
Concept explainers
(a)
Find the value of the cutoff frequency in hertz for the RL filter shown in given figure.
(a)
Answer to Problem 1P
The value of the cutoff frequency
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Refer to given figure in the textbook.
Formula used:
Write the expression to calculate the angular cutoff frequency.
Here,
Write the expression to calculate the cutoff frequency of the RL low-pass filter.
Here,
Calculation:
The given filter circuit is drawn as Figure 1.
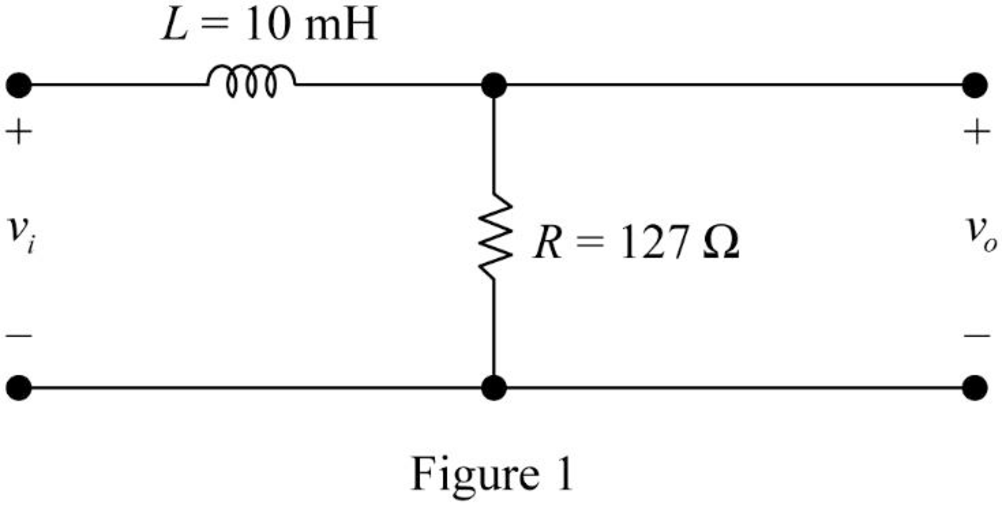
Substitute
Simplify the above equation to find
Substitute
Rearrange the above equation to find
Conclusion:
Thus, the value of the cutoff frequency
(b)
Find the value of the transfer function
(b)
Answer to Problem 1P
The value of the transfer function
Explanation of Solution
Formula used:
Write the expression to calculate the impedance of the passive elements resistor and inductor.
Calculation:
The impedance circuit of the Figure 1 is drawn as Figure 2 using the equations (3) and (4).
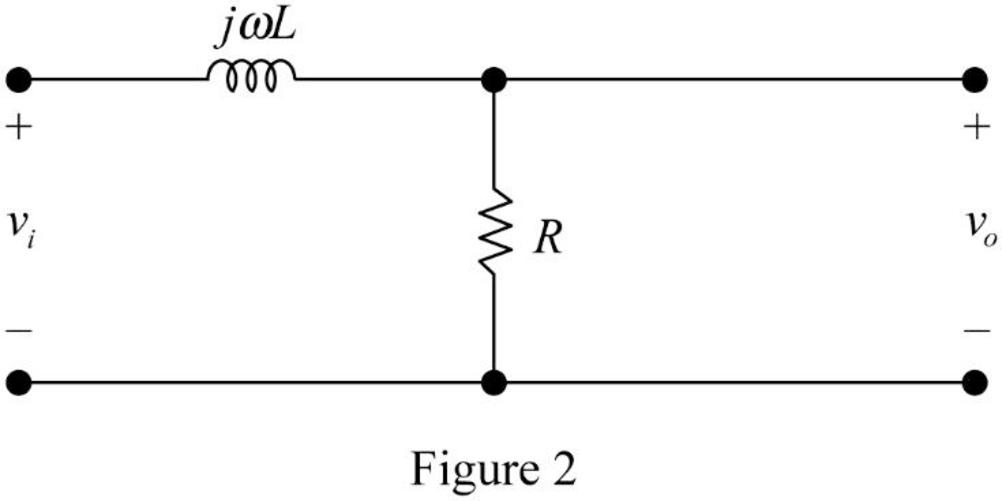
Apply voltage division rule on Figure 2 to find
Rearrange the above equation to find
Substitute the equation (2) in above equation to find
Write the expression to calculate the transfer function of the circuit in Figure 2.
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the value of the transfer function
(c)
Find the steady state expression for the output voltage
(c)
Answer to Problem 1P
The steady state expression for the output voltage
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The input voltage is,
Calculation:
From part (b),
Rearrange the above equation to find
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Simplify the above equation to find
Substitute
Substitute
Simplify the above equation to find
Substitute
Substitute
Simplify the above equation to find
Conclusion:
Thus, the steady state expression for the output voltage
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
EBK ELECTRIC CIRCUITS
- 5. A schematic diagram of a motor connected to a load by gears is shown. Both the motor and the load are modeled as rotating masses with viscous damping. Find the transfer functions Øm/Tm and ØL/Tm. bm Jm Tm 0m N₂ N₁ OL но JL b₁arrow_forward3. Find the transfer function X2/F of the mechanical system in Figure. Κι www b₁ M₁ K2 www M2 b2 X2 F b3arrow_forwardS1(t) Es/Ts 0 S3(t) 0 Es/Ts Ts t S2(t) Es/Ts 0 Es/Ts Ts |7|2 S4(t) Es/Ts t Ts t 0 Ts Ts Ts Es/TS 2 1/ Q1(t) 42(t) Ts 1JT 0 t 0 Ts Ts 2 32 FIGURE 7.3 Set of signals and orthonormal functions for Example 7.1. 53(t)=√√Esq₁(t) S4(t)=-√E542(t) t Tsarrow_forward
- 1. For each of the following differential equations, determine the transfer function Y/U. Determine if the transfer function is proper or strictly proper. is not strictly proper, determine the strictly proper part. If it (a) y(3) = -3y(2) - 3y(1) — 2y + u(2) — - (b) y(3)=-3.5y(2) — 3.5y(1) — y +u(3) — 3.5u(2) + 3.5u(¹) + 3uarrow_forward.4. Find the transfer function Ø2/T of the mechanical system in Figure. TG K 02 b₁ b₂ b3arrow_forwardMatlab problem: 1) A BFSK signal is transmitted through a channel with AWGN. Generate similar BFSK received signal plots as shown below. (20 pts) BFSK for eb=1 and npower=0.01 with 500 samples BFSK for eb=1 and npower=0.1 with 500 samples 2.5 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 -0.5 -1 2 1.5 1 0.5 0.5 -1 -1.5 1.5 -1.5 -1 -0.5 0 0.5 1.5 2 2.5 -1.5 -0.5 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5arrow_forward
- example 7.1 question EXAMPLE 7.1Consider the signals s1(t), s2(t), s3(t), and s4(t) shown in Figure 7.3. Using the Gram-Schmidt orthogonalization procedure, determine a set of orthonormal basis functions.Using the waveforms derived and shown in Example 7.1:a) Sketch the simplified block diagram of the transmitter and receiver as shown in figure 7.2b) Estimate the receive voltages for each transmit signal and for each branch in the receiver.arrow_forwardEXAMPLE 7.2 Consider the two equally-likely signals s₁ (t) and s2(t) that are transmitted, over an AWGN channel with the noise power spectral density of No/2, to represent bits 1 and 0, where we have: S1(t)=-S2(t)=√√2 exp(-2t)u(t) The receiver makes its decision solely based on observation of the received signal over a restricted interval of interest. Determine the average bit error rate in terms of Q-function, assuming the interval is [0,3]. Contrast numerically with the performance of an optimum receiver that observes. all the received signal, i.e., the interval of interest is (-∞, ∞).arrow_forward1) Compute the voltages at each receiver branch (Vo ad V₁ see block diagram next page) for each of the possible transmitted signals: Transmitted signals are generated as shown below: Binary wave in unipolar form (a) With basis functions: Inverter 41(t) Product modulator Product modulator 42(t) BFSK + signal + Si(t) P1(t)= √Eb = cos (2лfit+0₁) $2(t) 42(t)= √Eb 层 cos (2лf2t+ t+02) Generating signals: 2E Si(t) cos (2лfit+0₁), bit=0 Ть SBFSK (t) 2E |$2(t)= cos (2лf2t+02), bit=1arrow_forward
- Find the disruptive voltage and visual corona voltage for 3-phase line consisting of 2.5 cm diameter conductor spaced equilateral triangular formation of 4 m. The following data can be assumed, temperature 25°c, pressure 73 cm of mercury, surface factor 0.84, irregularity factor 0.72.arrow_forwardA 3-phase, 4-wire distributor supplies a balanced voltage of 400/230 V to a load consisting of 8 A at p.f. 0-7 lagging for R-phase, 10 A at p.f. 0-8 leading for Y phase and 12 A at unity p.f. for B phase. The resistance of each line conductor is 0.4 2. The reactance of neutral is 0.2 2. Calculate the neutral current, the suppl voltage for R phase and draw the phasor diagram. The phase sequence is RYB. VR Phasor diagramarrow_forwardThe three line leads of a 400/230 V, 3-phase, 4-wire supply are designated as R, Y and B respectively. The fourth wire or neutral wire is designated as N. The phase sequence is RYB. Compute the currents in the four wire when the following loads are connected to this supply: From R to N: 25 kW, unity power facto. From Y to N: 20 kVA, 0-7 lag. From B to N: 30 kVA, 0-6 lead.arrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





