
Concept explainers
What Is Static Equilibrium?
Problems 1–3 are grouped.
1. C A ball is attached to a strong, lightweight rod (Fig. P14.1). The rod is supported by a horizontal pin near the top. The ball is at rest. Is the ball in static equilibrium? If not, why not? If so, which type of equilibrium is it—stable, unstable, or neutral? Hint: What would happen if you displaced the ball slightly?
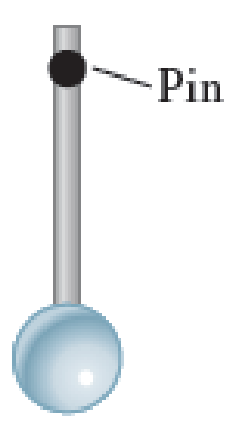
FIGURE P14.1
Whether the ball is in static equilibrium and if so the type of equilibrium in which the ball is present.
Answer to Problem 1PQ
The ball is in static equilibrium and it is stable equilibrium.
Explanation of Solution
Equilibrium is a special case of motion in which an object’s translational momentum and angular momentum are both constant. Static equilibrium is a special case in which the object’s translational momentum and angular momentum are zero. This also implies that for an object to be in static equilibrium, the total force and the total torque acting on the object must be zero. There are three types of static equilibrium namely stable static equilibrium, unstable static equilibrium and neutral static equilibrium. If an object returns to its equilibrium position after being released, it will be in stable equilibrium. If an object moves farther away from the equilibrium position after being released, it will be in unstable equilibrium. If an object is moved and released from a new position and does not move toward or away from its equilibrium position, then the object is in neutral equilibrium.
It is given that the ball in the figure is at rest so that it has no acceleration. This implies the net force and the torque acting on the ball are zero and the ball must be in static equilibrium. If the ball is displaced slightly, it will return to or pass through the equilibrium position. According to the definition, it is stable equilibrium.
Conclusion:
Thus, the ball is in stable static equilibrium since the net force and the torque acting on it is zero and it returns to its equilibrium position when it is displaced slightly.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
- RT = 4.7E-30 18V IT = 2.3E-3A+ 12 38Ω ли 56Ω ли r5 27Ω ли r3 28Ω r4 > 75Ω r6 600 0.343V 75.8A Now figure out how much current in going through the r4 resistor. |4 = unit And then use that current to find the voltage drop across the r resistor. V4 = unitarrow_forward7 Find the volume inside the cone z² = x²+y², above the (x, y) plane, and between the spheres x²+y²+z² = 1 and x² + y²+z² = 4. Hint: use spherical polar coordinates.arrow_forwardганм Two long, straight wires are oriented perpendicular to the page, as shown in the figure(Figure 1). The current in one wire is I₁ = 3.0 A, pointing into the page, and the current in the other wire is 12 4.0 A, pointing out of the page. = Find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field at point P. Express your answer using two significant figures. VO ΜΕ ΑΣΦ ? Figure P 5.0 cm 5.0 cm ₁ = 3.0 A 12 = 4.0 A B: μΤ You have already submitted this answer. Enter a new answer. No credit lost. Try again. Submit Previous Answers Request Answer 1 of 1 Part B X Express your answer using two significant figures. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ 0 = 0 ? below the dashed line to the right P You have already submitted this answer. Enter a new answer. No credit lost. Try again.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





