
Concept explainers
For Exercises 1 through 12, use the Kruskal-Wallis test and perform these steps.
a. State the hypotheses and identify the claim.
b. Find the critical value.
c. Compute the test value.
d. Make the decision.
e. Summarize the results.
Use the traditional method of hypothesis testing unless otherwise specified.
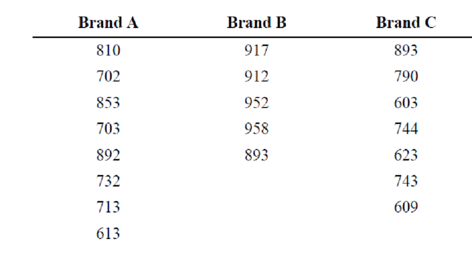
4. Sodium Content of Microwave Dinners Three brands of microwave dinners were advertised as low in sodium. Random samples of the three different brands show the following milligrams of sodium. At α = 0.05, is there a difference in the amount of sodium among the brands?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
Bluman, Elementary Statistics: A Step By Step Approach, © 2015, 9e, Student Edition (reinforced Binding) (a/p Statistics)
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
APPLIED STAT.IN BUS.+ECONOMICS
Elementary Algebra For College Students (10th Edition)
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Finite Mathematics for Business, Economics, Life Sciences and Social Sciences
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
- Q.2.4 There are twelve (12) teams participating in a pub quiz. What is the probability of correctly predicting the top three teams at the end of the competition, in the correct order? Give your final answer as a fraction in its simplest form.arrow_forwardThe table below indicates the number of years of experience of a sample of employees who work on a particular production line and the corresponding number of units of a good that each employee produced last month. Years of Experience (x) Number of Goods (y) 11 63 5 57 1 48 4 54 5 45 3 51 Q.1.1 By completing the table below and then applying the relevant formulae, determine the line of best fit for this bivariate data set. Do NOT change the units for the variables. X y X2 xy Ex= Ey= EX2 EXY= Q.1.2 Estimate the number of units of the good that would have been produced last month by an employee with 8 years of experience. Q.1.3 Using your calculator, determine the coefficient of correlation for the data set. Interpret your answer. Q.1.4 Compute the coefficient of determination for the data set. Interpret your answer.arrow_forwardCan you answer this question for mearrow_forward
- Techniques QUAT6221 2025 PT B... TM Tabudi Maphoru Activities Assessments Class Progress lIE Library • Help v The table below shows the prices (R) and quantities (kg) of rice, meat and potatoes items bought during 2013 and 2014: 2013 2014 P1Qo PoQo Q1Po P1Q1 Price Ро Quantity Qo Price P1 Quantity Q1 Rice 7 80 6 70 480 560 490 420 Meat 30 50 35 60 1 750 1 500 1 800 2 100 Potatoes 3 100 3 100 300 300 300 300 TOTAL 40 230 44 230 2 530 2 360 2 590 2 820 Instructions: 1 Corall dawn to tha bottom of thir ceraan urina se se tha haca nariad in archerca antarand cubmit Q Search ENG US 口X 2025/05arrow_forwardThe table below indicates the number of years of experience of a sample of employees who work on a particular production line and the corresponding number of units of a good that each employee produced last month. Years of Experience (x) Number of Goods (y) 11 63 5 57 1 48 4 54 45 3 51 Q.1.1 By completing the table below and then applying the relevant formulae, determine the line of best fit for this bivariate data set. Do NOT change the units for the variables. X y X2 xy Ex= Ey= EX2 EXY= Q.1.2 Estimate the number of units of the good that would have been produced last month by an employee with 8 years of experience. Q.1.3 Using your calculator, determine the coefficient of correlation for the data set. Interpret your answer. Q.1.4 Compute the coefficient of determination for the data set. Interpret your answer.arrow_forwardQ.3.2 A sample of consumers was asked to name their favourite fruit. The results regarding the popularity of the different fruits are given in the following table. Type of Fruit Number of Consumers Banana 25 Apple 20 Orange 5 TOTAL 50 Draw a bar chart to graphically illustrate the results given in the table.arrow_forward
- Q.2.3 The probability that a randomly selected employee of Company Z is female is 0.75. The probability that an employee of the same company works in the Production department, given that the employee is female, is 0.25. What is the probability that a randomly selected employee of the company will be female and will work in the Production department? Q.2.4 There are twelve (12) teams participating in a pub quiz. What is the probability of correctly predicting the top three teams at the end of the competition, in the correct order? Give your final answer as a fraction in its simplest form.arrow_forwardQ.2.1 A bag contains 13 red and 9 green marbles. You are asked to select two (2) marbles from the bag. The first marble selected will not be placed back into the bag. Q.2.1.1 Construct a probability tree to indicate the various possible outcomes and their probabilities (as fractions). Q.2.1.2 What is the probability that the two selected marbles will be the same colour? Q.2.2 The following contingency table gives the results of a sample survey of South African male and female respondents with regard to their preferred brand of sports watch: PREFERRED BRAND OF SPORTS WATCH Samsung Apple Garmin TOTAL No. of Females 30 100 40 170 No. of Males 75 125 80 280 TOTAL 105 225 120 450 Q.2.2.1 What is the probability of randomly selecting a respondent from the sample who prefers Garmin? Q.2.2.2 What is the probability of randomly selecting a respondent from the sample who is not female? Q.2.2.3 What is the probability of randomly…arrow_forwardTest the claim that a student's pulse rate is different when taking a quiz than attending a regular class. The mean pulse rate difference is 2.7 with 10 students. Use a significance level of 0.005. Pulse rate difference(Quiz - Lecture) 2 -1 5 -8 1 20 15 -4 9 -12arrow_forward
- The following ordered data list shows the data speeds for cell phones used by a telephone company at an airport: A. Calculate the Measures of Central Tendency from the ungrouped data list. B. Group the data in an appropriate frequency table. C. Calculate the Measures of Central Tendency using the table in point B. D. Are there differences in the measurements obtained in A and C? Why (give at least one justified reason)? I leave the answers to A and B to resolve the remaining two. 0.8 1.4 1.8 1.9 3.2 3.6 4.5 4.5 4.6 6.2 6.5 7.7 7.9 9.9 10.2 10.3 10.9 11.1 11.1 11.6 11.8 12.0 13.1 13.5 13.7 14.1 14.2 14.7 15.0 15.1 15.5 15.8 16.0 17.5 18.2 20.2 21.1 21.5 22.2 22.4 23.1 24.5 25.7 28.5 34.6 38.5 43.0 55.6 71.3 77.8 A. Measures of Central Tendency We are to calculate: Mean, Median, Mode The data (already ordered) is: 0.8, 1.4, 1.8, 1.9, 3.2, 3.6, 4.5, 4.5, 4.6, 6.2, 6.5, 7.7, 7.9, 9.9, 10.2, 10.3, 10.9, 11.1, 11.1, 11.6, 11.8, 12.0, 13.1, 13.5, 13.7, 14.1, 14.2, 14.7, 15.0, 15.1, 15.5,…arrow_forwardPEER REPLY 1: Choose a classmate's Main Post. 1. Indicate a range of values for the independent variable (x) that is reasonable based on the data provided. 2. Explain what the predicted range of dependent values should be based on the range of independent values.arrow_forwardIn a company with 80 employees, 60 earn $10.00 per hour and 20 earn $13.00 per hour. Is this average hourly wage considered representative?arrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning


