
A particle P moves with constant angular speed
(a) Find the velocity vector v and show that
(b) Show that the speed
(c) Find the acceleration vector a. Show that it is proportional to r and that it points toward the origin. An acceleration with this property is called a centripetal acceleration. Show that the magnitude of the acceleration vector is
(d) Suppose that the particle has mass m. Show that the magnitude of the force F that is required to produce this motion, called a centripetal force, is
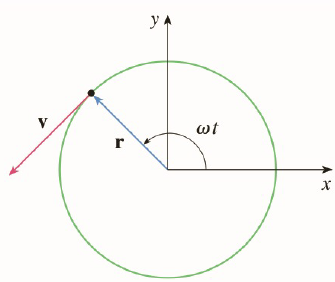
a)
To find:
The velocity vector
Answer to Problem 1P
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
1) Concept:
If
2) Given:
3) Calculation:
Consider
The velocity vector at time
Therefore, differentiating
Now
As
Since
Conclusion:
b)
To show:
The speed of particle
Answer to Problem 1P
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
1) Concept:
Speed of a particle is the magnitude of velocity vector
2) Given:
3) Calculation:
From part (a),
Therefore, as the speed of a particle is the magnitude of velocity vector
The period
At the speed
Therefore, period is
Conclusion:
The speed of particle
c)
To find:
Acceleration vector
Answer to Problem 1P
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
1) Concept:
The acceleration of a particle is
2) Calculation:
From part (a),
The acceleration of particle is
Therefore, differentiating
This concludes that acceleration is proportional to
The acceleration with this property is called centripetal acceleration.
Now, the magnitude of acceleration vector is given by
Conclusion:
The acceleration of particle is
Magnitude of acceleration vector is given by
d)
To show:
The magnitude of force required to produce this motion is
Answer to Problem 1P
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
1) Concept:
Here use Newton’s Second Law of motion.
Newton’s Second Law:
If at any time
2) Calculation:
By using Newton’s Second Law of motion,
Therefore, magnitude of force required to produce this motion is
From part (c),
Hence,
Conclusion:
The magnitude of force required to produce this motion is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Calculus (MindTap Course List)
- I need help in ensuring that I explain it propleryy in the simplifest way as possiblearrow_forwardI need help making sure that I explain this part accutartly.arrow_forwardPlease help me with this question as I want to know how can I perform the partial fraction decompostion on this alebgric equation to find the time-domain of y(t)arrow_forward
- Please help me with this question as I want to know how can I perform the partial fraction on this alebgric equation to find the time-domain of y(t)arrow_forwardEvaluate F³ - dr where ♬ = (4z, -4y, x), and C' is given by (t) = (sin(t), t, cos(t)), 0≤t≤ñ .arrow_forwardMid-Term Review Find the formula for (f + g)(x). f(x) = x² - 10x + 25 and g(x) = x² - 10x + 24 (f + g) (x) = [ 2 ]x² X + DELL Skip Sarrow_forward
- Calculus III May I please have some elaborations on Example 2 part a? Thank you.arrow_forward1. A bicyclist is riding their bike along the Chicago Lakefront Trail. The velocity (in feet per second) of the bicyclist is recorded below. Use (a) Simpson's Rule, and (b) the Trapezoidal Rule to estimate the total distance the bicyclist traveled during the 8-second period. t 0 2 4 6 8 V 10 15 12 10 16 2. Find the midpoint rule approximation for (a) n = 4 +5 x²dx using n subintervals. 1° 2 (b) n = 8 36 32 28 36 32 28 24 24 20 20 16 16 12 8- 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 12 8 4 1 2 3 4 5 6arrow_forward= 5 37 A 4 8 0.5 06 9arrow_forward
- Consider the following system of equations, Ax=b : x+2y+3z - w = 2 2x4z2w = 3 -x+6y+17z7w = 0 -9x-2y+13z7w = -14 a. Find the solution to the system. Write it as a parametric equation. You can use a computer to do the row reduction. b. What is a geometric description of the solution? Explain how you know. c. Write the solution in vector form? d. What is the solution to the homogeneous system, Ax=0?arrow_forward2. Find a matrix A with the following qualities a. A is 3 x 3. b. The matrix A is not lower triangular and is not upper triangular. c. At least one value in each row is not a 1, 2,-1, -2, or 0 d. A is invertible.arrow_forwardFind the exact area inside r=2sin(2\theta ) and outside r=\sqrt(3)arrow_forward
 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage LearningAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage LearningAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning


