
A projectile is fired from the origin with angle of elevation
α and initial speed
v0. Assuming that air resistance is negligible and that the only force acting on the projectile is gravity, g, we showed in Example 13.4.5 that the position
r(t)=(v0cosα)t i+[(v0sinα)t−12gt2]j
We also showed that the maximum horizontal distance of the projectile is achieved when α=45∘ and in this case the range is R=v20/g.
(a) At what angle should the projectile be fired to achieve maximum height and what is the maximum height?
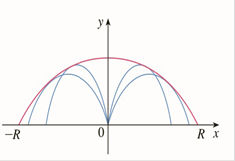
(b) Fix the initial speed v0 and consider the parabola x2+2Ry−R2=0, whose graph is shown in the figure at the left. Show that the projectile can hit any target inside or on the boundary of the region bounded by the parabola and the x-axis, and that it can’t hit any target outside this region.
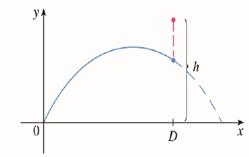
(c) Suppose that the gun is elevated to an angle of inclination α in order to aim at a target that is suspended at a height h directly over a point D units downrange (see the figure below). The target is released at the instant the gun is fired. Show that the projectile always hits the target, regardless of the value v0, provided the projectile does not hit the ground “before” D.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
Bundle: Calculus, 8th + Enhanced WebAssign - Start Smart Guide for Students + WebAssign Printed Access Card for Stewart's Calculus, 8th Edition, Multi-Term
- (14 points) Let f: R3 R and T: R3. →R³ be defined by f(x, y, z) = ln(x²+ y²+2²), T(p, 0,4)=(psin cos 0, psin sin, pcos). (a) (4 points) Write out the composition g(p, 0, 4) = (foT)(p,, ) explicitly. Then calculate the gradient Vg directly, i.e. without using the chain rule. (b) (4 points) Calculate the gradient Vf(x, y, z) where (x, y, z) = T(p, 0,4). (c) (6 points) Calculate the derivative matrix DT(p, 0, p). Then use the Chain Rule to calculate Vg(r,0,4).arrow_forward(10 points) Let S be the upper hemisphere of the unit sphere x² + y²+2² = 1. Let F(x, y, z) = (x, y, z). Calculate the surface integral J F F-dS. Sarrow_forward(8 points) Calculate the following line integrals. (a) (4 points) F Fds where F(x, y, z) = (x, y, xy) and c(t) = (cost, sint, t), tЄ [0,π] . (b) (4 points) F. Fds where F(x, y, z) = (√xy, e³, xz) where c(t) = (t², t², t), t = [0, 1] .arrow_forward
- review help please and thank you!arrow_forward(10 points) Let S be the surface that is part of the sphere x² + y²+z² = 4 lying below the plane 2√3 and above the plane z-v -√3. Calculate the surface area of S.arrow_forward(8 points) Let D = {(x, y) | 0 ≤ x² + y² ≤4}. Calculate == (x² + y²)³/2dA by making a change of variables to polar coordinates, i.e. x=rcos 0, y = r sin 0.arrow_forward
- x² - y² (10 points) Let f(x,y): = (a) (6 points) For each vector u = (1, 2), calculate the directional derivative Duƒ(1,1). (b) (4 points) Determine all unit vectors u for which Duf(1, 1) = 0.arrow_forwardSolve : X + sin x = 0. By the false positioning numerical methodarrow_forwardSolve: X + sin X = 0 by the false positionining numerical methodarrow_forward
- On from the equation: 2 u = C₁ + C₂ Y + Czy + Cu y³ Find C₁, C₂, C3 and Cy Using these following Cases : (a) 4=0 at y=0 (b) U = U∞ at y = 8 du (c) at Y = S ду --y. ди = 0 at y = 0 бугarrow_forwardTips S ps L 50. lim x2 - 4 x-2x+2 51. lim 22 - X 52. 53. x 0 Answer lim x 0 lim 2-5 X 2x2 2 x² Answer -> 54. lim T - 3x - - 25 +5 b+1 b3b+3 55. lim X x-1 x 1 Answer 56. lim x+2 x 2 x 2 57. lim x²-x-6 x-2 x²+x-2 Answer-> 23-8 58. lim 2-22-2arrow_forwardS 36. lim 5x+2 x-2 37. lim √√2x4 + x² x-3 Answer-> 2x3 +4 38. lim x12 √ x² + 1 √√x² + 8 39. lim x-1 2x+4 Answer 40. lim x3 2x x√x² + 7 √√2x+3arrow_forward
 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage LearningAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage LearningAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage

