
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
To determine how many peaks will the signal for the given structure of the indicated protons split.
Concept introduction:
NMR is the spectroscopic technique to observe the local magnetic fields around the atomic nuclei. The relative intensity of 1H NMR signals provide the information about the compound structure. The area under the NMR signal is proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
The height of each step is proportional to the area under the peak, which is in turn proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
Answer to Problem 14.44P
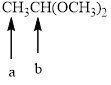
In the given structure, the indicated arrow “ a” split into doublet and “b” into quartet.
Explanation of Solution
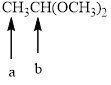
Splitting pattern determines the kind of proton of proton in the structure. First determine if two protons are equivalent or different. Only nonequivalent protons split each other and also determine if two nonequivalent protons are close enough to split each other's signals. Splitting is observed only for nonequivalent protons on the same carbon or adjacent carbons.
In the given structure the indicated arrow a and b are having nonequivalent protons. Thus methyl proton indicated by “ a” into doublet and “ b” into quartet.
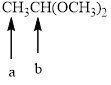
Thus in the given structure, for the indicated arrow “ a” split into doublet and “b” into quartet.
(b)
Interpretation:
To determine how many peaks will the signal for the given structure of the indicated protons split.
Concept introduction:
NMR is the spectroscopic technique to observe the local magnetic fields around the atomic nuclei. The relative intensity of 1H NMR signals provide the information about the compound structure. The area under the NMR signal is proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
The height of each step is proportional to the area under the peak, which is in turn proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
Answer to Problem 14.44P
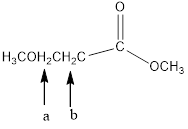
In the given structure, the indicated arrow “ a” and “b” split into doublet.
Explanation of Solution

Splitting pattern determines the kind of proton of proton in the structure. First determine if two protons are equivalent or different. Only nonequivalent protons split each other and also determine if two nonequivalent protons are close enough to split each other's signals. Splitting is observed only for nonequivalent protons on the same carbon or adjacent carbons.
In the given structure the indicated arrow a and b are having equivalent protons. Thus proton indicated by “ a” and “b” split into doublet.

Thus in the given structure for the indicated arrow “ a” and “b” split into doublet.
(c)
Interpretation:
To determine how many peaks will the signal for the given structure of the indicated protons split.
Concept introduction:
NMR is the spectroscopic technique to observe the local magnetic fields around the atomic nuclei. The relative intensity of 1H NMR signals provide the information about the compound structure. The area under the NMR signal is proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
The height of each step is proportional to the area under the peak, which is in turn proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
Answer to Problem 14.44P
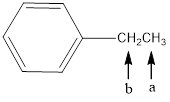
In the given structure, the indicated arrow “ a” split into triplet and “b” split into qaurtet.
Explanation of Solution

Splitting pattern determines the kind of proton of proton in the structure. First determine if two protons are equivalent or different. Only nonequivalent protons split each other and also determine if two nonequivalent protons are close enough to split each other's signals. Splitting is observed only for nonequivalent protons on the same carbon or adjacent carbons.
In the given structure the indicated arrow a and b are having nonequivalent protons. Thus proton indicated by “ a” split into triplet and “b” split into qaurtet.

Thus in the given structure for the indicated arrow “ a” split into triplet and “b” split into qaurtet.
(d)
Interpretation:
To determine how many peaks will the signal for the given structure of the indicated protons split.
Concept introduction:
NMR is the spectroscopic technique to observe the local magnetic fields around the atomic nuclei. The relative intensity of 1H NMR signals provide the information about the compound structure. The area under the NMR signal is proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
The height of each step is proportional to the area under the peak, which is in turn proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
Answer to Problem 14.44P
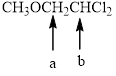
In the given structure, the indicated arrow “ a” split into doublet and “b” split into triplet.
Explanation of Solution
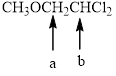
Splitting pattern determines the kind of proton of proton in the structure. First determine if two protons are equivalent or different. Only nonequivalent protons split each other and also determine if two nonequivalent protons are close enough to split each other's signals. Splitting is observed only for nonequivalent protons on the same carbon or adjacent carbons.
In the given structure the indicated arrow a and b are having nonequivalent protons. Thus proton indicated by “ a” split into doublet and “b” split into triplet.
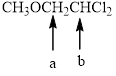
Thus in the given structure for the indicated arrow “ a” split into doublet and “b” split into triplet.
(e)
Interpretation:
To determine how many peaks will the signal for the given structure of the indicated protons split.
Concept introduction:
NMR is the spectroscopic technique to observe the local magnetic fields around the atomic nuclei. The relative intensity of 1H NMR signals provide the information about the compound structure. The area under the NMR signal is proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
The height of each step is proportional to the area under the peak, which is in turn proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
Answer to Problem 14.44P
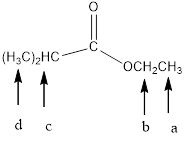
In the given structure, the indicated arrow “ a” split into triplet, “b” split into quartet,
“c” split into septet and “d” split into doublet.
Explanation of Solution
Splitting pattern determines the kind of proton of proton in the structure. First determine if two protons are equivalent or different. Only nonequivalent protons split each other and also determine if two nonequivalent protons are close enough to split each other's signals. Splitting is observed only for nonequivalent protons on the same carbon or adjacent carbons.
In the given structure the indicated arrow a, b, c and d are having nonequivalent protons. Thus proton indicated by “ a” split into triplet, “b” split into quartet, “c” split into septet and “d” split into doublet.


Thus in the given structure for the indicated arrow “ a” split into triplet, “b” split into quartet,
“c” split into septet and “d” split into doublet.
(f)
Interpretation:
To determine how many peaks will the signal for the given structure of the indicated protons split.
Concept introduction:
NMR is the spectroscopic technique to observe the local magnetic fields around the atomic nuclei. The relative intensity of 1H NMR signals provide the information about the compound structure. The area under the NMR signal is proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
The height of each step is proportional to the area under the peak, which is in turn proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
Answer to Problem 14.44P
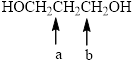
In the given structure, the indicated arrow “ a” split into quintet and “b” split into triplet.
Explanation of Solution
Splitting pattern determines the kind of proton of proton in the structure. First determine if two protons are equivalent or different. Only nonequivalent protons split each other and also determine if two nonequivalent protons are close enough to split each other's signals. Splitting is observed only for nonequivalent protons on the same carbon or adjacent carbons.
In the given structure the indicated arrow a and b are having nonequivalent protons. Thus proton indicated by “a” split into quintet and “b” split into triplet.
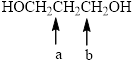
Thus in the given structure for the indicated “ a” split into quintet and “b” split into triplet.
(g)
Interpretation:
To determine how many peaks will the signal for the given structure of the indicated protons split.
Concept introduction:
NMR is the spectroscopic technique to observe the local magnetic fields around the atomic nuclei. The relative intensity of 1H NMR signals provide the information about the compound structure. The area under the NMR signal is proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
The height of each step is proportional to the area under the peak, which is in turn proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
Answer to Problem 14.44P
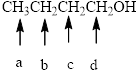
In the given structure, the indicated arrow “ a” split into triplet, “b” split into multiplet i.e it observe 5 peaks (12 peaks maximum), “c” split into multiplet i.e it observe 6 peaks (9 peaks maximum) and “d” split into triplet.
Explanation of Solution
Splitting pattern determines the kind of proton of proton in the structure. First determine if two protons are equivalent or different. Only nonequivalent protons split each other and also determine if two nonequivalent protons are close enough to split each other's signals. Splitting is observed only for nonequivalent protons on the same carbon or adjacent carbons.
In the given structure the indicated arrow protons are having nonequivalent protons. Thus proton indicated by “ a” split into triplet, “b” split into multiplet i.e it observe 5 peaks (12 peaks maximum), “c” split into multiplet i.e it observe 6 peaks (9 peaks maximum) and “d” split into triplet.
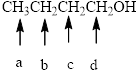
Thus in the given structure for the indicated “ a” split into triplet, “b” split into multiplet i.e it observe 5 peaks (12 peaks maximum), “c” split into multiplet i.e it observe 6 peaks (9 peaks maximum) and “d” split into triplet.
(h)
Interpretation:
To determine how many peaks will the signal for the given structure of the indicated protons split.
Concept introduction:
NMR is the spectroscopic technique to observe the local magnetic fields around the atomic nuclei. The relative intensity of 1H NMR signals provide the information about the compound structure. The area under the NMR signal is proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
The height of each step is proportional to the area under the peak, which is in turn proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
Answer to Problem 14.44P
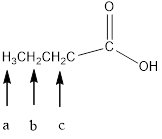
In the given structure, the indicated arrow “a” split into triplet, “b” split into multiplet i.e., it observe 6 peaks and “c” split into triplet.
Explanation of Solution
Splitting pattern determines the kind of proton of proton in the structure. First determine if two protons are equivalent or different. Only nonequivalent protons split each other and also determine if two nonequivalent protons are close enough to split each other's signals. Splitting is observed only for nonequivalent protons on the same carbon or adjacent carbons.
In the given structure the indicated arrow protons are having nonequivalent protons. Thus proton indicated by “a” split into triplet, “b” split into multiplet i.e., it observe 6 peaks and “c” split into triplet.

Thus in the given structure for the indicated “a” split into triplet, “b” split into multiplet i.e., it observe 6 peaks and “c” split into triplet.

(i)
Interpretation:
To determine how many peaks will the signal for the given structure of the indicated protons split.
Concept introduction:
NMR is the spectroscopic technique to observe the local magnetic fields around the atomic nuclei. The relative intensity of 1H NMR signals provide the information about the compound structure. The area under the NMR signal is proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
The height of each step is proportional to the area under the peak, which is in turn proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
Answer to Problem 14.44P
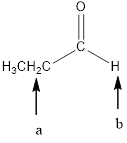
In the given structure, the indicated arrow “a” split into 8 peak (maximum) but observed singlet, “b” split into triplet.
Explanation of Solution
Splitting pattern determines the kind of proton of proton in the structure. First determine if two protons are equivalent or different. Only nonequivalent protons split each other and also determine if two nonequivalent protons are close enough to split each other's signals. Splitting is observed only for nonequivalent protons on the same carbon or adjacent carbons.
In the given structure the indicated arrow protons are having nonequivalent protons. Thus proton indicated by “a” split into 8 peak (maximum) but observed singlet, “b” split into triplet.

Thus in the given structure for the indicated “a” split into 8 peak (maximum) but observed singlet, “b” split into triplet.

(j)
Interpretation:
To determine how many peaks will the signal for the given structure of the indicated protons split.
Concept introduction:
NMR is the spectroscopic technique to observe the local magnetic fields around the atomic nuclei. The relative intensity of 1H NMR signals provide the information about the compound structure. The area under the NMR signal is proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
The height of each step is proportional to the area under the peak, which is in turn proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
Answer to Problem 14.44P
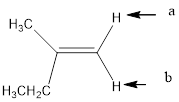
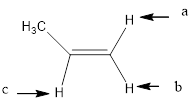
In the given structure, the indicated arrow “a” and “b” split into doublet.
Explanation of Solution
Splitting pattern determines the kind of proton of proton in the structure. First determine if two protons are equivalent or different. Only nonequivalent protons split each other and also determine if two nonequivalent protons are close enough to split each other's signals. Splitting is observed only for nonequivalent protons on the same carbon or adjacent carbons.
In the given structure the indicated arrow protons are having equivalent protons lie on the same carbon. Thus proton indicated by “a” and “b” split into doublet.
Thus in the given structure for the indicated “a” and “b” split into doublet.

(k)
Interpretation:
To determine how many peaks will the signal for the given structure of the indicated protons split.
Concept introduction:
NMR is the spectroscopic technique to observe the local magnetic fields around the atomic nuclei. The relative intensity of 1H NMR signals provide the information about the compound structure. The area under the NMR signal is proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
The height of each step is proportional to the area under the peak, which is in turn proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
Answer to Problem 14.44P
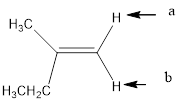
In the given structure, the indicated arrow “a” and “b” split into doublet.
Explanation of Solution
Splitting pattern determines the kind of proton of proton in the structure. First determine if two protons are equivalent or different. Only nonequivalent protons split each other and also determine if two nonequivalent protons are close enough to split each other's signals. Splitting is observed only for nonequivalent protons on the same carbon or adjacent carbons.
In the given structure the indicated arrow protons are having equivalent protons lie on the same carbon. Thus proton indicated by “a” and “b” split into doublet.
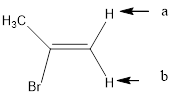
Thus in the given structure for the indicated “a” and “b” split into doublet.

(l)
Interpretation:
To determine how many peaks will the signal for the given structure of the indicated protons split.
Concept introduction:
NMR is the spectroscopic technique to observe the local magnetic fields around the atomic nuclei. The relative intensity of 1H NMR signals provide the information about the compound structure. The area under the NMR signal is proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
The height of each step is proportional to the area under the peak, which is in turn proportional to the number of absorbing protons.
Answer to Problem 14.44P
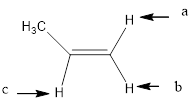
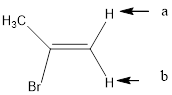
In the given structure, the indicated arrow “a” and “b” split into doublet of doublet and “c” split into maximum of 16 peaks.
Explanation of Solution
Splitting pattern determines the kind of proton of proton in the structure. First determine if two protons are equivalent or different. Only nonequivalent protons split each other and also determine if two nonequivalent protons are close enough to split each other's signals. Splitting is observed only for nonequivalent protons on the same carbon or adjacent carbons.
In the given structure the indicated arrow protons are having non-equivalent protons lie on the same carbon. Thus proton indicated by “a” and “b” split into doublet of doublet and “c” split into maximum of 16 peaks.

Thus in the given structure for the indicated “a” and “b” split into doublet of doublet and “c” split into maximum of 16 peaks.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Organic Chemistry-Package(Custom)
- What is the organic molecule X of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forwardWhat are is the organic molecule X and product Y of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forwardAt 300 K, in the decomposition reaction of a reactant R into products, several measurements of the concentration of R over time have been made (see table). Without using graphs, calculate the order of the reaction. t/s [R]/(mol L-1) 0 0,5 171 0,16 720 0,05 1400 0,027arrow_forward
- Predict the organic products that form in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic products. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forwardWhat are the missing reagents for the spots labeled 1 and 3? Please give a detailed explanation and include the drawings and show how the synthesis proceeds with the reagents.arrow_forwardWhat are the products of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forward
- What would happen if you added the HCI to the Grignard reagent before adding benzophenone? Draw a reaction mechanism to support your answer.arrow_forwardAt 300 K, in the decomposition reaction of a reactant R into products, several measurements of the concentration of R over time have been made (see table). Calculate the order of the reaction. t/s [R]/ (mol L-1) 0 0,5 171 0,16 720 0,05 1400 0,027arrow_forwardWrite the correct IUPAC names of the molecules in the picturearrow_forward
- How many grams of solid NaCN have to be added to 1.5L of water to dissolve 0.18 mol of Fe(OH)3 in the form Fe(CN)63 - ? ( For simplicity, ignore the reaction of CN - ion with water) Ksp for Fe(OH)3 is 2.8E -39, and Kform for Fe(CN)63 - is 1.0E31arrow_forwardDraw the most stable chair conformation of 1-ethyl-1-methylcyclohexane, clearly showing the axial and equatorial substituents. [4] Draw structures corresponding to the following IUPAC name for each of the following compounds; [5] i) 4-Isopropyl-2,4,5-trimethylheptane ii) trans-1-tert-butyl-4-ethylcyclohexane iii) Cyclobutylcycloheptane iv) cis-1,4-di-isopropylcyclohexane (chair conformation) v) 3-Ethyl-5-isobutylnonanearrow_forwardDraw and name molecules that meet the following descriptions; [4] a) An organic molecule containing 2 sp2 hybridised carbon and 1 sp-hybridised carbon atom. b) A cycloalkene, C7H12, with a tetrasubstituted double bond. Also answer question 2 from the imagearrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
