
Concept explainers
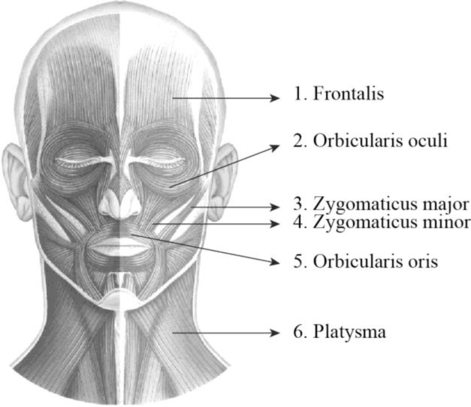
To label: The label the structures in figure 14.1 (a).
Introduction: A group of skeletal muscles that was supplied by the facial nerves is termed as the facial muscles. They are involved in controlling facial expression. It is also termed as mimetic muscles and it includes zygomaticus major, zygomaticus minor, orbicularis oculi, orbicularis oris, platysma, and occipitofrontalis muscle.
Answer to Problem 1.1BGL
Pictorial representation:
Explanation of Solution
1. Frontalis: It is a thin, quadrilateral form of muscle which is categorized as the frontal belly and occipital belly. The frontal belly lies over the frontal bone and is involved raising the eyebrows and wrinkling the forehead. The occipital belly lies over the occipital bone and involved in pulling the scalp posteriorly.
2. Orbicularis oculi: Orbicularis oculi is a facial muscle which is directly situated underneath the surface of the skin of the eyes. These muscles are involved in controlling the eye movement. It is a ring-like band of muscle that specifically encircles the eye. It is situated below the tissue of eyelid and makes the eyelid to blink or close.
3. Zygomaticus major: Zygomaticus major is a muscle of facial expression. It is involved in the superior and posterior motion of the mouth. This action of drawing the angle of mouth especially controls the smiling. This muscle is situated between the corner of the mouth and the zygomatic bone. It is located inferiorly within the zygomatic minor.
4. Zygomaticus minor: It is located between the zygomatic bone and the corner of the mouth. Raising the upper lip and exposing the upper teeth is the main function of this muscle.
5. Orbicularis oris: Orbicularis oris is a facial muscle involved in controlling the lip and mouth movements. These muscles are originated from the bones of upper and lower jaw and palates. It is a sphincter muscle that specifically encircles the mouth. These muscles are involved in closing and pursing of lips.
6. Platysma: It is a wide, flat muscle that covers the entire anterior neck and the lower mandible and it ends on the chest. It depresses the mandible and tenses the skin of the neck.
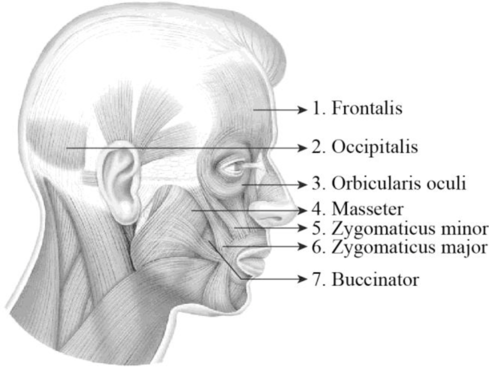
To label: The label the structures in figure 14.1 (c).
Answer to Problem 1.1BGL
Pictorial representation:
Explanation of Solution
1. Frontalis: It is a thin, quadrilateral form of muscle which is categorized as the frontal belly and occipital belly. The frontal belly lies over the frontal bone and is involved raising the eyebrows and wrinkling the forehead. The occipital belly lies over the occipital bone and involved in pulling the scalp posteriorly.
2. Occipitalis: It is situated over the inferior portion of the occipital bone. It is innervated by the facial nerve and is involved in the back movement of the skull.
3. Orbicularis oculi: Orbicularis oculi is a facial muscle which is directly situated underneath the surface of the skin of the eyes. These muscles are involved in controlling the eye movement. It is a ring-like band of muscle that specifically encircles the eye. It is situated below the tissue of eyelid and makes the eyelid to blink or close.
4. Masseter: The masseter is a facial muscle and it is located in the cheek area and it is one of the muscles of mastication or chewing process. It is a rectangular-shaped muscle and is situated in the anterior portion of the ear between the zygomatic arch and posterior part of the mandible. The main function of these muscles is the elevation and retraction of the mandible.
5. Zygomaticus minor: It is located between the zygomatic bone and the corner of the mouth. Raising the upper lip and exposing the upper teeth is the main function of this muscle.
6. Zygomaticus major: Zygomaticus major is a muscle of facial expression. It is involved in the superior and posterior motion of the mouth. This action of drawing the angle of mouth especially controls the smiling. This muscle is situated between the corner of the mouth and the zygomatic bone. It is located inferiorly within the zygomatic minor.
7. Buccinator: It is situated deep to the masseter and its fibers run transversely and form the fleshy part in the cheek. The function of this muscle is pressing the cheek inward to suck, blow, and whistle.
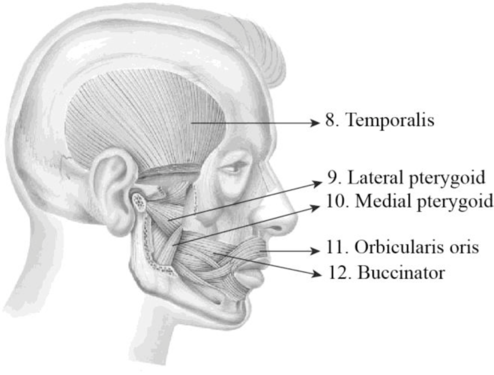
To label: The label the structures in figure 14.1 (d).
Answer to Problem 1.1BGL
Pictorial representation:
Explanation of Solution
8. Temporalis: The temporalis is a broad, fan-shaped muscle and it is located on each side of the head. It covers most of the temporal bone and it is one of the muscles of mastication or chewing process. The main function of these muscles is to move the lower jaw or mandible. It is specifically involved in the elevation and retraction of the mandible.
9. Lateral pterygoid: It is situated superior to the medial pterygoid and deep to masseter. It protracts, depresses, and moves the mandible in it sideways.
10. Medial pterygoid: It is situated inferior to the lateral pterygoid and deep to the masseter. It elevates, protrudes, and moves the mandibles in it sideways.
11. Orbicularis oculi: Orbicularis oculi is a facial muscle which is directly situated underneath the surface of the skin of the eyes. These muscles are involved in controlling the eye movement. It is a ring-like band of muscle that specifically encircles the eye. It is situated below the tissue of eyelid and makes the eyelid to blink or close.
12. Buccinator: It is situated deep to the masseter and its fibers run transversely and form the fleshy part in the cheek. The function of this muscle is pressing the cheek inward to suck, blow, and whistle.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Laboratory Manual for Anatomy and Physiology, 6e Loose-Leaf Print Companion
- Ch.21 What causes patients infected with the yellow fever virus to turn yellow (jaundice)? A. low blood pressure and anemia B. excess leukocytes C. alteration of skin pigments D. liver damage in final stage of disease — What is the advantage for malarial parasites to grow and replicate in red blood cells? A. able to spread quickly B. able to avoid immune detection C. low oxygen environment for growth D. cooler area of the body for growth — Which microbe does not live part of its lifecycle outside humans? A. Toxoplasma gondii B. Cytomegalovirus C. Francisella tularensis D. Plasmodium falciparum — explain your answer thoroughlyarrow_forwardCh.22 Streptococcus pneumoniae has a capsule to protect it from killing by alveolar macrophages, which kill bacteria by… A. cytokines B. antibodies C. complement D. phagocytosis — What fact about the influenza virus allows the dramatic antigenic shift that generates novel strains? A. very large size B. enveloped C. segmented genome D. over 100 genes — explain your answer thoroughlyarrow_forwardWhat is this?arrow_forward
- Molecular Biology A-C components of the question are corresponding to attached image labeled 1. D component of the question is corresponding to attached image labeled 2. For a eukaryotic mRNA, the sequences is as follows where AUGrepresents the start codon, the yellow is the Kozak sequence and (XXX) just represents any codonfor an amino acid (no stop codons here). G-cap and polyA tail are not shown A. How long is the peptide produced?B. What is the function (a sentence) of the UAA highlighted in blue?C. If the sequence highlighted in blue were changed from UAA to UAG, how would that affecttranslation? D. (1) The sequence highlighted in yellow above is moved to a new position indicated below. Howwould that affect translation? (2) How long would be the protein produced from this new mRNA? Thank youarrow_forwardMolecular Biology Question Explain why the cell doesn’t need 61 tRNAs (one for each codon). Please help. Thank youarrow_forwardMolecular Biology You discover a disease causing mutation (indicated by the arrow) that alters splicing of its mRNA. This mutation (a base substitution in the splicing sequence) eliminates a 3’ splice site resulting in the inclusion of the second intron (I2) in the final mRNA. We are going to pretend that this intron is short having only 15 nucleotides (most introns are much longer so this is just to make things simple) with the following sequence shown below in bold. The ( ) indicate the reading frames in the exons; the included intron 2 sequences are in bold. A. Would you expected this change to be harmful? ExplainB. If you were to do gene therapy to fix this problem, briefly explain what type of gene therapy youwould use to correct this. Please help. Thank youarrow_forward
- Molecular Biology Question Please help. Thank you Explain what is meant by the term “defective virus.” Explain how a defective virus is able to replicate.arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Explain why changing the codon GGG to GGA should not be harmful. Please help . Thank youarrow_forwardStage Percent Time in Hours Interphase .60 14.4 Prophase .20 4.8 Metaphase .10 2.4 Anaphase .06 1.44 Telophase .03 .72 Cytukinesis .01 .24 Can you summarize the results in the chart and explain which phases are faster and why the slower ones are slow?arrow_forward
- Can you circle a cell in the different stages of mitosis? 1.prophase 2.metaphase 3.anaphase 4.telophase 5.cytokinesisarrow_forwardWhich microbe does not live part of its lifecycle outside humans? A. Toxoplasma gondii B. Cytomegalovirus C. Francisella tularensis D. Plasmodium falciparum explain your answer thoroughly.arrow_forwardSelect all of the following that the ablation (knockout) or ectopoic expression (gain of function) of Hox can contribute to. Another set of wings in the fruit fly, duplication of fingernails, ectopic ears in mice, excess feathers in duck/quail chimeras, and homeosis of segment 2 to jaw in Hox2a mutantsarrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





