
(a)
To prove: The law of conservation of flow at a andat e.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Proof:
WE have given a directed network set V, the capacity of arc uv denoted
At a,
(b)
The value of the indicated flow;
(b)
Explanation of Solution
It is well known that, the value of flow
That the net amount of flow per unit time leaving the source or, entering the sink.
(c)
The capacity of the
(c)
Explanation of Solution
He capacity of an
Therefore, the capacity of the cut is
(d)
The flow be increased along the path sbft.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
No, the flow cannot be increased along the path sbft because, this path contains bf the saturated arc.
(e)
Whether the “given flow maximum” or not.
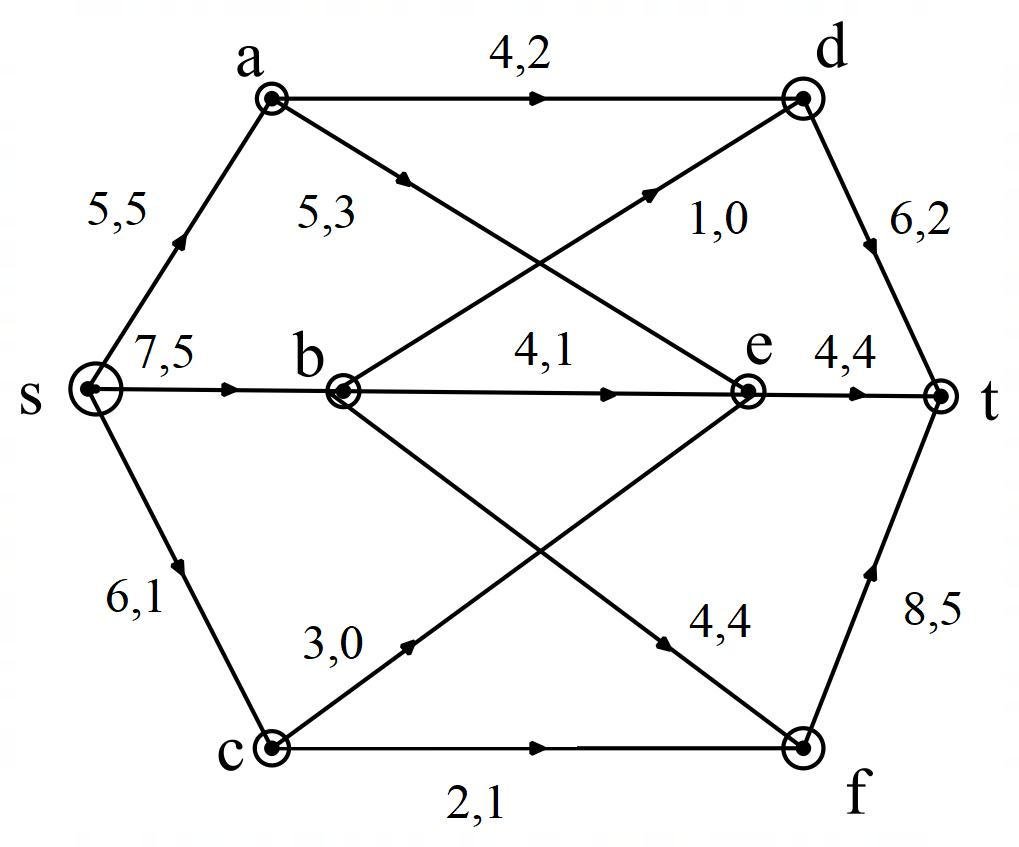
(e)
Explanation of Solution
The
Therefore the flow is not maximum.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Discrete Mathematics with Graph Theory (Classic Version) (3rd Edition) (Pearson Modern Classics for Advanced Mathematics Series)
- 2. Consider the matrix: A || 1 1 -3 14 2 1 01 4 1 2 2 -26 1 -3 1 5] a) What is rank(A)? b) Is A invertible? Justify. c) Find the nullspace(A). Justify. d) Is the trivial solution the only solution to Ax=0? Justify. e) What is the span of the column vectors of A? Justify.arrow_forwardE 5. Suppose that S={v € R²: v = [2x² - 3]}. Is S a subspace of R²? Prove or disprovearrow_forward6. Suppose that V1, V2 ER", show that span{v1, v2} is a subspace of Rn.arrow_forward
- Ra X 2) slots per pole per phase 3/31 180 Ko Sin (1) Kdl 1 sin (4) sin(3) Sin (30) اذا مرید شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3) Cos (30) 0.866 4) Rotating 5) Synchronous speed, 120 Fo lasa! G s.1000-950 20:05 1000 Capper losses: 5kw Rotor input lookw 0.05 ined sove in peaper I need a detailed solution on paper please 6) 1 ۳/۱ وه اذا ميريد شرح الكتب فقط look DC 7) rotov Find the general solution of the following equations: +4y=tan2x 3 7357 Find the general solution of the following equations: - Qll y + y (³) = 0. 101arrow_forwardNC Current Students - North Ce X | NC Canvas Login Links - North ( X Final Exam Comprehensive x Cengage Learning x WASTAT - Final Exam - STAT → C webassign.net/web/Student/Assignment-Responses/submit?dep=36055360&tags=autosave#question3659890_9 Part (b) Draw a scatter plot of the ordered pairs. N Life Expectancy Life Expectancy 80 70 600 50 40 30 20 10 Year of 1950 1970 1990 2010 Birth O Life Expectancy Part (c) 800 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 1950 1970 1990 W ALT 林 $ # 4 R J7 Year of 2010 Birth F6 4+ 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 Year of 1950 1970 1990 2010 Birth Life Expectancy Ox 800 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 Year of 1950 1970 1990 2010 Birth hp P.B. KA & 7 80 % 5 H A B F10 711 N M K 744 PRT SC ALT CTRLarrow_forwardB: 18060 msl Kd Ka, Sin (n) I sin () sin(30) Sin (30) اذا ميريد شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3) Cos (30) 0.866 4) Rotating 5) Synchronous speed, 120 x 50 G 5005 1000 s = 1000-950 Copper bosses 5kW /0001 Rotor input 5 : loo kw 0.05 6) 1 اذا ميريد شرح الكتب فقط ١٥٠ 7) rotov DC ined sove in Deaper I need a detailed solution on paper please dy x+2y-4 = dx 2x-y-3 Find the general solution of the following equations: 02//yl-4y+13y=esinarrow_forward
- 1) R₂ = X2 2) slots per pole per phase = 3/31 B msl kd 180 60 Kal Sin (1) I sin () sin(30) Sin (30) اذا ميريد شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3) Cos (30) 0.866 4) Rotating 5) Synchronous speed, 120 x 50 G 5005 1000 s = 1000-950 Copper bosses 5kW Rotor input: 5 0.05 loo kw 6) 1 /0001 اذا ميريد شرح الكتب فقط look 7) rotov DC ined sove in peaper I need a detailed solution on paper please Q1// Find the solution of: 'y' = x² +376 x4+316 xyo Q2 Find the solution of the initial-valued problems: ex-y y' +exarrow_forwardR₂ = X2 2) slots per pole per phase = 3/31 B-18060 msl kd Kasi Sin (1) I sin (6) sin(30) Sin (30) اذا ميريد شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3) Cos (30) 0.866 4) Rotating 5) Synchronous speed s = 1000-950 1000 Copper losses: 5kw Rotor input 5 0.05 6) 1 120 x 50 G loo kw ined sove in peaper I need a detailed solution on paper please Q3// x²y// +xy/ + (x² - ½) y = x³/². اذا ميريد شرح الكتب فقط look 7) rotor DC Q4// x²y// - (2x+x²)y/ + (2 + x)y = x³. dy 2x+2y+4 = dx 2x-y-3arrow_forward۳/۱ R2X2 2) slots per pole per phase = 3/31 B, 18060 msl Kas Sin() 1sin() sin(30) Sin (30) kd اذا ميريد شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3) Cos (30) 0.866 4) Rotating 5) Synchronous speeds S = 1000-950 1000 Copper bosses 5kw 120*50 loca G Rotor input 5 loo kw 6) 1 0.05 اذا ميريد شرح الكتب فقط lookw 7) rotor DC ined sove in peaper I need a detailed solution on paper please 064 Q1// Find the solution of QI/Find the solution of Inxy= 7357 x+2y³ y' = xy3arrow_forward
- R₂ = X2 2) slots per pole per phase 3/31 msl 180 60 Kd Ka Sin (1) Isin (6) sin(30) Sin (30) اذا ميريد شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3) Cos (30) 0.866 4) Rotating 5) Synchronous speed, 120*50 1000 6 S = 1000-950 1000 Copper bosses: 5kw Rotor input 5 0.05 : loo kw 6) 1 اذا ميريد شرح الكتب فقط 100 7) rotor DC ined sove in peaper I need a detailed solution on paper please Find the general solution of the following equations: Q2lyl-4y+13y=esinx. Find the general solution of the following equations: " Qly (49) - 16y= 0. 151arrow_forward۳/۱ R₂ = X2 2) slots per pole per phase = 3/31 B-18060 msl kd Kasi Sin (1) I sin (6) sin(30) Sin (30) اذا ميريد شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3) Cos (30) 0.866 4) Rotating 5) Synchronous speed s = 1000-950 1000 Copper losses: 5kw Rotor input 5 0.05 6) 1 120 x 50 G loo kw اذا میرید شرح الكتب فقط look 7) rotor DC ined sove in peaper I need a detailed solution on paper dy please 04 12=-cosx.y + 2cosx with y(x) = 1 か 'Oy + xlny + xe")dx + (xsiny + xlnx +*dy=0. 01arrow_forward٣/١ R2X2 2) slots per pole per phase = 3/31 B, 18060 msl kd Kas Sin (1) 1sin() sin(30) Sin (30) اذا ميريد شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3) Cos (30) 0.866 4) Rotating 5) Synchronous speeds S = 1000-950 1000 Copper bosses 5kw 120*50 loca G Rotor input 5 loo kw 0.05 6) 1 اذا ميريد شرح الكتب فقط lookw 7) rotor ined sove in peaper I need a detailed solution on paper please DC 口 04 on its wheels as shown in figure. The the door is 8 m below the free surface o is located at the center of the d no water leaks an accident and lands at the bottom of the lake 12m high and I m wide, and the top edge of water Determine the hydrostatic force on the discuss if the driver can open the door, if ong person can lift 100 kg, the passenger The door can be approximated as a vertical rec | 279|-|(23+2+12+20=2) AA Find the general solution of the following equations: 11 - 1/4+xy/-(1-x²³)= 0. 2arrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning

