjected to plane strain that has the following components:, Ɛx = 300 × 10-6, Ɛy = 150 × 10-6, Ɛxy = -750 x 10-6. Use the strain-transformation equations and determine the normal strain Ɛx in the X/ direction on an element oriented at an angle of 0 = 40°. Note, a positive angle, 0, is counter clockwise. x Enter your answer in micro strain to a precision of two decimal places. eg. if your answer is 300.15X106, please enter 300.15.arrow_forwardIf the 50 mm diameter shaft is made from brittle material having an ultimate strength of σult=595 MPa for both tension and compression, determine the factor of safety of the shaft against rupture. The applied force, F, is 140 kN. The applied torque T, is 5.0 kN⚫m. Enter your answer to a precision of two decimal places. T Farrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_iosRecommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY