
(a)
Find the Rankine’s active force per unit length of the wall.
Find the location of the resultant.
(a)
Answer to Problem 14.8P
The Rankine’s active force per unit length of the wall is
The location of the resultant is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The height (H) of the retaining wall is 3.05 m.
The depth
The unit weight
The saturated unit weight
The angle
The angle
The surcharge
Calculation:
Find the submerged unit weight
Here,
The unit weight
Substitute
The angle of internal friction above and below the water table is same. Therefore,
Find the coefficient of Rankine’s active earth pressure for frictionless wall
Substitute
Find the active earth pressure
Substitute
Find the active earth pressure
Substitute
Find the active earth pressure
Substitute
Find the pore water pressure
Substitute
Sketch the active earth pressure diagram as shown in Figure 1.
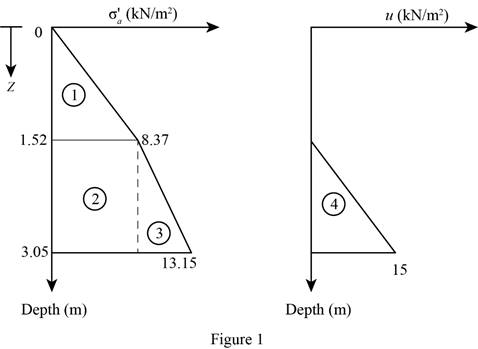
Find the active earth pressure per unit length at component 1
Substitute
Find the active earth pressure per unit length at component 2
Substitute
Find the active earth pressure per unit length at component 3
Substitute
Find the active earth pressure per unit length at component 4
Substitute
Find the total active earth pressure per unit length
Substitute
Therefore, the Rankine’s active force per unit length of the wall is
Refer Figure 1.
Find the location
Substitute
Find the location
Substitute
Find the location
Substitute
Find the location
Substitute
Find the location of resultant force
Take moment about the bottom of the wall.
Substitute
Therefore, the location of the resultant is
(b)
Find the Rankine’s active force per unit length of the wall.
Find the location of the resultant.
(b)
Answer to Problem 14.8P
The Rankine’s active force per unit length of the wall is
The location of the resultant is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The height (H) of the retaining wall is 6 m.
The depth
The unit weight
The saturated unit weight
The angle
The angle
The surcharge
Calculation:
Find the submerged unit weight
The unit weight
Substitute
Find the coefficient of Rankine’s active earth pressure for frictionless wall
Substitute
Find the coefficient of Rankine’s active earth pressure for frictionless wall
Substitute
Find the active earth pressure
Substitute
Find the active earth pressure
Substitute
Find the active earth pressure
Substitute
Find the active earth pressure
Substitute
Find the pore water pressure
Substitute
Sketch the active earth pressure diagram as shown in Figure 2.
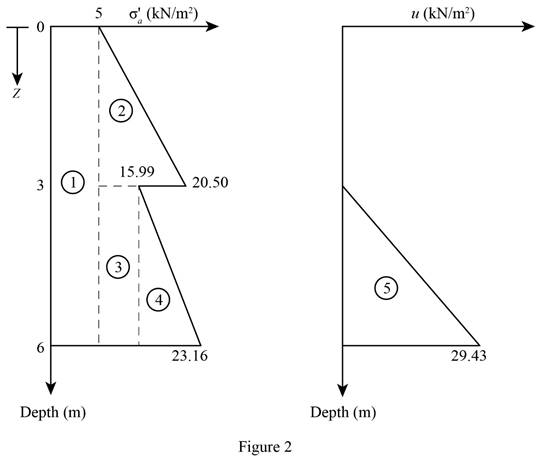
Find the active earth pressure of component 1 per unit length due to surcharge load
Substitute
Find the active earth pressure per unit length at component 2
Substitute
Find the active earth pressure per unit length at component 3
Substitute
Find the active earth pressure per unit length at component 4
Substitute
Find the active earth pressure per unit length at component 5
Substitute
Find the total active earth pressure per unit length
Substitute
Therefore, the Rankine’s active force per unit length of the wall is
Refer Figure 1.
Find the location
Substitute
Find the location
Substitute
Find the location
Substitute
Find the location
Substitute
Find the location
Substitute
Find the location of resultant force
Take moment about the bottom of the wall.
Substitute
Therefore, the location of the resultant is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
EBK FUNDAMENTALS OF GEOTECHNICAL ENGINE
- 13. The front of the platoon (truck) has a speed of 30 mph in question 12. According to the shockwave speed, the platoon is growing at a rate of:arrow_forwardA tank transmits 100 L/s of water to point C, where the pressure is maintained at 1.5 kg/cm². The first part, AB of the pipe, is 50 cm in diameter and 2.5 km long, and the second part BC is 25 cm in diameter and 1.5 km long. The friction coefficient is 0.005, and minor losses are ignored. Assuming the level at C is (0.0), find the water level (L) in the tank. L A B с hAB hBC bcarrow_forwardGiven a portion of a pipe network below. Determine the true discharge in each pipe using the Hardy-Cross method. Use the Darcy-Weisbach formula with f = 0.02 for all pipes. Pipe AB Length (m) Diameter (cm) 600 25 BC 400 25 CD 900 30 DA AC 1000 20 1500 20 Q₁₁ = 0.20 m³/s B Qc = 0.30 m³/s Loop I QA 0.10 m³/s A. C Loop II Q₁ = 0.20 m³/sarrow_forward
- The figures below shows the framing plan and section of a reinforced concrete floor system. Floor beams are shown as dotted lines. The weight of the ceiling and floor finishing is 6 psf, that of the mechanical and electrical systems is 7 psf, and the weight of the partitions is 180 psf. The floor live load is 105 psf. The 7 in. thick slab exterior bay (S-1) is reinforced with #5 rebars @ 10 in. o.c. as the main positive reinforcement at the mid span, and #4 @ 109 in. for the shrinkage and temperature reinforcement. The panel is simply supported on the exterior edge and monolithic with the beam at the interior edge. Check the adequacy of the slab. Use the ACI moment coefficients. fc’ = 6,000 psi and fy = 60,000 psi. The slab is in an interior location. Hint: • Estimate total dead load. Find factored maximum positive bending moment in the end span. • Find design positive moment capacity. • Compare and determine adequacy, including safety and economy.arrow_forwardQuestion 6 Two reservoirs have a 6 m difference in water levels and are connected by a pipe 60 cm in diameter and 3000 m long. Then, the pipe branches into two pipes, each 30 cm in diameter and 1500 m long. The friction coefficient is 0.01. Neglecting minor losses, determine the flow rates in the pipe system. Q Q3 ha h₁ = 6 marrow_forwardDesign a simply supported one-way pavement slab for a factored applied moment, Mu = 10 ft- kip. Use f c’ = 5,000 psi and f y = 60,000 psi. The slab is in permanent contact with soil. Hint: • Estimate a minimum slab thickness for deflection control. • Solve for the slab steel based on cover for soil contact.arrow_forward
- 20. In a deterministic queue, suppose vehicle arrive at a rate of 100 vph for the first hour and 60 vph for the second hour. The server can discharge 80 vehicles per hour. What is the standing queue at the end of two hours:arrow_forwardThe difference in water surface levels in two tanks, which are connected by three pipes in series of lengths 400 m, 200 m, and 300 m and of diameters 400 mm, 300 mm, and 200 mm, respectively, is 16m. Estimate the rate of flow of water if the coefficient of friction for these pipes is same and equal to 0.005, considering: (i) minor losses also (ii) neglecting minor losses.arrow_forwardThe difference in water surface levels in two tanks, which are connected by three pipes in series of lengths 300 m, 170 m, and 210 m, having diameters 300 mm, 200 mm, and 400 mm, respectively, is 12 m. Determine the rate of flow of water if coefficients of friction are 0.005, 0.0052, and 0.0048, respectively. Determine the discharge and velocity in each pipe, considering the minor losses and neglecting minor losses.arrow_forward
- Determine the heel and toe stresses and the factor of safeties for sliding and overturning for the gravity dam section shown in the figure below for the following loading conditions: - Horizontal earthquake (Kh) = 0.1 - Normal uplift pressure with gallery drain working - Silt deposit up to 30 m height - No wave pressure and no ice pressure -Unit weight of concrete = 2.4 Ton/m³ and unit weight of silty water = 1.4 Ton/m³ - Submerged weight of silt = 0.9 Ton/m³ - Coefficient of friction = 0.65 and angle of repose = 25° Solve this question with the presence of gallery and without gallery., discuss the issue in both cases.... Draw and Solve in table 4m 8m 6m 8m 7m 120marrow_forwardLand Use Hydrologic Area (acres) Soil Group A 25 Forestland-orchards B 30 B 45 Forest Oak-Aspen C 60 A 80 Open Spaces B 65 A 120 Residential (1/2-acre lots) B 155 Storm Hyetograph Time Rainfall Interval Intensity (hours) (in/hr) 0-1 1.2 1-2 1.3 2-3 1.9 3-4 1.5 4-5 1.3 5-6 1 6-7 0.8 1 Hour-Unit Hydrograph Time UH [hr] [cfs/in] 0 0 1 60 2 120 3 140 4 80 5 40 6 10 7 0arrow_forwardSecondary Treatment Based on a plant flow rate of 40 mgd, design an activated sludge, secondary treatment system with recycle which maintains a MLVSS = 2,000 mg/L in the aeration reactor and has an average Solids Retention Time (SRT) = 4 days. The biota kinetic constants are: Kinetic Coefficients for the Activated-sludge Process for the Removal of Organic Matter from Domestic Wastewater - Endogenous Decay Coefficient – k(d) Half-velocity constant – K(s) 0.1 15 Max. Specific Substrate Utilization Rate – k Biomass Yield - Y 6 0.45 gVSS/gVSS-day mg/L bsCOD g bsCOD/gVSS-day gVSS/g bsCOD used The laboratory has provided the information below for your influent from your primary clarifier. Unit mg/L Item Influent nbVSS - Xo Quantity 30 Fraction of the biomass which remains as cell debris (fd) Temperature 0.18 20 °C Quantity of Oxygen in air 0.017 Lb O₂/ft³ air Influent microorganism & substrate concentration as (So) Influent Inert Inorganics (TSS. – VSS.) 215 10 Mg/L bsCOD mg/L Aeration Basin…arrow_forward
 Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning



