
Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics; Modified Mastering Engineering with Pearson eText -- Standalone Access Card -- for Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780134229294
Author: HIBBELER
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 13.5, Problem 9FP
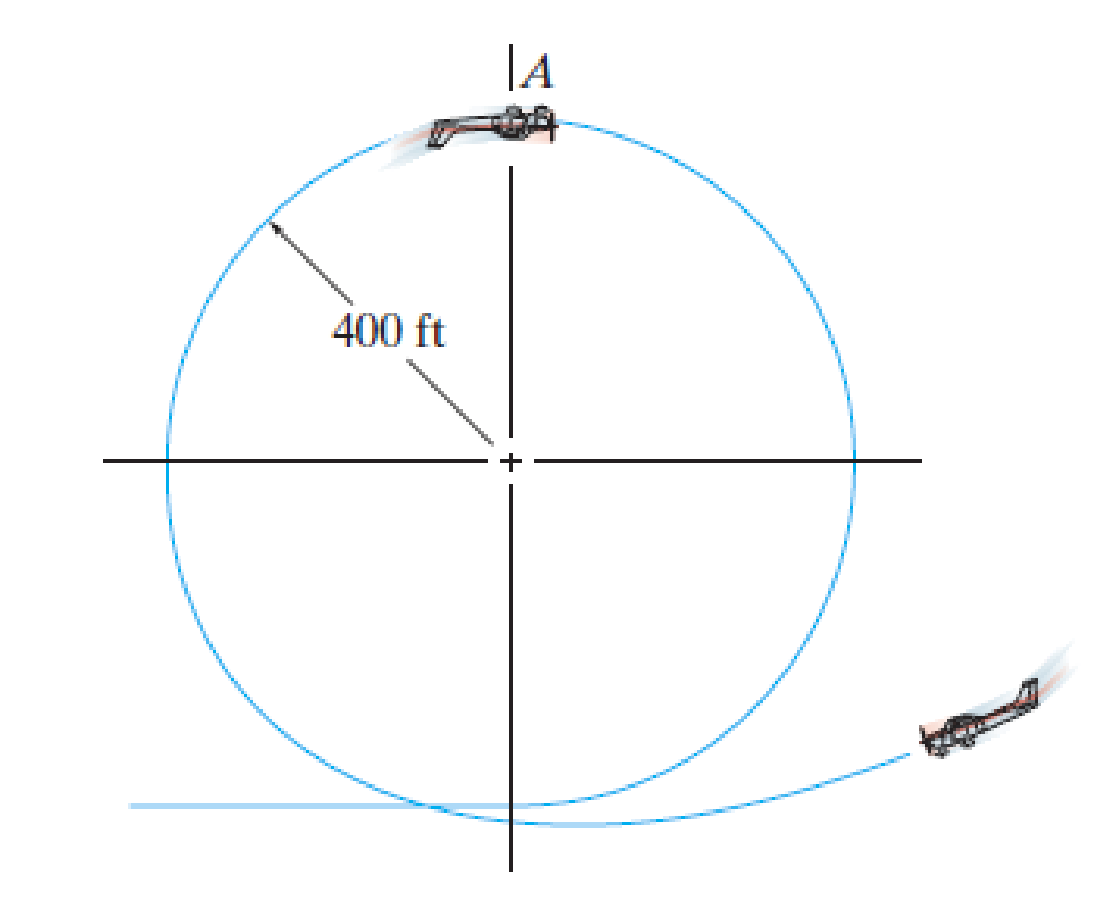
A pilot weighs 150 lb and is traveling at a constant speed of 120 ft/ s. Determine the normal force he exerts on the seat of the plane when he is upside down at A. The loop has a radius of curvature of 400ft.
Prob. F13-9
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule03:24
Students have asked these similar questions
Pearson eText
Study Area
Document Sharing
User Settings
mylabmastering.pearson.com
Access Pearson
P Pearson MyLab and Mastering
Problem 14.69
Part A
P Course Home
b Answered: HW_02.pdf EE 213-01 > Assignments HW_#...
1 of 8
Review
The 5-kg collar has a velocity of 7 m/s to the right when
it is at A. It then travels down along the smooth guide
shown in (Figure 1). The spring has an unstretched
length of 100 mm and B is located just before the end
of the curved portion of the rod.
Determine the speed of the collar when it reaches point B, which is located just before the end of the curved portion of the rod.
Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
Figure
1 of 1
με
v =
Value
Units
Submit
Request Answer
Part B
?
What is the normal force on the collar at this instant?
Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
☐
μÅ
?
N =
Value
Units
Submit
Request Answer
Provide Feedback
Next >
Pearson eText
Study Area
mylabmastering.pearson.com
Access Pearson
P Pearson MyLab and Mastering
Problem 15.106
P Course Home
b Answered: HW_02.pdf EE 213-01 > Assignments HW_#...
8 of 8
Document Sharing
User Settings
The two spheres A and B each have a mass of 400 g.
The spheres are fixed to the horizontal rods as shown in
(Figure 1) and their initial velocity is 2 m/s. The mass of
the supporting frame is negligible and it is free to rotate.
Neglect the size of the spheres.
Part A
If a couple moment of M = 0.3 N · m is applied to the frame, determine the speed of the spheres in 3 s.
Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
Figure
1 of 1
☐
?
v =
Value
Units
Units input for part A
Submit
Request Answer
Return to Assignment
Provide Feedback
■Review
Pearson eText
Study Area
Access Pearson
mylabmastering.pearson.com
P Pearson MyLab and Mastering
Problem 15.79
P Course Home
b Answered: HW_02.pdf EE 213-01 > Assignments HW_#...
6 of 8
>
Document Sharing
User Settings
The two disks A and B have a mass of 4 kg and 5 kg,
respectively. They collide with the initial velocities shown.
The coefficient of restitution is e = 0.65. Suppose that
(VA)1 = 6 m/s, (VB)1 = 8 m/s. (Figure 1)
Part A
Determine the magnitude of the velocity of A just after impact.
Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
Figure
1 of 1
μÅ
(VA)2 =
Value
Units
Submit
Request Answer
Part B
?
Review
Determine the angle between the x axis and the velocity of A just after impact, measured clockwise from the negative x axis.
Express your answer in degrees to three significant figures.
ΕΠΙ ΑΣΦ
vec
01
Submit
Request Answer
Part C
?
Determine the magnitude of the velocity of B just after impact.
Express your answer to three significant…
Chapter 13 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics; Modified Mastering Engineering with Pearson eText -- Standalone Access Card -- for Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics (14th Edition)
Ch. 13.4 - In each case, determine its velocity when t = 2 s...Ch. 13.4 - In each case, determine its velocity at s = 8 m if...Ch. 13.4 - Determine the initial acceleration of the 10-kg...Ch. 13.4 - Write the equations of motion in the x and y...Ch. 13.4 - The motor winds n the cable with a constant...Ch. 13.4 - If motor M exerts a force of F = (10t2 + 100) N on...Ch. 13.4 - A spring of stiffness k = 500 N/m is mounted...Ch. 13.4 - The spring has a stiffness k = 200 N/m and is...Ch. 13.4 - Block B rests upon a smooth surface. If the...Ch. 13.4 - The 6-lb particle is subjected to the action of...
Ch. 13.4 - The two boxcars A and B have a weight of 20 000 lb...Ch. 13.4 - If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the...Ch. 13.4 - If the 50-kg crate starts from rest and achieves a...Ch. 13.4 - If blocks A and B of mass 10 kg and 6 kg...Ch. 13.4 - The 10-lb block has a speed of 4 ft/s when the...Ch. 13.4 - The 10-lb block has a speed of 4 ft/s when the...Ch. 13.4 - The speed of the 3500-lb sports car is plotted...Ch. 13.4 - The conveyor belt is moving at 4 m/s. If the...Ch. 13.4 - The conveyor belt is designed to transport...Ch. 13.4 - Determine the time needed to pull the cord at B...Ch. 13.4 - Cylinder B has a mass m and is hoisted using the...Ch. 13.4 - Block A has a weight of 8 lb and block B has a...Ch. 13.4 - The 2-Mg truck is traveling at 15 m/s when the...Ch. 13.4 - The motor lifts the 50-kg crate with an...Ch. 13.4 - The 75-kg man pushes on the 150-kg crate with a...Ch. 13.4 - The coefficient of kinetic friction is k, and the...Ch. 13.4 - A 40-lb suitcase slides from rest 20 ft down the...Ch. 13.4 - Solve Prob. 13-18 if the suitcase has an initial...Ch. 13.4 - If the coefficient of kinetic friction between...Ch. 13.4 - The conveyor belt delivers each 12-kg crate to the...Ch. 13.4 - The 50-kg block A is released from rest. Determine...Ch. 13.4 - If the supplied force F = 150 N, determine the...Ch. 13.4 - A 60-kg suitcase slides from rest 5 m down the...Ch. 13.4 - Solve Prob. 13-24 if the suitcase has an initial...Ch. 13.4 - The 1.5 Mg sports car has a tractive force of F =...Ch. 13.4 - The conveyor belt is moving downward at 4 m/s. If...Ch. 13.4 - At the instant shown the 100-lb block A is moving...Ch. 13.4 - Determine the velocity of the 200-lb crate when t...Ch. 13.4 - Determine the velocity of the 400-kg crate A when...Ch. 13.4 - The tractor is used to lift the 150-kg load B with...Ch. 13.4 - If the tractor travels to the right with an...Ch. 13.4 - Block A and B each have a mass m. Determine the...Ch. 13.4 - The 4-kg smooth cylinder is supported by the...Ch. 13.4 - The coefficient of static friction between the...Ch. 13.4 - If the spring is unstretched when s = 0 and the...Ch. 13.4 - Neglecting the mass of the rope and pulley, and...Ch. 13.4 - Determine the force in the cable when t = 5 s, if...Ch. 13.4 - An electron of mass m is discharged with an...Ch. 13.4 - The 400-lb cylinder at A is hoisted using the...Ch. 13.4 - What is their velocity at this instant?Ch. 13.4 - Block A has a mass mA and is attached to a spring...Ch. 13.4 - A parachutist having a mass m opens his parachute...Ch. 13.4 - Neglect the mass of the motor and pulleys.Ch. 13.4 - If the force exerted on cable AB by the motor is F...Ch. 13.4 - Blocks A and B each have a mass m. Determine the...Ch. 13.4 - Blocks A and Beach have a mass m. Determine the...Ch. 13.4 - If the board AC pushes on the block at an angle ...Ch. 13.4 - If a horizontal force P = 12lb is applied to block...Ch. 13.4 - A freight elevator, including its load, has a mass...Ch. 13.4 - The block A has a mass mA and rests on the pan B,...Ch. 13.5 - P13-5.Set up the n, t axes and write the equations...Ch. 13.5 - P13-6.Set up the n, b, t axes and write the...Ch. 13.5 - The block rests at a distance of 2 m from the...Ch. 13.5 - Prob. 8FPCh. 13.5 - A pilot weighs 150 lb and is traveling at a...Ch. 13.5 - The sports car is traveling along a 30 banked road...Ch. 13.5 - If the 10-kg ball has a velocity of 3m/ s when it...Ch. 13.5 - The motorcycle has a mass of 0.5 Mg and a...Ch. 13.5 - Prob. 52PCh. 13.5 - Prob. 53PCh. 13.5 - The 2-kg block B and 15-kg cylinder A are...Ch. 13.5 - Determine the maximum constant speed at which the...Ch. 13.5 - Cartons having a mass of 5 kg are required to move...Ch. 13.5 - Prob. 57PCh. 13.5 - Prob. 58PCh. 13.5 - Prob. 59PCh. 13.5 - Prob. 60PCh. 13.5 - At the instant B = 60, the boys center of mass G...Ch. 13.5 - A girl having a mass of 25 kg sits at the edge of...Ch. 13.5 - The pendulum bob B has a weight of 5 lb and is...Ch. 13.5 - The pendulum bob B has a mass m and is released...Ch. 13.5 - Determine the constant speed of the passengers on...Ch. 13.5 - A motorcyclist in a circus rides his motorcycle...Ch. 13.5 - The vehicle is designed to combine the feel of a...Ch. 13.5 - The 0.8-Mg car travels over the hill having the...Ch. 13.5 - The 0.8-Mg car travels over the hill having the...Ch. 13.5 - When it reaches the curved portion AB, it is...Ch. 13.5 - Determine the resultant normal and frictional...Ch. 13.5 - If he rotates about the z axis with a constant...Ch. 13.5 - Determine the maximum speed at which the car with...Ch. 13.5 - Determine the maximum constant speed at which the...Ch. 13.5 - The box has a mass m and slides down the smooth...Ch. 13.5 - Prove that if the block is released from rest at...Ch. 13.5 - The cylindrical plug has a weight of 2 lb and it...Ch. 13.5 - When crossing an intersection, a motorcyclist...Ch. 13.5 - The airplane, traveling at a constant speed of 50...Ch. 13.5 - The 2-kg pendulum bob moves in the vertical plane...Ch. 13.5 - The 2-kg pendulum bob moves in the vertical plane...Ch. 13.5 - If it has a speed of 1.5 m/s when y = 0.2 m,...Ch. 13.5 - The ball has a mass m and is attached to the cord...Ch. 13.6 - If the attached spring has a stiffness k = 2...Ch. 13.6 - Determine the constant angular velocity of the...Ch. 13.6 - If = ( t2) rad, where t is in seconds, determine...Ch. 13.6 - The 2-Mg car is traveling along the curved road...Ch. 13.6 - The 0.2-kg pin P is constrained to move in the...Ch. 13.6 - If the cam is rotating at a constant rate of 6...Ch. 13.6 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force...Ch. 13.6 - Determine the magnitude of the unbalanced force...Ch. 13.6 - Rod OA rotates counterclockwise with a constant...Ch. 13.6 - The boy of mass 40 kg is sliding down the spiral...Ch. 13.6 - Using a forked rod, a 0.5-kg smooth peg P is...Ch. 13.6 - The arm is rotating at a rate of = 4 rad/s when ...Ch. 13.6 - If arm OA rotates with a constant clockwise...Ch. 13.6 - Determine the normal and frictional driving forces...Ch. 13.6 - A smooth can C, having a mass of 3 kg, is lifted...Ch. 13.6 - Prob. 96PCh. 13.6 - Prob. 97PCh. 13.6 - The particle has a mass of 0.5 kg and is confined...Ch. 13.6 - A car of a roller coaster travels along a track...Ch. 13.6 - The 0.5-lb ball is guided along the vertical...Ch. 13.6 - The ball of mass misguided along the vertical...Ch. 13.6 - Using a forked rod, a smooth cylinder P, having a...Ch. 13.6 - The pilot of the airplane executes a vertical loop...Ch. 13.6 - The collar has a mass of 2 kg and travels along...Ch. 13.6 - The particle has a mass of 0.5 kg and is confined...Ch. 13.6 - Solve Prob. 13-105 If the arm has an angular...Ch. 13.6 - The forked rod is used to move the smooth 2-lb...Ch. 13.6 - Prob. 108PCh. 13.6 - Rod OA rotates counterclockwise at a constant...Ch. 13.6 - Solve Prob. 13-109 if motion is in the vertical...Ch. 13.7 - If his speed is a constant vP = 80 ft/s, determine...Ch. 13.7 - The earth has an orbit with eccentricity 0.0167...Ch. 13.7 - Prob. 114PCh. 13.7 - Determine the speed of a satellite launched...Ch. 13.7 - Prob. 116PCh. 13.7 - Prove Keplers third law of motion. Hint: Use Eqs....Ch. 13.7 - Prob. 118PCh. 13.7 - Prob. 119PCh. 13.7 - Determine the constant speed of satellite S so...Ch. 13.7 - Prob. 121PCh. 13.7 - Prob. 122PCh. 13.7 - Prob. 123PCh. 13.7 - Prob. 124PCh. 13.7 - The rocket is traveling around the earth in free...Ch. 13.7 - Prob. 127PCh. 13.7 - Prob. 128PCh. 13.7 - Prob. 129PCh. 13.7 - Prob. 130PCh. 13.7 - The rocket is traveling around the earth in free...Ch. 13.7 - Prob. 132PCh. 13.7 - Prob. 3CPCh. 13.7 - If the trailer has a mass of 250 kg and coasts 45...Ch. 13.7 - The coefficient of kinetic friction between the...Ch. 13.7 - Block B rests on a smooth surface. If the...Ch. 13.7 - If the motor draws in the cable at a rate of v =...Ch. 13.7 - The ball has a mass of 30 kg and a speed v = 4 m/s...Ch. 13.7 - If the coefficient of static friction between the...Ch. 13.7 - If at the instant it reaches point A it has a...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Show that for circular motion, force = mass * velocity squared/radius.
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
Big data Big data describes datasets with huge volumes that are beyond the ability of typical database manageme...
Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm (16th Edition)
How is the hydrodynamic entry length defined for flow in a pipe? Is the entry length longer in laminar or turbu...
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
The variable j starts with the value 10. The variable k starts with the value 2. The variable starts with the ...
Starting Out with C++ from Control Structures to Objects (9th Edition)
Give an example of each of the following, other than those described in this chapter, and clearly explain why y...
Modern Database Management
What is an object? What is a control?
Starting Out With Visual Basic (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 40.00 30.00 100.00- 100.00 P = 1000 N A=167 d=140.00 100.00- -b 20.00 200.00 Weld Strength P = 273 N/mm^2 Electrod E60 Safety factor S₁ = 3 Force P = 1000 N Using by SOLIDWORKSarrow_forwardWhat are the reaction forces in A and B?arrow_forwardPearson eText Study Area Access Pearson mylabmastering.pearson.com P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Problem 15.6 P Course Home b Answered: HW_02.pdf EE 213-01 > Assignments HW_#... 3 of 8 ■ Review Document Sharing User Settings The jet plane has a mass of 250 Mg and a horizontal velocity of 100 m/s when t = 0. Part A If both engines provide a horizontal thrust which varies as shown in the graph in (Figure 1), determine the plane's velocity in 5 s. Neglect air resistance and the loss of fuel during the motion. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure 1 of 1 > ☐ μÅ ? v = Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback Next >arrow_forward
- Access Pearson mylabmastering.pearson.com P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Problem 15.43 P Course Home b Answered: HW_02.pdf EE 213-01 > Assignments HW_#... Pearson eText Study Area Document Sharing User Settings The 20-g bullet is travelling at 400 m/s when it becomes embedded in the 2-kg stationary block. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the plane is μk = 0.2. (Figure 1) Part A Determine the distance the block will slide before it stops. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure 1 of 1 με S = Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback ? 4 of 8 Review Next >arrow_forwardAccess Pearson mylabmastering.pearson.com P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Problem 15.64 P Course Home b Answered: HW_02.pdf EE 213-01 > Assignments HW_#... 5 of 8 Pearson eText Study Area Document Sharing User Settings Ball A has a mass of 3 kg and is moving with a velocity of (VA)1 = 8 m/s when it makes a direct collision with ball B, which has a mass of 2.5 kg and is moving with a velocity of (VB) 1 = 4 m/s. Suppose that e = 0.7. Neglect the size of the balls. (Figure 1) Part A Determine the velocity of A just after the collision. ■Review Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Assume the positive direction is to the right. Figure 1 of 1 ◎ на ? (VA)2= Value Units Submit Request Answer Part B Determine the velocity of B just after the collision. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Assume the positive direction is to the right. μÅ ? (VB)2= = Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback Next…arrow_forwardI only need help with number 3, actually just the theta dot portion. Thanks! I have Vr = 10.39 ft/sarrow_forward
- Only 100% sure experts solve it correct complete solutions okk don't use guidelines or ai answers okk will dislike okkk. Only human experts solved itarrow_forwardAirplanes A and B, flying at constant velocity and at the same altitude, are tracking the eye of hurricane C. The relative velocity of C with respect to A is 300 kph 65.0° South of West, and the relative velocity of C with respect to B is 375 kph 50.0° South of East. A 120.0 km B 1N 1. Determine the relative velocity of B with respect to A. A ground-based radar indicates that hurricane C is moving at a speed of 40.0 kph due north. 2. Determine the velocity of airplane A. 3. Determine the velocity of airplane B. Consider that at the start of the tracking expedition, the distance between the planes is 120.0 km and their initial positions are horizontally collinear. 4. Given the velocities obtained in items 2 and 3, should the pilots of planes A and B be concerned whether the planes will collide at any given time? Prove using pertinent calculations. (Hint: x = x + vt) 0arrow_forwardOnly 100% sure experts solve it correct complete solutions okk don't use guidelines or ai answers okk will dislike okkk.arrow_forward
- Solve this probem and show all of the workarrow_forwardThe differential equation of a cruise control system is provided by the following equation: WRITE OUT SOLUTION DO NOT USE A COPIED SOLUTION Find the closed loop transfer function with respect to the reference velocity (vr) . a. Find the poles of the closed loop transfer function for different values of K. How does the poles move as you change K? b. Find the step response for different values of K and plot in MATLAB. What can you observe?arrow_forwardSolve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Dynamics - Lesson 1: Introduction and Constant Acceleration Equations; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aMiZ3b0Ieg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY