
Concept explainers
COST ALLOCATION AND LOWER-OF-COST-OR-MARKET Hall Company’s beginning inventory and purchases during the fiscal year ended December 31, 20--, were as follows:
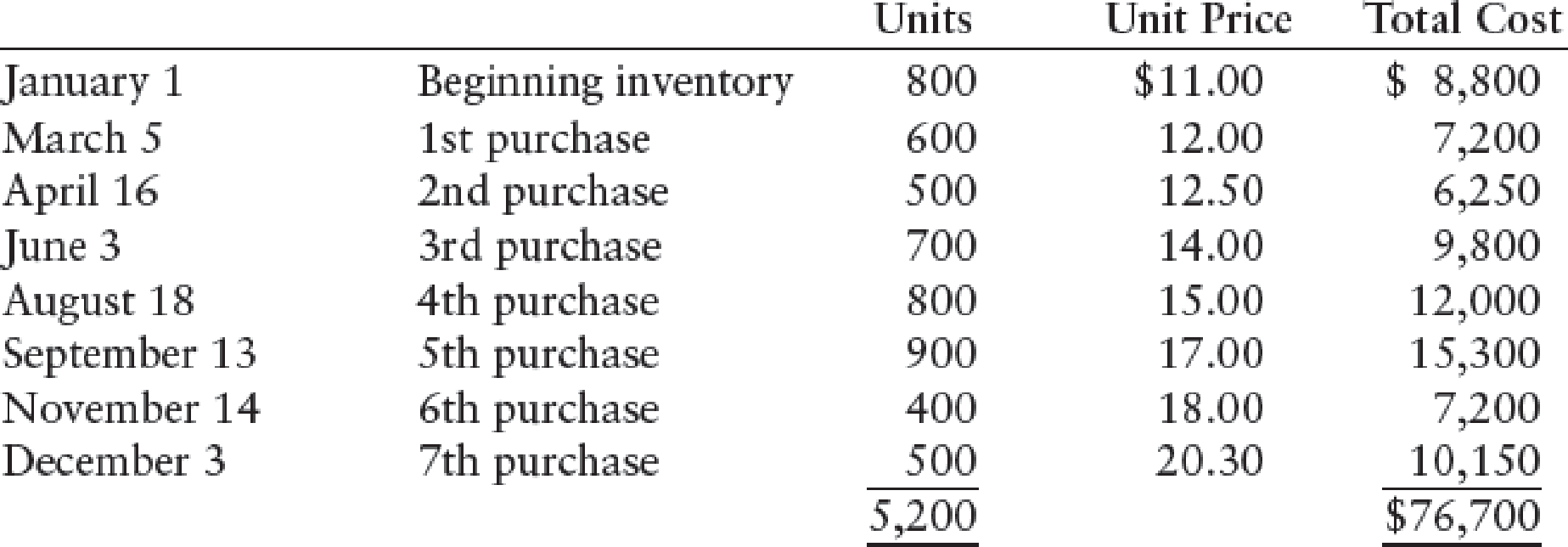
There are 1,100 units of inventory on hand on December 31.
REQUIRED
- 1. Calculate the total amount to be assigned to the ending inventory and cost of goods sold on December 31 under each of the following methods:
- (a) FIFO
- (b) LIFO
- (c) Weighted-average (round calculations to two decimal places)
- 2. Assume that the market price per unit (cost to replace) of Hall’s inventory on December 31 was $16. Calculate the total amount to be assigned to the ending inventory on December 31 under each of the following methods:
- (a) FIFO lower-of-cost-or-market
- (b) Weighted-average lower-of-cost-or-market
- 3. Prepare required entries to apply:
- (a) FIFO lower-of-cost-or-market
- (b) Weighted-average lower-of-cost-or-market
1.
(a)
Calculate the total amount of cost of goods sold and cost of ending inventory on September 30, 20-2 under FIFO method.
Explanation of Solution
First-in-First-Out (FIFO): In First-in-First-Out method, the first purchased items are sold first. The value of the ending inventory consists of the recently purchased items.
Calculate the total amount of cost of goods sold and cost of ending inventory on September 30, 20-2 under FIFO method:
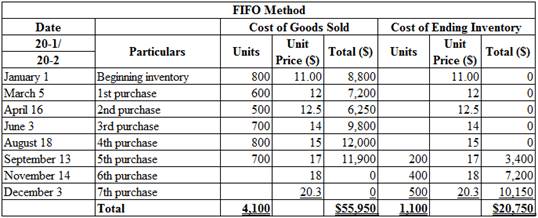
Table (1)
Therefore, the cost of sold and cost of ending inventory under FIFO (Periodic inventory system) is $55,950 and $20,750.
2.
(b)
Calculate the total amount of cost of goods sold and cost of ending inventory on September 30, 20-2 under LIFO method.
Explanation of Solution
Last-in-First-Out (LIFO): In Last-in-First-Out method, the last purchased items are sold first. The value of the closing stock consists of the initially purchased items.
Calculate the total amount of cost of goods sold and cost of ending inventory on September 30, 20-2 under LIFO method:
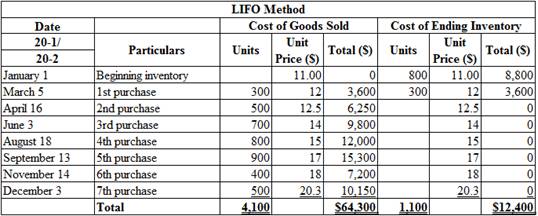
Table (2)
Therefore, the cost of sold and cost of ending inventory under LIFO (Periodic inventory system) is $64,300 and $12,400.
3.
(c)
Calculate the total amount of cost of goods sold and cost of ending inventory on September 30, 20-2 under weighted average cost method.
Explanation of Solution
Weighted-average cost method: Under average cost method inventories are priced at the average of all available inventories. Average cost is the quotient of total cost of goods available for sale and total units available for sale.
Calculate the total amount of cost of goods sold and cost of ending inventory on September 30, 20-2 under weighted average cost method:
Step 1: Calculate the weighted-average cost.
Step 2: Calculate the amount of ending inventory.
Step 3: Calculate the amount of cost of goods sold.
Therefore, the cost of sold and cost of ending inventory under weighted average cost method (Periodic inventory system) is $60,475 and $16,225.
2.
(a)
Calculate the cost of ending inventory under FIFO method (Lower of cost or market).
Explanation of Solution
Lower-of-cost-or-market: The lower-of-cost-or-market (LCM) is a method which requires the reporting of the ending merchandise inventory in the financial statement of a company, at its current market value or at is historical cost price, whichever is less.
First-in-First-Out (FIFO): In First-in-First-Out method, the first purchased items are sold first. The value of the ending inventory consists of the recently purchased items.
Calculate the cost of ending inventory under FIFO (Lower of cost or market):
|
Particulars |
FIFO Cost (A) |
Market Cost (B) |
LCM Valuation (C = A or B ) Whichever is lesser |
| Ending inventory under FIFO | $20,750 | $17,600 | $17,600 |
Table (2)
Working note:
Calculate the market cost.
Therefore, the cost of ending inventory under FIFO method (Lower of cost or market) is $17,600.
2.
(b)
Calculate the cost of ending inventory under weighted average cost method (Lower of cost or market).
Explanation of Solution
Weighted-average cost method: Under average cost method inventories are priced at the average of all available inventories. Average cost is the quotient of total cost of goods available for sale and total units available for sale.
Calculate the cost of ending inventory under weighted average cost (Lower of cost or market):
|
Particulars |
Weighted Average Cost (A) |
Market Cost (B) |
LCM Valuation (C = A or B ) Whichever is lesser |
| Ending inventory under weighted average cost | $16,225 | $17,600 | $16,225 |
Table (3)
Working note:
Calculate the market cost.
Therefore, the cost of ending inventory under weighted average cost method (Lower of cost or market) is $16,225.
3.
(a)
Show the journal entry would be made under lower-of-cost-or-market.
Explanation of Solution
Lower-of-cost-or-market: The lower-of-cost-or-market (LCM) is a method which requires the reporting of the ending merchandise inventory in the financial statement of a company, at its current market value or at is historical cost price, whichever is less.
Journal entry: Journal entry is a set of economic events which can be measured in monetary terms. These are recorded chronologically and systematically.
Show the journal entry would be made under lower-of-cost-or-market:
| Section | Particulars | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| (a) | Loss on write-down of inventory | 3,150 | |
| Merchandise inventory | 3,150 | ||
| (To record the loss on inventory) |
Table (2)
Working note:
Calculate the amount of loss on inventory.
3.
(b)
Show the journal entry would be made under lower-of-cost-or-market.
Explanation of Solution
No entry required for part b.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Study Guide for Working Papers for Heintz/Parry's College Accounting, Chapters 16-27, 23rd
- Please see an attachment for details of this financial accountingarrow_forwardBonnie and Clyde are the only two shareholders in Getaway Corporation. Bonnie owns 60 shares with a basis of $3,000, and Clyde owns the remaining 40 shares with a basis of $12,000. At year-end, Getaway is considering different alternatives for redeeming some shares of stock. Evaluate whether each of these stock redemption transactions qualify for sale or exchange treatment. Getaway redeems 29 of Bonnie’s shares for $10,000. Getaway has $26,000 of E&P at year-end and Bonnie is unrelated to Clyde.arrow_forwardNovak supply company a newly formed corporation , incurred the following expenditures related to the land , to buildings, and to machinery and equipment. abstract company's fee for title search $1,170 architect's fee $7,133 cash paid for land and dilapidated building thereon $195,750 removal of old building $45,000 LESS: salvage $12,375 $32,625 Interest on short term loans during construction…arrow_forward
- Year Cash Flow 0 -$ 27,000 1 11,000 2 3 14,000 10,000 What is the NPV for the project if the required return is 10 percent? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answer to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16. NPV $ 1,873.28 At a required return of 10 percent, should the firm accept this project? No Yes What is the NPV for the project if the required return is 26 percent?arrow_forwardThe following were selected from among the transactions completed by Babcock Company during November of the current year: Nov. 3 Purchased merchandise on account from Moonlight Co., list price $85,000, trade discount 25%, terms FOB destination, 2/10, n/30. 4 Sold merchandise for cash, $37,680. The cost of the goods sold was $22,600. 5 Purchased merchandise on account from Papoose Creek Co., $47,500, terms FOB shipping point, 2/10, n/30, with prepaid freight of $810 added to the invoice. 6 Returned merchandise with an invoice amount of $13,500 ($18,000 list price less trade discount of 25%) purchased on November 3 from Moonlight Co. 8 Sold merchandise on account to Quinn Co., $15,600 with terms n/15. The cost of the goods sold was $9,400. 13 Paid Moonlight Co. on account for purchase of November 3, less return of November 6. 14 Sold merchandise with a list price of $236,000 to customers who used VISA and who redeemed $8,000 of pointof- sale coupons. The cost…arrow_forwardHello teacher please solve this questionsarrow_forward
 College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





