
BASIC BIOMECHANICS
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259913877
Author: Hall
Publisher: RENT MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 13, Problem 9AP
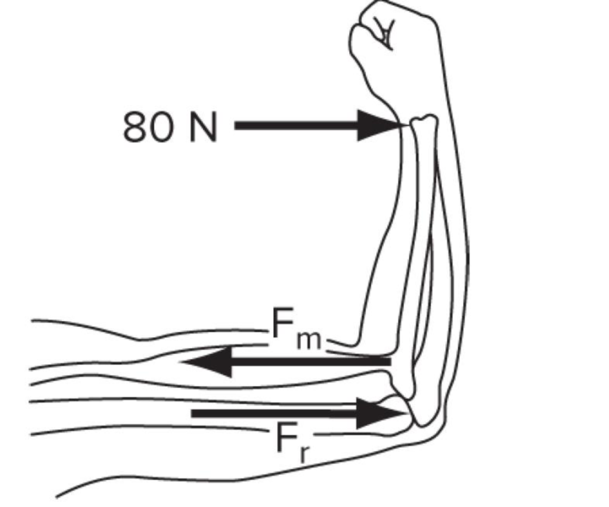
A therapist applies a lateral force of 80 N to the forearm at a distance of 25 cm from the axis of rotation at the elbow. The biceps attaches to the radius at a 90° angle and at a distance of 3 cm from the elbow joint center.
a. How much force is required of the biceps to stabilize the arm in this position?
b. What is the magnitude of the reaction force exerted by the humerus on the ulna? (Answers: a. 666.7 N; b. 586.7 N)
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
BASIC BIOMECHANICS
Ch. 13 - Why does a force directed through an axis of...Ch. 13 - Why does the orientation of a force acting on a...Ch. 13 - A 23-kg boy sits 1.5 m from the axis of rotation...Ch. 13 - Prob. 4IPCh. 13 - Two people push on opposite sides of a swinging...Ch. 13 - Prob. 6IPCh. 13 - Prob. 7IPCh. 13 - Prob. 8IPCh. 13 - A 10-kg block sits motionless on a table in spite...Ch. 13 - Prob. 10IP
Ch. 13 - A 35-N hand and forearm are held at a 45 angle to...Ch. 13 - A hand exerts a force of 90 N on a scale at 32 cm...Ch. 13 - A patient rehabilitating a knee injury performs...Ch. 13 - A worker leans over and picks up a 90-N box at a...Ch. 13 - A man carries a 3 m, 32-N board over his shoulder....Ch. 13 - A therapist applies a lateral force of 80 N to the...Ch. 13 - Tendon forces Ta and Tb are exerted on the...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, bioengineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The movement during which the knees or elbows are bent to decrease the angle of the joints is known as _______________.arrow_forwardInflamed and swollen tendons caught in the narrow space between the bones within the shoulder joint cause the condition known as ____________________. impingement syndrome intermittent claudicationarrow_forward
Recommended textbooks for you
 Comprehensive Medical Assisting: Administrative a...NursingISBN:9781305964792Author:Wilburta Q. Lindh, Carol D. Tamparo, Barbara M. Dahl, Julie Morris, Cindy CorreaPublisher:Cengage Learning
Comprehensive Medical Assisting: Administrative a...NursingISBN:9781305964792Author:Wilburta Q. Lindh, Carol D. Tamparo, Barbara M. Dahl, Julie Morris, Cindy CorreaPublisher:Cengage Learning Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira...Health & NutritionISBN:9781305634350Author:Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. SchroederPublisher:Cengage Learning
Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira...Health & NutritionISBN:9781305634350Author:Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. SchroederPublisher:Cengage Learning

Comprehensive Medical Assisting: Administrative a...
Nursing
ISBN:9781305964792
Author:Wilburta Q. Lindh, Carol D. Tamparo, Barbara M. Dahl, Julie Morris, Cindy Correa
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira...
Health & Nutrition
ISBN:9781305634350
Author:Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. Schroeder
Publisher:Cengage Learning



GCSE PE - ANTAGONISTIC MUSCLE ACTION - Anatomy and Physiology (Skeletal and Muscular System - 1.5); Author: igpe_complete;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6hm_9jQRoO4;License: Standard Youtube License