
Concept explainers
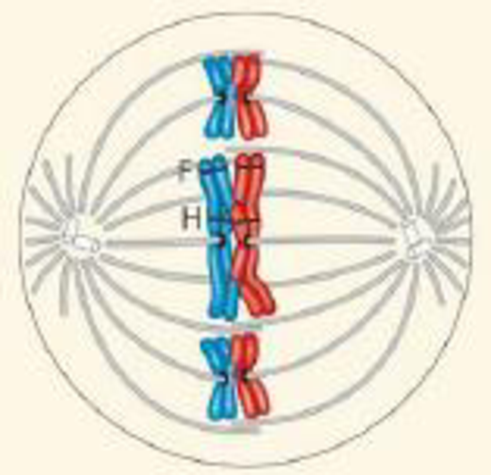
DRAW IT The diagram shows a cell in meiosis.
(a) Label the appropriate structures with these terms: chromosome (label as duplicated or unduplicated), centromere, kinetochore, sister chromatids, nonsister chromatids, homologous pair (use a bracket when labeling), homolog (label each one), chiasma, sister chromatid cohesion, and gene loci, labeling the alleles of the F and H genes.
(b) Describe the makeup of a haploid set and a diploid set.
(c) Identify the stage of meiosis shown.
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 13 Solutions
Campbell Biology, Books a la Carte Plus Mastering Biology with eText -- Access Card Package (10th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
- Briefly explain the 6 domain of interprofessional collaboration: Role clarification, Team functioning, Interprofessional communication, Patient/client/family/community-centered care, Interprofessional conflict resolution, Collaborative leadership. Provide a specific negative events that nursing student would observe in a clinical setting for each domain.arrow_forwardwhat is an intermittent water course and what kind of fish habitat it would providearrow_forwardwhy are native freshwater mussels are an important part of great lakes ecosystemarrow_forward
- what morphological features differentiate the lamprey species and other species in the great lakesarrow_forwardThere are a wide range of therapeutic applications available as options for patients. Medical professionals should be aware of these applications so they can make informed recommendations to patients. To gain a better understanding of some therapeutic applications and how they are related to RNA and mRNA, research long non-coding RNA. Respond to the following in a minimum of 175 words: What is lncRNA and what does it do? How does IncRNA differ from mRNA? What are some therapeutic applications associated with lncRNA? Think about possible future uses of this application. What are the advantages and disadvantages of this application and its continued use?arrow_forwardfour fish or mussel species that are native to the great lakesarrow_forward
- There are a wide range of therapeutic applications available as options for patients. Medical professionals should be aware of these applications so they can make informed recommendations to patients. To gain a better understanding of some therapeutic applications and how they are related to RNA and mRNA, research long non-coding RNA. Respond to the following in a minimum of 175 words: What is lncRNA and what does it do? How does IncRNA differ from mRNA? What are some therapeutic applications associated with lncRNA? Think about possible future uses of this application. What are the advantages and disadvantages of this application and its continued use?arrow_forwardfour physial characteristics of a fish or a mussel that would help you identify it to a speciesarrow_forwarddescribe what you would do in this situation, you are working ona. river and it will take 20 minutes by boat to get back to the field truck, you are 1 hour from finishing the field work on the last day of field trip. you hear thunder int he dsitnace, what did you do?arrow_forward
- unu grow because auxin is still produced in the tip to Another of Boysen and Jensen's experiments included the use of mica, explain why one of the shoots was able to show phototropism and the other was not. Mica Wafer Ligh c. They then t but this time permeable n shoot. Why phototropis Light Mica Wafer Coleoptile tips Tips removed: agar Explain why the shoo direction after the ag the cut shoot, even tarrow_forwardDiscussion entries must be at least 250 words to fulfill the assignment requirements. You must complete your entry before you will be able to see the responses of other students. Responses to other students are encouraged but not required. Grading for discussion entries will be based on application of course concepts, proper grammar, and correct punctuation. Read one the attached article and explore the Human Development Index (https://hdr.undp.org/data-center/human-development-index#/indicies/HDI). In your opinion, is the Human Development Index a good measure of the well- being of the people of a nation? Are the items measured in the HDI valid and relevant in the modern global economy? How are they related to the political economy of a nation? The attached articles propose some alternative measures of well-being. In your opinion, are there other measures of well-being that might be better alternatives to the items in the current HDI?arrow_forwardA patient visits her doctor with symptoms typical of a bladder infection. She is immediately prescribed an 800 mgdose of antibiotic (bioavailability = 1/2, t½ = 12 h). The corresponding plasma concentration of drug is found to be 96 micrograms/ml. What is the volume of distribution of this drug? Please round to the nearest liter.arrow_forward
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning





