
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bromination:

2-methyl propane undergoes radical bromination which yields the 2-bromo-2-methylpropane.because bromination will occur where the tertiary radical is present.(Bromination reactions are more selective reaction).
The mechanism of monobromination of ethane (as an example) includes three steps,
- (i) Initiation
- (ii) Propagation
- (iii) Termination
Thus the mechanism of monobromination of ethane is shown below,
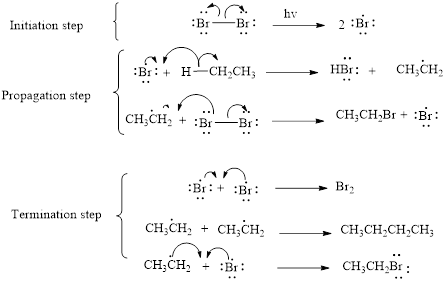
In a halogenation reaction, one or more halogen atoms are introduced into an organic compound. Generally, these reactions are initiated in the presence of light or heat.
Bromination will occur on tertiary radical than the secondary than primary radical, tertiary radical is more stable radical than the other radicals.
(a)
Answer to Problem 12P
3-methyl hexane undergoes radical bromination and yields the 3-bromo-3-methylhexane which is shown below
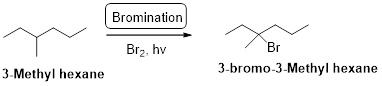
Explanation of Solution
3-methyl hexane undergoes radical bromination and yields the 3-bromo-3-methylhexane according to the above mentioned mechanism steps. The reaction is shown below,
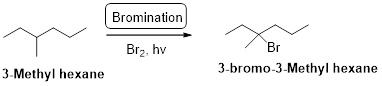
(b)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Chlorination:
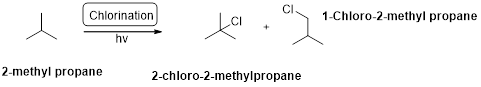
2-methyl propane undergoes radical chlorination and yields the 2-bromo-2-methylpropane and 1-bromo-2-methyl propane.
The mechanism of monochlorination of ethane includes three steps,
- (i) Initiation
- (ii) Propagation
- (iii) Termination
The mechanism of monochlorination of ethane is shown below,
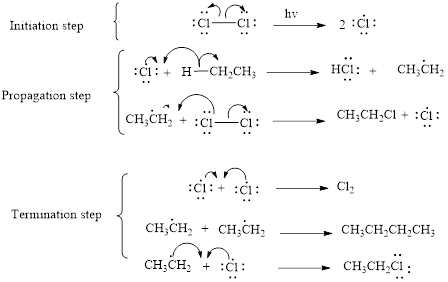
In a halogenation reaction, one or more halogen atoms are introduced into an organic compound. Generally, these reactions are initiated in the presence of light or heat.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
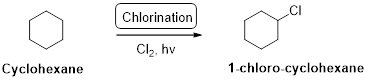
Cyclohexane undergoes radical chlorination; all the carbons in cyclohexane are secondary. Therefore, it yields the 1-chloro cyclohexane according to the above mentioned mechanism steps. And the reaction is shown above.
(c)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Chlorination:
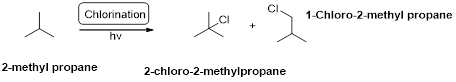
2-methyl propane undergoes radical chlorination and yields the 2-bromo-2-methylpropane and 1-bromo-2-methyl propane.
The mechanism of monochlorination of ethane includes three steps,
- (i) Initiation
- (ii) Propagation
- (iii) Termination
The mechanism of monochlorination of ethane is shown below,

In a halogenation reaction, one or more halogen atoms are introduced into an organic compound. Generally, these reactions are initiated in the presence of light or heat.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
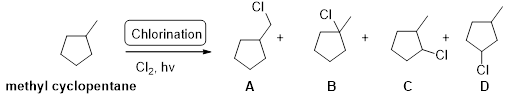
Methyl cyclopentane undergoes radical chlorination; the carbons in cyclopentane are secondary and primary. Therefore, it yields the four types of chlorocyclopentane according to the above mentioned mechanism steps. And the reaction is shown below
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
EBK ESSENTIAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- What is the missing reactant R in this organic reaction? ་ ་ ་ ་ ་ ་ ་ ་ ་ ་ +R H3O+ • Draw the structure of R in the drawing area below. N • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds if it's necessary to draw one particular enantiomer. Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardWrite the systematic name of each organic molecule: H structure H OH OH H OH name ☐ OHarrow_forwardDetermine whether each of the following molecules is a hemiacetal, acetal, or neither and select the appropriate box in the table. CH3O OH OH OH hemiacetal acetal neither hemiacetal acetal neither Xarrow_forward
- What is the missing reactant R in this organic reaction? N N དལ་ད་་ + R • Draw the structure of R in the drawing area below. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds if it's necessary to draw one particular enantiomer. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ㄖˋarrow_forwardDraw the condensed structure of 4-hydroxy-3-methylbutanal. Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure.arrow_forwardUsing the bond energy values, calculate the energy that must be supplied or is released upon the polymerization of 755 monomers. If energy must be supplied, provide a positive number; if energy is released, provide a negative number. Hint: Avogadro’s number is 6.02 × 1023.arrow_forward
- -AG|F=2E|V 3. Before proceeding with this problem you may want to glance at p. 466 of your textbook where various oxo-phosphorus derivatives and their oxidation states are summarized. Shown below are Latimer diagrams for phosphorus at pH values at 0 and 14: Acidic solution -0.93 +0.38 -0.51 -0.06 H3PO4 →H4P206 H3PO3 H3PO2 → P→ PH3 -0.28 -0.50 → -0.50 Basic solution 3-1.12 -1.57 -2.05 -0.89 PO HPO →→H2PO2 P PH3 -1.73 a) Under acidic conditions, H3PO4 can be reduced into H3PO3 directly (-0.28V), or via the formation and reduction of H4P2O6 (-0.93/+0.38V). Calculate the values of AG's for both processes; comment. (3 points) 0.5 PH, 0.0 -0.5- 2 3 9 3 -1.5 -2.0 Pa H,PO H,PO H,PO -3 -1 0 2 4 Oxidation state, N 2 b) Frost diagram for phosphorus under acidic conditions is shown. Identify possible disproportionation and comproportionation processes; write out chemical equations describing them. (2 points) c) Elemental phosphorus tends to disproportionate under basic conditions. Use data in…arrow_forwardThese two reactions appear to start with the same starting materials but result in different products. How do the chemicals know which product to form? Are both products formed, or is there some information missing that will direct them a particular way?arrow_forwardWhat would be the best choices for the missing reagents 1 and 3 in this synthesis? 1. PPh3 3 1 2 2. n-BuLi • Draw the missing reagents in the drawing area below. You can draw them in any arrangement you like. • Do not draw the missing reagent 2. If you draw 1 correctly, we'll know what it is. • Note: if one of your reagents needs to contain a halogen, use bromine. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Priva ×arrow_forward
- Predict the products of this organic reaction: Explanation Check IN NaBH3CN H+ ? Click and drag to start drawing a structure. D 5 C +arrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: H3O+ + ? • Draw all the reasonable products in the drawing area below. If there are no products, because no reaction will occur, check the box under the drawing area. • Include both major and minor products, if some of the products will be more common than others. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds if you need to distinguish between enantiomers. No reaction. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. dmarrow_forwardIarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

