
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The deepest
Concept introduction:
The rate law of the chemical reaction states that the rate of reaction is the function of the concentration of the reactants and the products present in that specific reaction. The rate is actually predicted by the slowest step of the reaction.
(a)
Answer to Problem 14.2P
The deepest
Explanation of Solution
The given minimum respiration rate of a chipmunk is
The given corresponding volumetric rate of gas intake is
The given value of diffusivity is
The diameter of hole is
The hole is shown below.
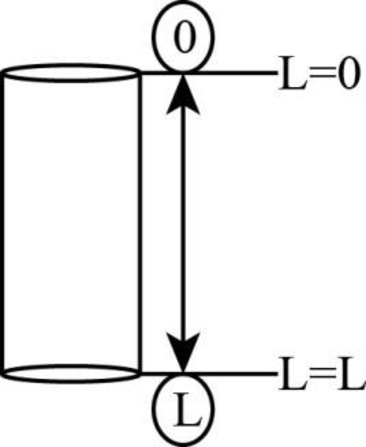
Figure 1
There are two points at top and bottom of hole which are
The corresponding concentration at
The expression for the relation between molar flow rate of A and cross sectional area is given below.
Where,
The expression for the molar flux at the direction L is given below.
Where,
Substitute
The area of the hole is expressed as follows.
Where,
Substitute
The relation between molar flow rate and volumetric flow rate is given below.
Where,
Substitute
The expression for
Where,
If air occupies only
The value of universal gas constant is
The atmospheric pressure at STP is
Substitute the value
Substitute the values of
Therefore, the deepest
(b)
Interpretation:
The deepest
Concept introduction:
The rate law of the chemical reaction states that the rate of reaction is the function of the concentration of the reactants and the products present in that specific reaction. The rate is actually predicted by the slowest step of the reaction.
(b)
Answer to Problem 14.2P
The deepest
Explanation of Solution
The given minimum respiration rate of a chipmunk is
The given corresponding volumetric rate of gas intake is
The given value of diffusivity is
The diameter of hole is
The hole is shown below.
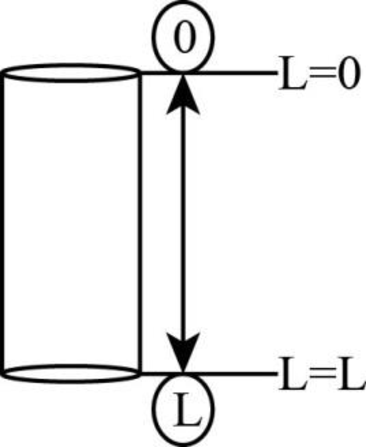
Figure 1
There are two points at top and bottom of hole which are
The corresponding concentration at
The expression for the relation between molar flow rate of A and cross sectional area is given below.
Where,
The expression for the molar flux at the direction L is given below.
Where,
Substitute
The area of the hole is expressed as follows.
Where,
Substitute
The relation between molar flow rate and volumetric flow rate is given below.
Where,
Substitute
The expression for
Where,
If air occupies only
The value of universal gas constant is
The atmospheric pressure in Colorado at STP is
Substitute the value
Substitute the values of
Therefore, the deepest
(c)
Interpretation:
The deepest
Concept introduction:
The rate law of the chemical reaction states that the rate of reaction is the function of the concentration of the reactants and the products present in that specific reaction. The rate is actually predicted by the slowest step of the reaction.
(c)
Answer to Problem 14.2P
The deepest
Explanation of Solution
The given minimum respiration rate of a chipmunk is
The given corresponding volumetric rate of gas intake is
The given value of diffusivity is
The diameter of hole is
There are two points at top and bottom of hole which are
The corresponding concentration at
The standard temperature is
The conversion of
The expression for the relation between diffusivity, two temperatures and two pressures is given below.
Substitute the value
If air occupies only
The value of universal gas constant is
The atmospheric pressure in Colorado at STP is
For Ann arbor, Michigan, substitute the value
For, Ann, Arbor Substitute the values of
For Boulder, Colorado, substitute the value
For, Boulder, Colorado, Substitute the values of
Therefore, the deepest
(d)
Interpretation:
The criticism and the extension of the given problem is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The rate law of the chemical reaction states that the rate of reaction is the function of the concentration of the reactants and the products present in that specific reaction. The rate is actually predicted by the slowest step of the reaction.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The most important base of the given problem is the composition of air that is air occupies only
If carbon dioxide is added in the air, then the extension of the above calculations takes place by adding the percentage of carbon dioxide in the problem.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Edition) (Prentice Hall International Series in the Physical and Chemical Engineering Sciences)
- Propane is burned completely with excess oxygen. The product gas contains 24.5 mole% CO2, 6.10% CO, 40.8% H2O, and 28.6% O2. (a) Calculate the percentage excess O2 fed to the furnace. (b) A student wrote the stoichiometric equation of the combustion of propane to form CO2 and CO as: 2C3H8 + 11O2 → 3CO2 + 3CO + 8H2O According to this equation, CO2 and CO should be in a ratio of 1/1 in the reaction products, but in the product gas of Part (a) they are in a ratio of 24.8/6.12. Is that result possible? (Hint: Yes.) Explain howarrow_forwardEnumerate the various methods for catalyst preparation and discuss vividly any one of the methodsarrow_forward2. Design a spherical tank, with a wall thickness of 2.5 cm that will ensure that no more than 45 kg of hydrogen will be lost per year. The tank, which will operate at 500 °C, can be made from nickel, aluminum, copper, or iron (BCC). The diffusion coefficient of hydrogen and the cost per pound for each available material is listed in Table 1. Material Do (m2/s) Q (J/mol) Cost ($/kg) Nickel 5.5 x 10-7 37.2 16.09 Aluminium 1.6 x 10-5 43.2 2.66 Copper 1.1 x 10-6 39.3 9.48 Iron (BCC) 1.2 × 10-7 15.1 0.45 Table 1: Diffusion data for hydrogen at 500 °C and the cost of material.arrow_forward
- A flash drum at 1.0 atm is separating a feed consisting of methanol and water. If the feed rate is 2000 kg/h and the feed is 45 wt % methanol, what are the values of L (kg/h), V (kg/h), yM, xM (weight fractions), and Tdrum if 35% by weight of the feed is vaporized? VLE data are in Table 2-8.arrow_forwardQ1.B. Make a comparison between current control PWM rectifier in the abc reference frame and dq reference frame.arrow_forwardstep by steparrow_forward
- The power out of an adiabatic steam turbine is 5 MW and the steam enters turbine at 2 MPa and velocity of 50 m/s, specific enthalpy (h) of 3248 kJ/kg. The elevation of the inlet is 10 m higher than at the datum. The vapor mixture exits at 15 kPa and a velocity of 180 m/s, specific enthalpy (h) of 2361.01 kJ/kg. The elevation of the exit is 6 m higher than at the datum. Let g = 9.81 m/s². Assuming the ideal gas model and R = 0.462 KJ/(kg.K). The steam specific heat ratio is 1.283. Calculate:arrow_forwardstep by step pleasearrow_forwardstep by step pleasearrow_forward
- step by steparrow_forwardThe power out of an adiabatic steam turbine is 5 MW and the steam enters turbine at 2 MPa and velocity of 50 m/s, specific enthalpy (h) of 3248 kJ/kg. The elevation of the inlet is 10 m higher than at the datum. The vapor mixture exits at 15 kPa and a velocity of 180 m/s, specific enthalpy (h) of 2361.01 kJ/kg. The elevation of the exit is 6 m higher than at the datum. Let g = 9.81 m/s². Assuming the ideal gas model and R = 0.462 KJ/(kg.K). The steam specific heat ratio is 1.283. Calculate:arrow_forwardThe power out of an adiabatic steam turbine is 5 MW and the steam enters turbine at 2 MPa and velocity of 50 m/s, specific enthalpy (h) of 3248 kJ/kg. The elevation of the inlet is 10 m higher than at the datum. The vapor mixture exits at 15 kPa and a velocity of 180 m/s, specific enthalpy (h) of 2361.01 kJ/kg. The elevation of the exit is 6 m higher than at the datum. Let g = 9.81 m/s². Assuming the ideal gas model and R = 0.462 KJ/(kg.K). The steam specific heat ratio is 1.283. Calculate:arrow_forward
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The





