
What are the forms of cash dividends?
To discuss: The forms of cash dividend.
Introduction:
A portion of profits payable to the shareholders by the company on a regular period is termed as dividend. The members of board of the company declare these dividends.
The different forms of dividends are as follows:
- Cash dividend
- Bonus shares
- Share repurchase
- Property dividend
- Scrip dividend
- Liquidating dividend
Explanation of Solution
Regular cash dividend:
Regular cash dividends are payable four times a year on a regular basis. These cash dividends are payable directly to the shareholders.
Extra dividends:
A onetime payment made to the shareholders of the company on a quarterly or various ranges of periods are termed as extra dividends. These dividends may or may not be declared for the upcoming years.
Special dividends:
Special dividends are those, which are same as extra dividend, but they cannot be declared again. Thus, this payment is the onetime payment.
Liquidating dividends:
These are the dividends which are payable during the liquidation period. The dividends paid at the time of complete or partial closure of business is termed as liquidating dividends.
Pictorial representation:
The forms of cash dividend are as follows:
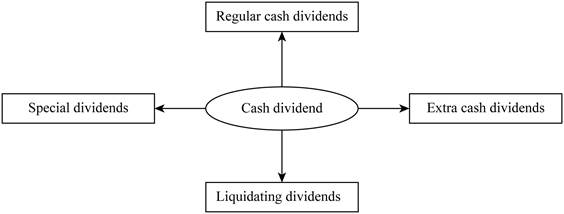
Thus, the above-mentioned are the various forms of cash dividends declared by the board of company and taxable as income to the beneficiary.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
ESSENTIALS CORPORATE FINANCE + CNCT A.
- Your firm is considering an expansion of its operations into a nearby geographic area that the firm is currently not serving. This would require an up-front investment (startup cost) of $989,060.00, to be made immediately. Here are the forecasts that were prepared for this project, shown in the image. The long-term growth rate for cash flows after year 4 is expected to be 4.73%. The cost of capital appropriate for this project is 12.48%. What is the NPV, Profitability Index, IRR and payback in this case?arrow_forwardUse the binomial method to determine the value of an American Put option at time t = 0. The option expires at time t = T = 1/2 and has exercise price E = 55. The current value of the underlying is S(0) = 50 with the underlying paying continuous dividends at the rate D = 0.05. The interest rate is r = 0.3. Use a time step of St = 1/6. Consider the case of p = 1/2 and suppose the volatility is σ = 0.3. Perform all calculations using a minimum of 4 decimal places of accuracy. =arrow_forwardConsider a European chooser option with exercise price E₁ and expiry date T₁ where the relevant put and call options, which depend on the value of the same underlying asset S, have the same exercise price E2 and expiry date T₂. Determine, in terms of other elementary options, the value of the chooser option for the special case when T₁ = T2. Clearly define all notation that you use.arrow_forward
- The continuous conditional probability density function pc(S, t; S', t') for a risk neutral lognormal random walk is given by Pc(S, t; S', t') = 1 σS'√2π(t' - t) - (log(S/S) (ro²)(t − t)] exp 202 (t't) In the binomial method, the value of the underlying is Sm at time step môt and the value of the underlying at time step (m + 1)St is Sm+1. For this case evaluate Ec[(Sm+1)k|Sm] = [°° (S')*pc(S™, mdt; S', (m + 1)8t)dS' showing all steps, where k is a positive integer with k ≥ 1. You may assume that 1 e (x-n)2 2s2dx = 1 for all real numbers n and s with s > 0.arrow_forwardJohn and Jane Doe, a married couple filing jointly, have provided you with their financial information for the year, including details of federal income tax withheld. They need assistance in preparing their tax return. W-2 Income: John earns $150,000 with $35,000 withheld for federal income tax. Jane earns $85,000 with $15,500 withheld for federal income tax. Interest Income: They received $2500 in interest from a savings account, with no tax withheld. Child Tax Credit: They have two children under the age of 17. Mortgage Interest: Paid $28,000 in mortgage interest on their primary residence. Property Taxes: Paid $4,800 in property taxes on their primary residence. Charitable Donations: Donated $22,000 to qualifying charitable organizations. Other Deductions: They have no other deductions to claim. You will gather the appropriate information and complete the forms provided in Blackboard (1040, Schedule A, and Schedule B in preparation of their tax file.arrow_forwardOn the issue date, you bought a 20-year maturity, 5.85% semi-annual coupon bond. The bond then sold at YTM of 6.25%. Now, 5 years later, the similar bond sells at YTM of 5.25%. If you hold the bond now, what is your realized rate of return for the 5-year holding period?arrow_forward
- Bond Valuation with Semiannual Payments Renfro Rentals has issued bonds that have an 11% coupon rate, payable semiannually. The bonds mature in 17 years, have a face value of $1,000, and a yield to maturity of 9.5%. What is the price of the bonds? Round your answer to the nearest cent.arrow_forwardanalyze at least three financial banking products from both the liability side (like time deposits, fixed income, stocks, structure products, etc). You will need to examine aspects such as liquidity, risk, and profitability from a company and an individual point of view.arrow_forwardHow a does researcher ensure that consulting recommendations are data-driven? What does make it effective, and sustainable? Please help explain and give the example How does DMAC help researchers to improve their business processes? How to establish feedback loops for ongoing refinement. Please give the examplesarrow_forward
 Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,




