
WACC AND OPTIMAL CAPITAL STRUCTURE Elliott Athletics is trying to determine its optimal capital structure, which now consists of only debt and common equity. The firm dots not currently use
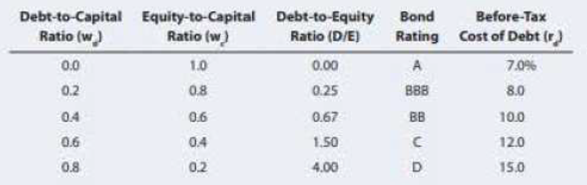
Elliott uses the
- a. What is the firm's optimal capital structure, and what would be its WACC at the optimal capital structure?
- b. If Elliott's managers anticipate that the company's business risk will increase in the future, what effect would this likely have on the firm's target capital structure?
- c. If Congress were to dramatically increase the corporate tax rate, what effect would this likely have on Elliott's target capital structure?
- d. Plot a graph of the after-tax cost of debt, the
cost of equity , and the WACC versus (1) - e. the debt/capital ratio and (2) the debt /equity ratio.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 14 Solutions
Bundle: Fundamentals of Financial Management, 14th + LMS Integrated for MindTap Finance, 1 term (6 months) Printed Access Card
- Consider a situation involving determining right and wrong. Do you believe utilitarianism provides a more objective viewpoint than moral rights in this context? Why or why not? How about when comparing utilitarianism to principles of justice? Share your thoughts. Reflect on this statement: "Every principle of distributive justice, whether that of the egalitarian, the capitalist, the socialist, the libertarian, or Rawls, in the end is illegitimately advocating some type of equality." Do you agree or disagree with this assertion? Why might someone claim this, and how would you respond?arrow_forwardI need help checking my spreadsheet. Q: Assume that Temp Force’s dividend is expected to experience supernormal growth of 73%from Year 0 to Year 1, 47% from Year 1 to Year 2, 32% from Year 2 to Year 3 and 21% from year3 to year 4. After Year 4, dividends will grow at a constant rate of 2.75%. What is the stock’sintrinsic value under these conditions? What are the expected dividend yield and capital gainsyield during the first year? What are the expected dividend yield and capital gains yield duringthe fifth year (from Year 4 to Year 5)?arrow_forwardwhat are the five components of case study design? Please help explain with examplesarrow_forward
- Commissions are usually charged when a right is exercised. a warrant is exercised. a right is sold. all of the above will have commissions A and B are correct, C is not correctarrow_forwardWhat is Exploratory Research Case Study? What is the main purpose of Exploratory Research?arrow_forwardplease help with how to solve this thank you.arrow_forward
- Question 25 Jasmine bought a house for $225 000. She already knows that for the first $200 000, the land transfer tax will cost $1650. Calculate the total land transfer tax. (2 marks) Land Transfer Tax Table Value of Property Rate On the first $30 000 0% On the next $60 000 0.5% (i.e., $30 001 to $90 000) On the next $60 000 1.0% (i.e., $90 001 to $150 000) On the next $50 000 1.5% (i.e., $150 001 to $200 000) On amounts in excess of $200 000 2.0% 22 5000–200 000. 10 825000 2.5000.00 2 x 25000 =8500 2 maarrow_forwardQuestion 25 Jasmine bought a house for $225 000. She already knows that for the first $200 000, the land transfer tax will cost $1650. Calculate the total land transfer tax. (2 marks) Land Transfer Tax Table Value of Property Rate On the first $30 000 0% On the next $60 000 0.5% (i.e., $30 001 to $90 000) On the next $60 000 1.0% (i.e., $90 001 to $150 000) On the next $50 000 1.5% (i.e., $150 001 to $200 000) On amounts in excess of $200 000 2.0% 225000–200 000 = 825000 25000.002 × 25000 1= 8500 16 50+ 500 2 marksarrow_forwardSuppose you deposit $1,000 today (t = 0) in a bank account that pays an interest rate of 7% per year. If you keep the account for 5 years before you withdraw all the money, how much will you be able to withdraw after 5 years? Calculate using formula. Calculate using year-by-year approach. Find the present value of a security that will pay $2,500 in 4 years. The opportunity cost (interest rate that you could earn from alternative investments) is 5%. Calculate using the formula. Calculate using year-by-year discounting approach. Solve for the unknown in each of the following: Present value Years Interest rate Future value $50,000 12 ? $152,184 $21,400 30 ? $575,000 $16,500 ? 14% $238,830 $21,400 ? 9% $213,000 Suppose you enter into a monthly deposit scheme with Chase, where you have your salary account. The bank will deduct $25 from your salary account every month and the first payment (deduction) will be made…arrow_forward
 Fundamentals Of Financial Management, Concise Edi...FinanceISBN:9781337902571Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals Of Financial Management, Concise Edi...FinanceISBN:9781337902571Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Fundamentals of Financial Management, Concise Edi...FinanceISBN:9781285065137Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management, Concise Edi...FinanceISBN:9781285065137Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Financial Management, Concise Edi...FinanceISBN:9781305635937Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management, Concise Edi...FinanceISBN:9781305635937Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning





