
Concept explainers
BIO A Cricket Thermometer, by Jiminy
Insects are ectothermic, which means their body temperature is largely determined by the temperature of their surroundings. This can have a number of interesting consequences. For example, the wing coloration in some butterfly species is determined by the ambient temperature, as is the body color of several species of dragonfly. In addition, the wing beat frequency of beetles taking flight varies with temperature due to changes in the resonant frequency of their thorax.
The origin of such temperature effects can be traced back to the fact that molecules have higher speeds and greater energy as temperature is increased (see Chapters 16 and 17). Thus, for example, molecules that collide and react as part of the
One of the most interesting thermal effects is the temperature dependence of chirp rate in certain insects. This behavior has been observed in cone-headed grasshoppers, as well as several types of cricket. A particularly accurate connection between chirp rate and temperature is found in the snowy tree cricket (Oecanthus fultoni Walker), which chirps at a rate that follows the expression N = T − 39, where N is the number of chirps in 13 seconds, and T is the numerical value of the temperature in degrees Fahrenheit. This formula, which is known as Dolbear’s law, is plotted in Figure 13-46 (green line) along with data points (blue dots) for the snowy tree cricket.
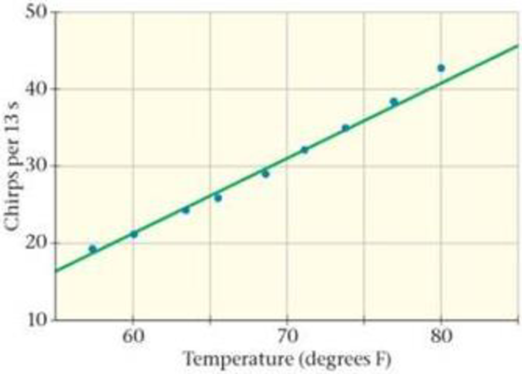
Figure 13-46 Problems 93, 94, 95, and 96
93. • If the temperature is increased by 10 degrees Fahrenheit, how many additional chirps are heard in a 13-s interval?
- A. 5
- B. 10
- C. 13
- D. 39
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
Physics (5th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
- Discuss the differences between the Biot-Savart law and Coulomb’s law in terms of their applicationsand the physical quantities they describe.arrow_forwardExplain why Ampere’s law can be used to find the magnetic field inside a solenoid but not outside.arrow_forward3. An Atwood machine consists of two masses, mA and m B, which are connected by an inelastic cord of negligible mass that passes over a pulley. If the pulley has radius RO and moment of inertia I about its axle, determine the acceleration of the masses mA and m B, and compare to the situation where the moment of inertia of the pulley is ignored. Ignore friction at the axle O. Use angular momentum and torque in this solutionarrow_forward
- A 0.850-m-long metal bar is pulled to the right at a steady 5.0 m/s perpendicular to a uniform, 0.650-T magnetic field. The bar rides on parallel metal rails connected through a 25-Ω, resistor (Figure 1), so the apparatus makes a complete circuit. Ignore the resistance of the bar and the rails. Please explain how to find the direction of the induced current.arrow_forwardFor each of the actions depicted, determine the direction (right, left, or zero) of the current induced to flow through the resistor in the circuit containing the secondary coil. The coils are wrapped around a plastic core. Immediately after the switch is closed, as shown in the figure, (Figure 1) in which direction does the current flow through the resistor? If the switch is then opened, as shown in the figure, in which direction does the current flow through the resistor? I have the answers to the question, but would like to understand the logic behind the answers. Please show steps.arrow_forwardWhen violet light of wavelength 415 nm falls on a single slit, it creates a central diffraction peak that is 8.60 cm wide on a screen that is 2.80 m away. Part A How wide is the slit? ΟΙ ΑΣΦ ? D= 2.7.10-8 Submit Previous Answers Request Answer × Incorrect; Try Again; 8 attempts remaining marrow_forward
- Two complex values are z1=8 + 8i, z2=15 + 7 i. z1∗ and z2∗ are the complex conjugate values. Any complex value can be expessed in the form of a+bi=reiθ. Find θ for (z1-z∗2)/z1+z2∗. Find r and θ for (z1−z2∗)z1z2∗ Please show all stepsarrow_forwardCalculate the center of mass of the hollow cone shown below. Clearly specify the origin and the coordinate system you are using. Z r Y h Xarrow_forward12. If all three collisions in the figure below are totally inelastic, which will cause more damage? (think about which collision has a larger amount of kinetic energy dissipated/lost to the environment? I m II III A. I B. II C. III m m v brick wall ע ע 0.5v 2v 0.5m D. I and II E. II and III F. I and III G. I, II and III (all of them) 2marrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University





