
Concept explainers
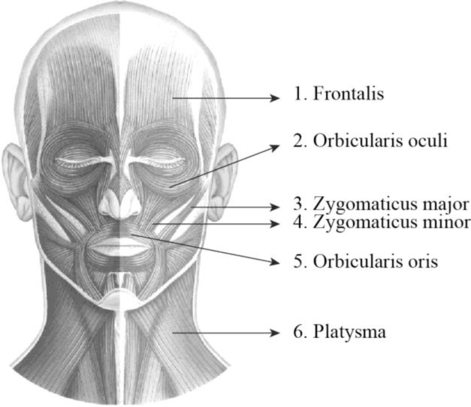
To label: The label the structures in figure 14.1 (a).
Introduction: A group of skeletal muscles that was supplied by the facial nerves is termed as the facial muscles. They are involved in controlling facial expression. It is also termed as mimetic muscles and it includes zygomaticus major, zygomaticus minor, orbicularis oculi, orbicularis oris, platysma, and occipitofrontalis muscle.
Answer to Problem 1.1BGL
Pictorial representation:
Explanation of Solution
1. Frontalis: It is a thin, quadrilateral form of muscle which is categorized as the frontal belly and occipital belly. The frontal belly lies over the frontal bone and is involved raising the eyebrows and wrinkling the forehead. The occipital belly lies over the occipital bone and involved in pulling the scalp posteriorly.
2. Orbicularis oculi: Orbicularis oculi is a facial muscle which is directly situated underneath the surface of the skin of the eyes. These muscles are involved in controlling the eye movement. It is a ring-like band of muscle that specifically encircles the eye. It is situated below the tissue of eyelid and makes the eyelid to blink or close.
3. Zygomaticus major: Zygomaticus major is a muscle of facial expression. It is involved in the superior and posterior motion of the mouth. This action of drawing the angle of mouth especially controls the smiling. This muscle is situated between the corner of the mouth and the zygomatic bone. It is located inferiorly within the zygomatic minor.
4. Zygomaticus minor: It is located between the zygomatic bone and the corner of the mouth. Raising the upper lip and exposing the upper teeth is the main function of this muscle.
5. Orbicularis oris: Orbicularis oris is a facial muscle involved in controlling the lip and mouth movements. These muscles are originated from the bones of upper and lower jaw and palates. It is a sphincter muscle that specifically encircles the mouth. These muscles are involved in closing and pursing of lips.
6. Platysma: It is a wide, flat muscle that covers the entire anterior neck and the lower mandible and it ends on the chest. It depresses the mandible and tenses the skin of the neck.
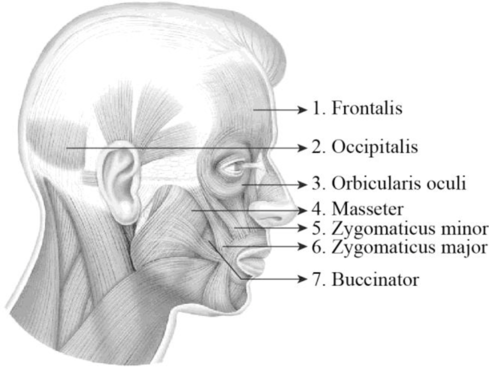
To label: The label the structures in figure 14.1 (c).
Answer to Problem 1.1BGL
Pictorial representation:
Explanation of Solution
1. Frontalis: It is a thin, quadrilateral form of muscle which is categorized as the frontal belly and occipital belly. The frontal belly lies over the frontal bone and is involved raising the eyebrows and wrinkling the forehead. The occipital belly lies over the occipital bone and involved in pulling the scalp posteriorly.
2. Occipitalis: It is situated over the inferior portion of the occipital bone. It is innervated by the facial nerve and is involved in the back movement of the skull.
3. Orbicularis oculi: Orbicularis oculi is a facial muscle which is directly situated underneath the surface of the skin of the eyes. These muscles are involved in controlling the eye movement. It is a ring-like band of muscle that specifically encircles the eye. It is situated below the tissue of eyelid and makes the eyelid to blink or close.
4. Masseter: The masseter is a facial muscle and it is located in the cheek area and it is one of the muscles of mastication or chewing process. It is a rectangular-shaped muscle and is situated in the anterior portion of the ear between the zygomatic arch and posterior part of the mandible. The main function of these muscles is the elevation and retraction of the mandible.
5. Zygomaticus minor: It is located between the zygomatic bone and the corner of the mouth. Raising the upper lip and exposing the upper teeth is the main function of this muscle.
6. Zygomaticus major: Zygomaticus major is a muscle of facial expression. It is involved in the superior and posterior motion of the mouth. This action of drawing the angle of mouth especially controls the smiling. This muscle is situated between the corner of the mouth and the zygomatic bone. It is located inferiorly within the zygomatic minor.
7. Buccinator: It is situated deep to the masseter and its fibers run transversely and form the fleshy part in the cheek. The function of this muscle is pressing the cheek inward to suck, blow, and whistle.
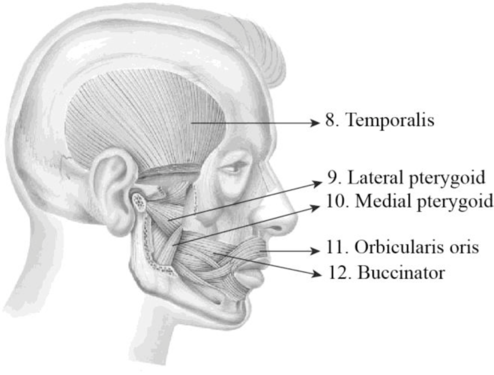
To label: The label the structures in figure 14.1 (d).
Answer to Problem 1.1BGL
Pictorial representation:
Explanation of Solution
8. Temporalis: The temporalis is a broad, fan-shaped muscle and it is located on each side of the head. It covers most of the temporal bone and it is one of the muscles of mastication or chewing process. The main function of these muscles is to move the lower jaw or mandible. It is specifically involved in the elevation and retraction of the mandible.
9. Lateral pterygoid: It is situated superior to the medial pterygoid and deep to masseter. It protracts, depresses, and moves the mandible in it sideways.
10. Medial pterygoid: It is situated inferior to the lateral pterygoid and deep to the masseter. It elevates, protrudes, and moves the mandibles in it sideways.
11. Orbicularis oculi: Orbicularis oculi is a facial muscle which is directly situated underneath the surface of the skin of the eyes. These muscles are involved in controlling the eye movement. It is a ring-like band of muscle that specifically encircles the eye. It is situated below the tissue of eyelid and makes the eyelid to blink or close.
12. Buccinator: It is situated deep to the masseter and its fibers run transversely and form the fleshy part in the cheek. The function of this muscle is pressing the cheek inward to suck, blow, and whistle.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
EBK LABORATORY MANUAL FOR ANATOMY AND P
- If a bacterium using aerobic respiration was to degrade one small protein molecule into 8 molecules of pyruvic acid, how many ATP would that cell make? Assume there is no other carbon source. Units cannot be entered in this style of question but the units of your answer should be in molecules of ATP.arrow_forwardIf a bacterium using aerobic respiration was to degrade a 30 mM solution of citric acid, how many ATP would that cell make? Assume no other carbon source is available. Units cannot be entered in this style of question but the units of your answer should be in mM of ATP.arrow_forwardHow much ATP will be produced during the following metabolic scenario: Aerobic respiration of a 5mM lipid solution that is made up of one glycerol and an 8-carbon fatty acid and 12-carbon fatty acid. Recall that when glycerol breaks down to Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate it costs one ATP but your get an extra FADH2. Every two carbons of a fatty acid break down to one acetyl-CoA. (pathways will be provided on the exam) Units cannot be entered in this style of question but the units of your answer should be in mM of ATP.arrow_forward
- When beta-lactamase was isolated from Staphylcoccus aureus and treated with a phosphorylating agent, only the active site, serine was phosphorylated. Additionally, the serine was found to constitute 0.35% (by weight) of this beta-lactamase enzyme. Using this, calculate the molecular weight of this enzyme and estimate the number of amino acids present in the polypeptide.arrow_forwardBased on your results from the Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA) media, which of your bacteria were mannitol fermenters and which were not mannitol fermenters?arrow_forwardhelp tutor pleasearrow_forward
- Q8. A researcher wants to study the effectiveness of a pill intended to reduce stomach heartburn in pregnant women. The researcher chooses randomly 400 women to participate in this experiment for 9 months of their pregnancy period. They all need to have the same diet. The researcher designs two groups of 200 participants: One group take the real medication intended to reduce heartburn, while the other group take placebo medication. In this study what are: Independent variable: Dependent variable: Control variable: Experimental group: " Control group: If the participants do not know who is consuming the real pills and who is consuming the sugar pills. This study is It happens that 40% of the participants do not find the treatment helpful and drop out after 6 months. The researcher throws out the data from subjects that drop out. What type of bias is there in this study? If the company who makes the medication funds this research, what type of bias might exist in this research work?arrow_forwardHow do I determine the inhertiance pattern from the pedigree diagram?arrow_forwardits an open book assignemntarrow_forward
- Describe two different gene regulation mechanisms involving methylationarrow_forwardWhat is behavioral adaptarrow_forward22. Which of the following mutant proteins is expected to have a dominant negative effect when over- expressed in normal cells? a. mutant PI3-kinase that lacks the SH2 domain but retains the kinase function b. mutant Grb2 protein that cannot bind to RTK c. mutant RTK that lacks the extracellular domain d. mutant PDK that has the PH domain but lost the kinase function e. all of the abovearrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





