
(a)
Find the coefficient of restitution between A and B
(a)
Answer to Problem 13.178P
The coefficient of restitution between A and B
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The weight of the block A
The weight of the block B
The weight of the block C
The coefficient of friction between the block and plane
The initial speed of the block A
The blocks B and C are at rest.
The distance between the blocks (d) is
The width of the each blocks (b) is
The acceleration due to gravity (g) is
Calculation:
Calculate the mass of the block A
Substitute
Calculate the mass of the block B
Substitute
Calculate the mass of the block C
Substitute
Show the diagram of the block A just before its impact with block B as in Figure (1).
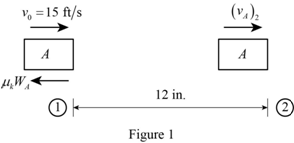
The expression for the initial kinetic energy of the block A at position ‘1’
Here,
The expression for the kinetic energy of the block A at position ‘2’ just before its impact with blocks B
Here,
The expression for the work done by the block A to overcome frictional force
The expression for the principle of work and energy to the block A at position ‘1’ and position ‘2’ just before its impact with block B as follows:
Substitute
Substitute
Show the diagram of the block A just after its impact with block B as in Figure (2).
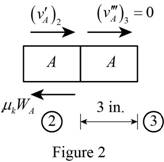
The expression for the kinetic energy of the block A immediately after the impact
Here,
The block finally comes to stop after the impact. Thus,
The expression for the work done by the block A after the collision to overcome the frictional force
The expression for the principle of work and energy to the block A after it collides with block B to find the velocity of the block A after its impact with B as follows:
Substitute
Substitute
Show the momentum impact diagram of the blocks A and B as in Figure (3).
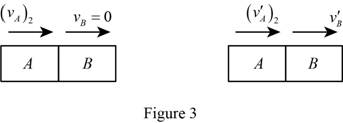
The expression for the principle of conservation of momentum to the collision between the block A and block B as follows:
Here,
Substitute
Calculate the coefficient of restitution for the impact between the block A and block B
Substitute 0 for
Therefore, the coefficient of restitution between A and B
(b)
Find the displacement (x) of block C.
(b)
Answer to Problem 13.178P
The displacement (x) of block C is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The weight of the block A
The weight of the block B
The weight of the block C
The coefficient of friction between the block and plane
The initial speed of the block A
The blocks B and C are at rest.
The distance between the blocks (d) is
The width of the each blocks (b) is
The acceleration due to gravity (g) is
Calculation:
Show the diagram of the block B just before its impact with block C as in Figure (4).
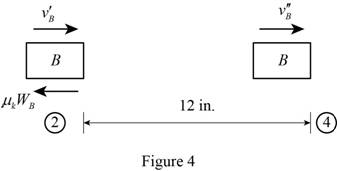
The expression for the kinetic energy of the block B at position ‘2’ just after the impact with block A
The expression for the kinetic energy of the block B just before its impact with blocks C at the position ‘4’
Here,
The expression for the work done by the block B to overcome the frictional force in reaching position ‘4’ from position ‘2’ as follows:
The expression for the principle of work and energy to the block B just before its impact with block C at the position ‘2’ and position ‘4’ as follows:
Substitute
Substitute
Show the momentum impact diagram of the blocks B and C as in Figure (5).
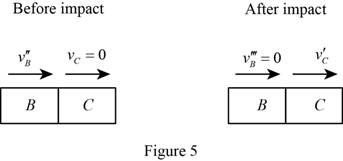
The expression for the principle of conservation of momentum to the collision between the block B and block C as follows:
Substitute
Here,
Substitute
Calculate the coefficient of restitution for the impact between the block B and block C
Substitute 0 for
Show the diagram of the block C after its impact with Block B as in Figure (6).
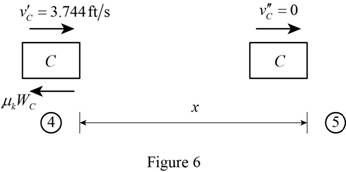
The expression for the kinetic energy of the block C immediately after its impact with blocks B at position ‘4’
Finally, at the position ‘5’, the block C comes to rest. Thus,
The expression for the work done by the block C to overcome the frictional force in reaching the position ‘5’
Here, x is the distance travelled by the block C before coming to rest.
The expression for the principle of work and energy to the block C after its impact with block B as follows:
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, displacement (x) of block C is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
VECTOR MECHANIC
- Calculate the cutting time for a 4 in length of cut, given that the feed rate is 0.030 ipr at a speed of 90 fpm.arrow_forwardfor the values: M1=0.41m, M2=1.8m, M3=0.56m, please account for these in the equations. also please ensure that the final answer is the flow rate in litres per second for each part. please use bernoullis equation where needed if an empirical solutions i srequired. also The solutions should include, but not be limited to, the equations used tosolve the problems, the charts used to solve the problems, detailed working,choice of variables, the control volume considered, justification anddiscussion of results etc.If determining the friction factor, the use of both Moody chart and empiricalequations should be used to verify the validity of the valuearrow_forwardSolve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forward
- Solve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forwardProblem 2: An athlete, starting from rest, pulls handle A to the left with a constant force of P = 150 [N]. Knowing that after the handle A has been pulled 0.5 [m], its velocity is 5 [m/s] to the left, determine: a) A position constraint equation using the given coordinate system. b) An acceleration constraint equation. c) The acceleration of A using kinematics equations. d) The acceleration of B using your constraint equation. e) How much weight (magnitude) the athlete is lifting in pounds using Newton's 2nd Law. You must draw a FBD and KD of the circled assembly, assuming the pulleys are massless. Note: 1 [lbf] = 4.448 [N]. ХА Увarrow_forwardProblem 1: For each of the following images, draw a complete FBD and KD for the specified objects. Then write the equations of motion using variables for all unknowns (e.g., mass, friction coefficient, etc.), plugging in kinematic expressions and simplifying where appropriate. Assume motion in all cases, so any friction would be kinetic. M (a) Blocks A & B (Be careful with acceleration of B relative to accelerating block A) 30° (b) Block A being pulled up my motor M (use rotated rectangular coordinate system) 20° (c) Ball at C, top of swing (use path coordinates) (d) Parasailer/Person (use polar coordinates)arrow_forward
- where M1=0.41m, M2=1.8m, M3=0.56m, please use bernoulis equation where necessary and The solutions should include, but not be limited to, the equations used tosolve the problems, the charts used to solve the problems, detailed working,choice of variables, the control volume considered, justification anddiscussion of results etc.If determining the friction factor, the use of both Moody chart and empiricalequations should be used to verify the validity of the value.arrow_forwardQ3. The attachment shown in Fig.2 is made of 1040 HR. Design the weldment (give the pattern, electrode number, type of weld, length of weld, and leg size). All dimensions in mm 120 Fig.2 12 17 b =7.5 5 kN 60 60°arrow_forward15 mm DA 100 mm 50 mm Assuming the load applied P 80 kN. Determine the maximum stress in the bar shown assuming the diameter of the whole A is DA = 25 mm.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





