
(a)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure of
Concept-Introduction:
Lewis structure:
Electron dot structure also known as Lewis dot structure represents the number of valence electrons of an atom or constituent atoms bonded in a molecule. Each dot corresponds to one electron.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The Lewis electron dot structure for given molecules are determined by first drawing the skeletal structure for the given molecules, then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecules are determined.
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed considering each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
Draw Lewis structure of
Outer valence electrons of Carbon and Oxygen are four and six respectively.
Here, one triple bond is required to complete the complete the octets of all the atoms.
After the distribution of electrons, both Carbon and Oxygen atoms gets a lone pair of electrons.
The Lewis structure of

Draw Lewis structure of
Outer valence electrons of Carbon and Nitrogen are four and five respectively.
Here, one triple bond is required to complete the complete the octets of all the atoms.
After the distribution of electrons, both Carbon and Nitrogen atoms gets a lone pair of electrons.
The Lewis structure of

Draw Lewis structure of
Outer valence electrons of Carbon are four.
Here, one triple bond is required to complete the complete the octets of all the atoms.
After the distribution of electrons, both Carbon and Carbon atoms gets a lone pair of electrons.
The Lewis structure of
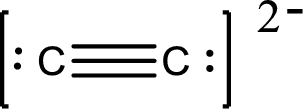
(b)
Interpretation:
MO diagrams of
Concept-Introduction:
Molecular orbital (MO) theory: It is a method for determining molecular structure in which electrons are not assigned to individual bonds between atoms, but are treated as moving under the influence of the nuclei in the whole molecule.
According to this theory there are two types of orbitals,
- (1) Bonding orbitals
- (2) Antibonding orbitals
Electrons in molecules are filled in accordance with the energy; the anti-bonding orbital has more energy than the bonding orbitals.
The electronic configuration of oxygen molecule
The * represent the antibonding orbital
Orbital diagram represents each orbital with a box, with orbital’s in the same subshell in connected boxes, electrons are shown as arrows in the boxes, pointing up or down to indicate their spins.
Bond order: It is the measure of number of electron pairs shared between two atoms.
Bond length is inversely proportional to the bond order.
If two or more different chemical species having same number of valence electrons are known as isoelectronic species.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
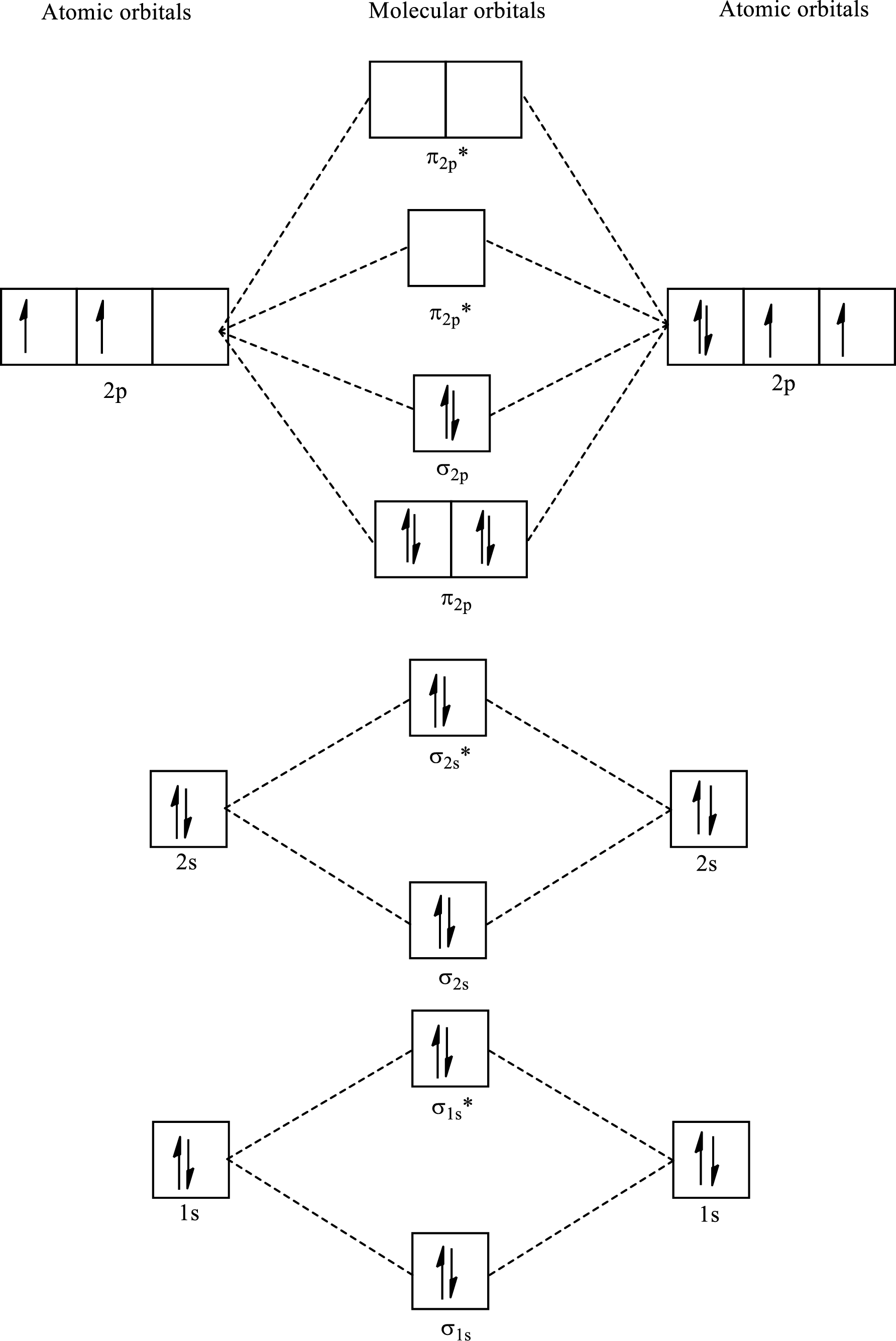
Determine the electron configuration:
Determine the bond order:
Here, number of bonding orbitals is
The number of electrons present in bonding and antibonding orbitals is same for these compounds. Hence,
The bond order for
The bond order for
Draw the MO diagram:
Molecular Orbital diagram for
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change
- Using a cell of known pathlength b = 1.25115 x 10-3 cm, a water absorption spectrum was measured. The band at 1645 cm-1, assigned to the O-H bending, showed an absorbance, A, of 1.40. a) Assuming that water density is 1.00 g/mL, calculate the water molar concentration c (hint: M= mole/L) b) Calculate the molar absorptivity, a, of the 1645 cm-1 band c) The transmitted light, I, can be written as I= Ioexp(-xb), where x is the absorption coefficient (sometimes designated as alpha), Io is the input light, and b is the cell pathlength. Prove that x= (ln10)*x*c. (Please provide a full derivation of the equation for x from the equation for I). d) Calculate x for the 1645 cm-1 bandarrow_forwardI need help with the follloaingarrow_forwardFor a CARS experiment on a Raman band 918 cm-1, if omega1= 1280 nm, calculate the omega2 in wavelength (nm) and the CARS output in wavelength (nm).arrow_forward
- I need help with the following questionarrow_forwardFor CARS, which statement is not true regarding its advantages? a) Contrast signal based on vibrational characteristics, no need for fluorescent tagging. b) Stronger signals than spontaneous Raman. c) Suffers from fluorescence interference, because CARS signal is at high frequency. d) Faster, more efficient imaging for real-time analysis. e) Higher resolution than spontaneous Raman microscopy.arrow_forwardDraw the major product of the Claisen condensation reaction between two molecules of this ester. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Incorrect, 5 attempts remaining 1. NaOCH3/CH3OH 2. Acidic workup Select to Draw O Incorrect, 5 attempts remaining The total number of carbons in the parent chain is incorrect. Review the reaction conditions including starting materials and/or intermediate structures and recount the number of carbon atoms in the parent chain of your structure. OKarrow_forward
- Using a cell of known pathlength b = 1.25115 x 10-3 cm, a water absorption spectrum was measured. The band at 1645 cm-1, assigned to the O-H bending, showed an absorbance, A, of 1.40. a) Assuming that water density is 1.00 g/mL, calculate the water molar concentration c (hint: M= mole/L) b) Calculate the molar absorptivity, a, of the 1645 cm-1 band c) The transmitted light, I, can be written as I= Ioexp(-xb), where x is the absorption coefficient (sometimes designated as alpha), Io is the input light, and b is the cell pathlength. Prove that x= (ln10)*x*c d) Calculate x for the 1645 cm-1 bandarrow_forwardConvert 1.38 eV into wavelength (nm) and wavenumber (cm-1) (c = 2.998 x 108 m/s; h = 6.626 x 10-34 J*s).arrow_forwardCan you help me understand the CBC method on metal bridging by looking at this problem?arrow_forward
- A partir de Aluminio y Co(NO3)2ꞏ6H2O, indicar las reacciones a realizar para obtener Azul de Thenard (Al2CoO4).arrow_forwardTo obtain Thenard Blue (Al2CoO4), the following reaction is correct (performed in an oven):Al(OH)3 + Co(OH)2 → Al2CoO4 + 4 H2Oarrow_forwardProblem 38 can u explain and solve thanks april 24arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





