
Concept explainers
You’ve inherited your great-grandmother’s mantle clock. The clock’s timekeeping is established by a pendulum consisting of a 15.0-cm-long rod and a disk 6.35 cm in diameter. The rod passes through a hole in the disk, and the disk is supported at its bottom by a decorative nut mounted on the bottom portion of the rod, which is threaded: see Fig. 13.38. As shown, the bottom of the disk is 1.92 cm above the bottom of the rod. There are 20.0 threads per cm, meaning that one full turn of the decorative nut moves the disk up or down by 1/20 cm. The clock is beautiful, but it isn’t accurate; you note that it’s losing 1.5 minutes per day. But you realize that the decorative nut is an adjustment mechanism, and you decide to adjust the clock’s timekeeping.
- (a) Should you turn the nut to move the disk up or down?
- (b) How many times should you turn the nut? Note: The disk is massive enough that you can safely neglect the mass of the rod and nut. But you can’t neglect the disk’s size compared with the rod length, so you don’t have a simple pendulum. Furthermore, note that both the effective length of the pendulum and its rotational inertia change as the disk moves up or down the shaft. You can either solve a quadratic or you can use calculus to get an approximate but nevertheless very accurate answer.
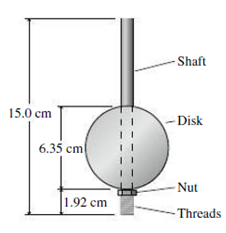
FIGURE 13.38 Problem 85
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
Essential University Physics (3rd Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
- Show that the units 1 v2/Q = 1 W, as implied by the equation P = V²/R. Starting with the equation P = V²/R, we can get an expression for a watt in terms of voltage and resistance. The units for voltage, V, are equivalent to [? v2 v2 A, are equivalent to J/C ✓ X . Therefore, 1 = 1 = 1 A V1 J/s Ω V-A X = 1 W. . The units for resistance, Q, are equivalent to ? The units for current,arrow_forwardPlease solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardPlease solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
- According to the provided information answer the question accorrding to grade 11 physics Jerry has decided to give up his part-time job for a new career, cat-burglar! Jerry loves the idea of dressing up like a cat all day and of course the chance of meeting Cat Woman! On Jerry's first "job" he figures out his escape plan. He travels 3.0 km south for 15 minutes and then 8.0 km west for 1.5 hours before reaching his house. Draw a sketch diagram of the path he took with all the appropriate labels.arrow_forwardPlease solve and answer all parts of the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardPlease solve and answer this question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





