
a)
Interpretation: The products for the given transformations are to be predicted.
Concept Introduction:
Ether analogs of Sulphur called Sulphide or Thioethers. Common names of these compounds are given by fixing the suffix Sulphide instead of Ether.
Preparation of Sulphides from Thiols is given below,
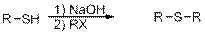
Mechanism:
In the first step, deprotonation of thiol takes place to form thiolate ions.

In the second step, thiolate acts as nucleophile and attacks the
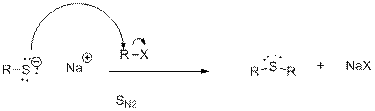
b)
Interpretation: The products for the given transformations are to be predicted.
Concept Introduction:
Ether analogs of Sulphur called Sulphide or Thioethers. Common names of these compounds are given by fixing the suffix Sulphide instead of Ether.
Preparation of Sulphides from Thiols is given below,
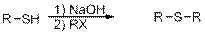
Mechanism:
In the first step, deprotonation of thiol takes place to form thiolate ions.

In the second step, thiolate acts as nucleophile and attacks the alkyl halide.
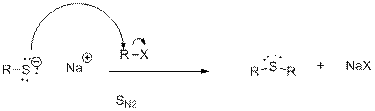
c)
Interpretation: The products for the given transformations are to be predicted.
Concept Introduction:
Ether analogs of Sulphur called Sulphide or Thioethers. Common names of these compounds are given by fixing the suffix Sulphide instead of Ether.
Preparation of Sulphides from Thiols is given below,
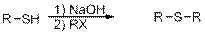
Mechanism:
In the first step, deprotonation of thiol takes place to form thiolate ions.

In the second step, thiolate acts as nucleophile and attacks the alkyl halide.
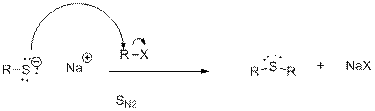
d)
Interpretation: The products for the given transformations are to be predicted.
Concept Introduction:
Ether analogs of Sulphur called Sulphide or Thioethers. Common names of these compounds are given by fixing the suffix Sulphide instead of Ether.
Preparation of Sulphides from Thiols is given below,
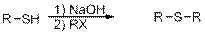
Mechanism:
In the first step, deprotonation of thiol takes place to form thiolate ions.

In the second step, thiolate acts as nucleophile and attacks the alkyl halide.
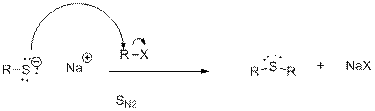
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY, WITH SOL. MAN/ STUDY
- Hi I need help on the question provided in the image.arrow_forwardDraw a reasonable mechanism for the following reaction:arrow_forwardDraw the mechanism for the following reaction: CH3 CH3 Et-OH Et Edit the reaction by drawing all steps in the appropriate boxes and connecting them with reaction arrows. Add charges where needed. Electron-flow arrows should start on the electron(s) of an atom or a bond and should end on an atom, bond, or location where a new bond should be created. H± EXP. L CONT. י Α [1] осн CH3 а CH3 :Ö Et H 0 N о S 0 Br Et-ÖH | P LL Farrow_forward
- 20.00 mL of 0.150 M NaOH is titrated with 37.75 mL of HCl. What is the molarity of the HCl?arrow_forward20.00 mL of 0.025 M HCl is titrated with 0.035 M KOH. What volume of KOH is needed?arrow_forward20.00 mL of 0.150 M NaOH is titrated with 37.75 mL of HCl. What is the molarity of the HCl?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





