
Concept explainers
To match: The given terms with the anatomical parts of the brain and the functional areas.
Introduction: The human brain is a fascinating organ that weighs about 1.4 kilograms and contains about 100 billion neurons. The brain along with the spinal cord makes up the central nervous system and controls the functions and abilities of the human body.
Answer to Problem 1P
Pictorial representation: Fig.1 shows a diagram of the anatomical parts of the brain and functional areas.
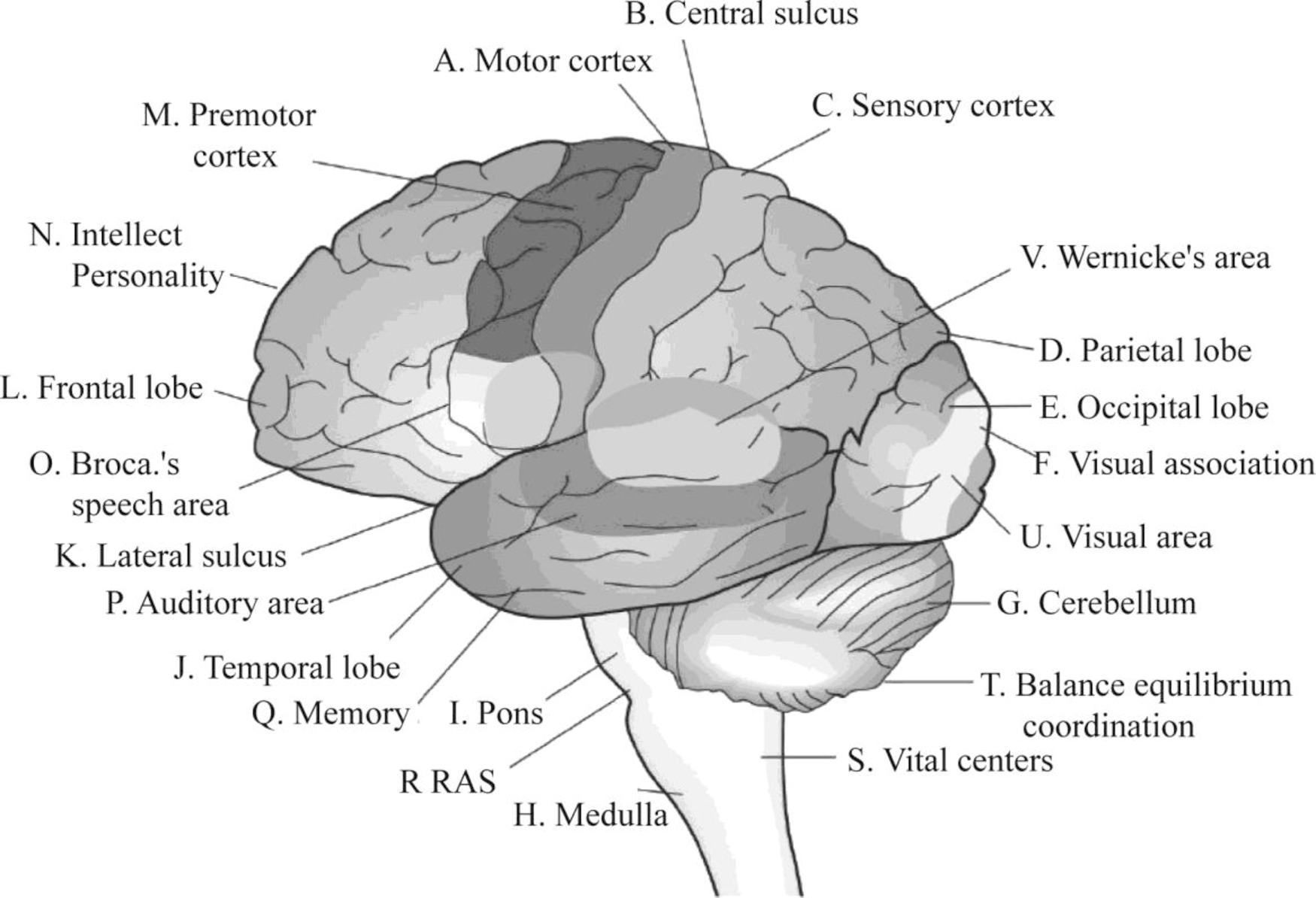
Fig 1 Anatomical structure of the brain and functional areas
Explanation of Solution
Anatomic Features:
A. Motor Cortex: The motor cortex of the brain is the region of the cerebral cortex located in the posterior part of the frontal lobe. The main function of the motor cortex is the planning, control, and execution of voluntary muscle movement to perform a specific task.
B. Central sulcus: The central sulcus is a fold in the cerebral cortex of the brain. The central sulcus, also called as the Rolandic fissure, plays a crucial role in separating the parietal lobe from the frontal lobe, the sensory, and the motor areas of the brain.
C. Sensory cortex: The sensory cortex includes all sensory areas associated with sensory function including the occipital cortex, most of the temporal and parietal cortex. The sensory cortical regions of the brain mainly regulate the auditory, visual, olfactory, gustatory, and somatosensory sensations.
D. Parietal lobe: The parietal lobe is located behind the frontal lobe, in front of the occipital lobe, and above the temporal lobe. The main functions of the parietal lobe include cognition, information processing, touch sensation, movement coordination, and spatial orientation.
E. Occipital lobe: The occipital lobe is one of the four lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain. It is positioned at the back of the brain and is separated by the cerebral fissure. The primary function of the occipital lobe is processing and interpretation of vision and visual stimuli.
F. Visual association: The visual association cortex is that part of the cerebral cortex of the brain located in the occipital lobe. This region is involved in processing visual information. The optic nerves from the eye run straight through the primary visual cortex to the visual association cortex.
G. Cerebellum: The cerebellum is located in a dorsal position to the pons and medulla oblongata. The cerebellum is responsible for intelligence, personality, thinking, reasoning, and language processing.
H. Medulla: The medulla is located in the brainstem anterior and inferior to the cerebellum. It is mainly responsible for involuntary functions like vomiting and sneezing. The medulla relays nerve signals between the brain and spinal cord. The medulla is responsible for the coordination of bodily movement and mood regulation.
I. Pons: The pons is a portion of the brain stem that is located above the medulla oblongata and below the cerebellum. The main function of the pons include regulation of respiration, control of involuntary action, control of motor movements like eye movement, facial expressions, chewing and swallowing, control of sensory actions like touch, hearing, and taste.
J. Temporal lobe: The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the brain. The temporal lobe plays an important role in auditory perception, long-term memory, personality, and behavior.
K. Lateral sulcus: The lateral sulcus is a fold in the cerebral cortex and serves to isolate the temporal and parietal lobes.
L. Frontal lobe: The frontal lobe is located at the front of the cerebral hemisphere separated from the parietal lobe by the central sulcus and from the temporal lobe by the lateral sulcus. The frontal lobe is involved in several functions of the body including motor functions, reasoning, and judgment.
M. Premotor cortex: The premotor cortex lies within the frontal lobe anterior to the primary motor cortex. It plays a direct role in control of behavior. The premotor cortex is also involved in planning, control, and execution of voluntary movements.
Functional Features:
N. Intellect personality: The size of different parts of people’s brains corresponds to their personality. The lateral prefrontal cortex is involved in the planning and control of behavior.
O. Broca’s speech area: The Broca’s speech area is a region located in the left hemisphere of the brain. It is involved in language comprehension, sensorimotor learning and integration, and in motor activities associated with hand movements.
P. Auditory area: The primary auditory cortex is the auditory area of the cerebral cortex responsible for the ability to hear. It performs higher functions in hearing ability specifically related to language switching.
Q. Memory: The memory of the human brain is in the hippocampus where the actual processing of the memory occurs.
R. RAS: The reticular activating system (RAS) connects the brain stem to the cerebral cortex through the thalamus. The RAS system has a deep connection with the awareness function of the brain. The RAS system filters and prioritizes sensory information and influences behavior in humans.
S. Vital centers: The medulla oblongata is the vital center of the brain. The medulla oblongata governs cough reflex, swallowing, and vomiting. The vital functions of breathing and cardiovascular function are controlled by the medulla oblongata.
T. Balance equilibrium coordination: The cerebellum and the brain stem play an important role in control of balance and the coordination of muscles. The cerebellum controls posture and coordinates skilled muscular movements.
U. Visual area: The visual area is the part of the visual cortex that receives sensory signals from the thalamus. Visual nerves from the eye lead to the visual association cortex through the primary visual cortex. This area of the brain processes visual information.
V. Wernicke’s area: The Wernicke’s area is located in the posterior temporal lobe and connects to the prefrontal, visual, and auditory areas. It is the integration center where comprehension of both spoken and written language takes place.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Study Guide for Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Professions
- how is mental health nursing independent from general nursing?arrow_forwardThe importance of monitoring resident's wound healing (bed sores, cuts, and scrapes, etc.) and how can a nutritionist utilize this in their career? Please not just a short explanation.arrow_forwardThe importance of seeing how it is to work as a chief in a nursing home and how they accommodate for special diets (low sodium, low sugar, heart healthy, etc.) and how can a nutritionist utilize this in their career? Please not just a short explanation.arrow_forward
- The importance of dealing with work confrontation (different healthcare departments fighting; diet aide and CNA) as a manager of a kitchen and how can a nutritionist utilize this in their career? Please not just a short explanation.arrow_forwardQuestion 1: You are the Community Dietitian for the local public health agency. Recent news coverage has highlighted the state of food insecurity and child hunger in your county. Initial reports indicate that 15% of the population is food insecure. Of this group, 28.4% are children. It is estimated that 86% of the food insecure population is eligible for federal nutrition assistance. You are asked to conduct a community needs assessment and, ultimately, develop an appropriate intervention aimed at reducing hunger. First, however, you must submit a plan for the needs assessment. Complete the following: 1. State the nutritional problem (10 pts) 2. Set the parameters of the assessment (20 pts, 5 pts per bullet) A. State the purpose of the assessment B. Identify the community and target population for this assessment C. Develop 2 goals and 2 SMART objectives for each goal D. Discuss the major categories of community data and target population data E. Specify the types of data you might…arrow_forwardAssignment Instructions: Nursing Research Essay Objective: Select a specific area of nursing that captivates your interest. Compose a comprehensive essay, ranging from 300 to 500 words, that delves into the intricacies of nursing research within your chosen area. It is recommended that you consider the topic carefully as this topic, should be the topic for your course research project: see week 4 assignments. Your essay should elucidate the following points: The Significance of Nursing Research: Explore how nursing research in your selected area contributes to advancements in applied medicine. Discuss the potential achievements and innovations that can arise from dedicated nursing research in this field. Articulate the value and impact of such research on patient care, healthcare practices, and overall medical knowledge. Research Methods and Approaches: Identify the most effective methods for conducting nursing research in your chosen area. Highlight specific topics or research…arrow_forward
- The importance of understanding low meal consumption of residents in a nursing home and how can a nutritionist utilize this in their career? Please not just a short explanation.arrow_forwardThe importance of accommodating special diets (diabetic, low sodium, etc.) in a nursing home and how can a nutritionist utilize this in their career? Please not just a short explanation.arrow_forwardThe importance of making a weekly clean list for kitchen staff in a nursing home and how can a nutritionist utilize this in their career? Please not just a short explanation.arrow_forward
- The importance of keeping a clean food pantry in a nursing home and how can a nutritionist utilize this in their career? Please not just a short explanation.arrow_forwardI’m finding it a bit difficult to understand the Arrhenius equation and how shelf life relates to pH and temperature. Also in the question that says ‘this solution maintains 80% potency at 30C’, am I correct in thinking the formula would be:t = ln(0.8)/ -karrow_forward4.24 mmmarrow_forward
 Phlebotomy EssentialsNursingISBN:9781451194524Author:Ruth McCall, Cathee M. Tankersley MT(ASCP)Publisher:JONES+BARTLETT PUBLISHERS, INC.
Phlebotomy EssentialsNursingISBN:9781451194524Author:Ruth McCall, Cathee M. Tankersley MT(ASCP)Publisher:JONES+BARTLETT PUBLISHERS, INC. Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Profession...NursingISBN:9780323414425Author:Robert J Hubert BSPublisher:Saunders
Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Profession...NursingISBN:9780323414425Author:Robert J Hubert BSPublisher:Saunders Fundamentals Of NursingNursingISBN:9781496362179Author:Taylor, Carol (carol R.), LYNN, Pamela (pamela Barbara), Bartlett, Jennifer L.Publisher:Wolters Kluwer,
Fundamentals Of NursingNursingISBN:9781496362179Author:Taylor, Carol (carol R.), LYNN, Pamela (pamela Barbara), Bartlett, Jennifer L.Publisher:Wolters Kluwer, Fundamentals of Nursing, 9eNursingISBN:9780323327404Author:Patricia A. Potter RN MSN PhD FAAN, Anne Griffin Perry RN EdD FAAN, Patricia Stockert RN BSN MS PhD, Amy Hall RN BSN MS PhD CNEPublisher:Elsevier Science
Fundamentals of Nursing, 9eNursingISBN:9780323327404Author:Patricia A. Potter RN MSN PhD FAAN, Anne Griffin Perry RN EdD FAAN, Patricia Stockert RN BSN MS PhD, Amy Hall RN BSN MS PhD CNEPublisher:Elsevier Science Study Guide for Gould's Pathophysiology for the H...NursingISBN:9780323414142Author:Hubert BS, Robert J; VanMeter PhD, Karin C.Publisher:Saunders
Study Guide for Gould's Pathophysiology for the H...NursingISBN:9780323414142Author:Hubert BS, Robert J; VanMeter PhD, Karin C.Publisher:Saunders Issues and Ethics in the Helping Professions (Min...NursingISBN:9781337406291Author:Gerald Corey, Marianne Schneider Corey, Cindy CoreyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Issues and Ethics in the Helping Professions (Min...NursingISBN:9781337406291Author:Gerald Corey, Marianne Schneider Corey, Cindy CoreyPublisher:Cengage Learning





