
BIOLOGY-TEXT
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781260169621
Author: BROOKER
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 14, Problem 1COQ
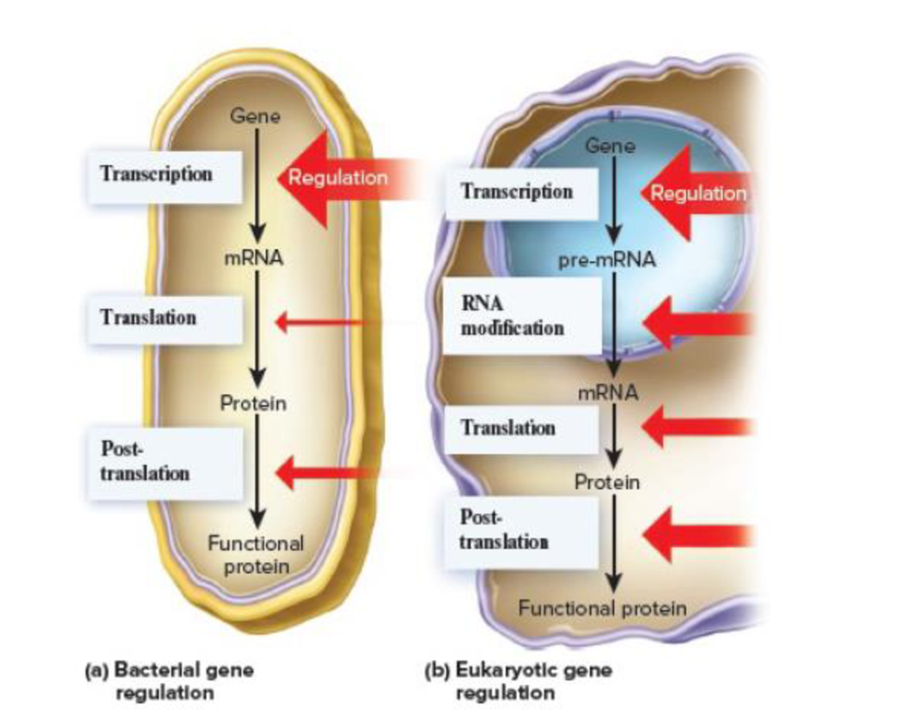
Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of genetic regulation at the different levels shown in Figure 14.4.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Biology laboratory problem
Please help. thank you
You have 20 ul of DNA solution and 6X DNA loading buffer solution. You have to mix your DNA solution and DNA loading buffer before load DNA in an agarose gel. The concentration of the DNA loading buffer must be 1X in the DNA and DNA-loading buffer mixture after you mix them. For that, I will add _____ ul of 6X loading buffer to the 20 ul DNA solution.
Biology lab problem
To make 20 ul of 5 mM MgCl2 solution using 50 mM MgCl2 stock solution and distilled water, I will mix ________ ul of 50 mM MgCl2 solution and ________ ul of distilled water.
Please help . Thank you
Biology
Please help. Thank you.
Biology laboratory question
You need 50 ml of 1% (w/v) agarose gel. Agarose is a powder. How would you make it? You can ignore the volume of agarose powder. Don't forget the unit.TBE buffer is used to make an agarose gel, not distilled water. I will add _______ of agarose powder into 50 ml of distilled water (final 50 ml).
Chapter 14 Solutions
BIOLOGY-TEXT
Ch. 14.1 - Prob. 1CCCh. 14.2 - Which genes are under the control of the lac...Ch. 14.2 - With regard to regulatory proteins and small...Ch. 14.2 - What were the key observations made by Jacob,...Ch. 14.2 - CoreSKILL What was the eventual hypothesis...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 3EQCh. 14.2 - Core Skill: Connections Look back at Fig 9.12....Ch. 14.2 - What are the advantages of having both an...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 2CSCh. 14.3 - Prob. 1CC
Ch. 14.4 - What are the two opposing effects that histone...Ch. 14.4 - Prob. 1CSCh. 14.5 - Prob. 1CCCh. 14.5 - Prob. 2CCCh. 14 - Prob. 1TYCh. 14 - Prob. 2TYCh. 14 - Transcription factors that bind to DNA and...Ch. 14 - Prob. 4TYCh. 14 - For the lac operon, what would be the expected...Ch. 14 - Prob. 6TYCh. 14 - The trp operon is considered _____ blank operon...Ch. 14 - Prob. 8TYCh. 14 - Prob. 9TYCh. 14 - _____ blank refers to the process that allows a...Ch. 14 - Prob. 1CQCh. 14 - Transcriptional regulation often involves a...Ch. 14 - Prob. 3CQCh. 14 - Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of...Ch. 14 - Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Give the IUPAC name for each compound.
Organic Chemistry
How does the removal of hydrogen atoms from nutrient molecules result in a loss of energy from the nutrient mol...
SEELEY'S ANATOMY+PHYSIOLOGY
Practice Problem 1.22 Which of the following alkenes can exist as cis-trans isomers? Write their structures. Bu...
Organic Chemistry
4. 38 Strontium has four naturally occurring isotopes, with mass numbers 84, 86, 87, arid 88.
a. Write the atom...
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life (5th Edition)
Single penny tossed 20 times and counting heads and tails: Probability (prediction): _______/20 heads ________/...
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
An obese 55-year-old woman consults her physician about minor chest pains during exercise. Explain the physicia...
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- An urgent care center experienced the average patient admissions shown in the Table below during the weeks from the first week of December through the second week of April. Week Average Daily Admissions 1-Dec 11 2-Dec 14 3-Dec 17 4-Dec 15 1-Jan 12 2-Jan 11 3-Jan 9 4-Jan 9 1-Feb 12 2-Feb 8 3-Feb 13 4-Feb 11 1-Mar 15 2-Mar 17 3-Mar 14 4-Mar 19 5-Mar 13 1-Apr 17 2-Apr 13 Forecast admissions for the periods from the first week of December through the second week of April. Compare the forecast admissions to the actual admissions; What do you conclude?arrow_forwardAnalyze the effectiveness of the a drug treatment program based on the needs of 18-65 year olds who are in need of treatment by critically describing 4 things in the program is doing effectively and 4 things the program needs some improvement.arrow_forwardI have the first half finished... just need the bottom half.arrow_forward
- 13. Practice Calculations: 3 colonies were suspended in the following dilution series and then a viable plate count and microscope count was performed. Calculate IDF's, TDF's and then calculate the CFU/mL in each tube by both methods. Finally calculate the cells in 1 colony by both methods. Show all of your calculations in the space provided on the following pages. 3 colonies 56 cells 10 μL 10 μL 100 μL 500 με m OS A B D 5.0 mL 990 με 990 με 900 με 500 μL EN 2 100 με 100 μL 118 colonies 12 coloniesarrow_forwardDescribe and give a specific example of how successionary stage is related to species diversity?arrow_forwardExplain down bellow what happens to the cell in pictures not in words: Decreased pH in mitochondria Increased ATP Decreased pH in cytosol Increased hydrolysis Decreasing glycogen and triglycerides Increased MAP kinase activity Poor ion transport → For each one:→ What normally happens?→ What is wrong now?→ How does it mess up the cell?arrow_forward
- 1.) Community Diversity: The brown and orange line represent two different plant communities. a. Which color represents the community with a higher species richness? b. Which color represents the community with a higher species evenness? Relative abundance 0.1 0.04 0.001 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 Rank abundance c. What is the maximum value of the Simpson's diversity index (remember, Simpson's index is D = p², Simpson's diversity index is 1-D)? d. If the Simpson's diversity index equals 1, what does that mean about the number of species and their relative abundance within community being assessed?arrow_forward1.) Community Diversity: The brown and orange line represent two different plant communities. a. Which color represents the community with a higher species richness? b. Which color represents the community with a higher species evenness? Relative abundance 0.1 0.04 0.001 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 Rank abundance c. What is the maximum value of the Simpson's diversity index (remember, Simpson's index is D = p², Simpson's diversity index is 1-D)? d. If the Simpson's diversity index equals 1, what does that mean about the number of species and their relative abundance within community being assessed?arrow_forwardwhat measures can a mother to take to improve the produce of her to milk to her newborn baby ?arrow_forward
- 1. Color the line that represents all ancestors of the Eastern white pine tree green (but only the ancestral line NOT shared with other organisms) 2. Oncle the last common ancestor of the Colorado blue spruce tree and Eastern white pine tree. 3. Put a box around the last common ancestor of the sugar maple tree and the dogwood tree. 4. Put a triangle around the last common ancestor of the red pine tree and the american holly bush. 5. Color the line that represents all ancestors of the Ponderosa pine tree red (including all shared ancestors). 6. Color the line that represents all ancestors of the American elm tree blue (including all shared ancestors). 7 Color the line that represents all ancestors of the Sabal palm tree purple (including all shared ancestors) 8. Using a yellow highlighter or colored pencil, circle the clade that includes all pine trees. 9. Using a orange highlighter or colored pencil, circle the clade that includes all gymnosperms 10. Can you tell…arrow_forwardYou have been hired as a public relations specialist to give invertebrates a good name. After all, they are much more than just creepy crawly bugs! Your first task though is to convince yourself that is true. The best way to do that is to start close to home. Find something in your house that is a product obtained directly from an invertebrate or only due to an invertebrate’s actions. Describe the product, its function and utility, as well as any human manufactured alternatives. Be sure to highlight the advantages of obtaining this directly from nature. Keep in mind, a product can be something you use, wear, eat, or enjoy for its visual appeal.arrow_forwardUse the following tree diagram to answer Questions #8-10. 8) Which of the following two animals are the most closely related based on the tree to the left? a) Pig and camel b) Hippo and pig c) Deer and cow 9) CIRCLE on the tree diagram where the common ancestor between a hippo and a cow is. 10) Put a SQUARE on the tree diagram where the common ancestor between a pig and a peccary is.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...
Biology
ISBN:9781305117396
Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Concepts of Biology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168116
Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James Wise
Publisher:OpenStax College

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Mitochondrial mutations; Author: Useful Genetics;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GvgXe-3RJeU;License: CC-BY