
Concept explainers
Refer to the Baseball 2012 data, which reports information on the 2012 Major League Baseball season. Let attendance be the dependent variable and total team salary, in millions of dollars, be the independent variable. Determine the regression equation and answer the following questions.
- a. Draw a
scatter diagram . From the diagram, does there seem to be a direct relationship between the two variables? - b. What is the expected attendance for a team with a salary of $80.0 million?
- c. If the owners pay an additional $30 million, how many more people could they expect to attend?
- d. At the .05 significance level, can we conclude that the slope of the regression line is positive? Conduct the appropriate test of hypothesis.
- e. What percentage of the variation in attendance is accounted for by salary?
- f. Determine the
correlation between attendance and team batting average and between attendance and team ERA. Which is stronger? Conduct an appropriate test of hypothesis for each set of variables.
a.
Construct a scatter diagram.
Check whether there is a direct or indirect relationship between the two variables.
Answer to Problem 63DE
The scatter diagram of the data is as follows:
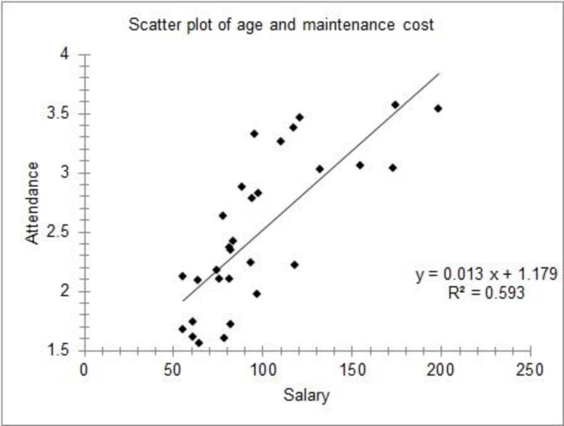
There seems to be a direct relationship between the team’s salary and attendance.
Explanation of Solution
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the scatterplot using the MegaStat software:
- In an EXCEL sheet enter the data values of x and y.
- Go to Add-Ins > MegaStat > Correlation/Regression > Scatterplot.
- Enter horizontal axis as $A$1:$A$81 and vertical axis as $B$1:$B$81.
- Click on OK.
The scatterplot of the data indicates an increasing trend. Therefore, the relationship between the two variables is direct.
b.
Find the expected attendance for a team with a salary of $80.0 million.
Answer to Problem 63DE
The expected attendance for a team with a salary of $80.0 million is 2.25295.
Explanation of Solution
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the ‘regression equation’ using the MegaStat software:
- In an EXCEL sheet enter the data values of x and y.
- Go to Add-Ins > MegaStat > Correlation/Regression > Regression Analysis.
- Select input range as ‘Sheet1!$B$2:$B$81’ under Y/Dependent variable.
- Select input range ‘Sheet1!$A$2:$A$81’ under X/Independent variables.
- Select ‘Type in predictor values’.
- Enter 80.0 as ‘predictor values’ and 95% as ‘confidence level’.
- Click on OK.
Output obtained using the MegaStat software is given below:
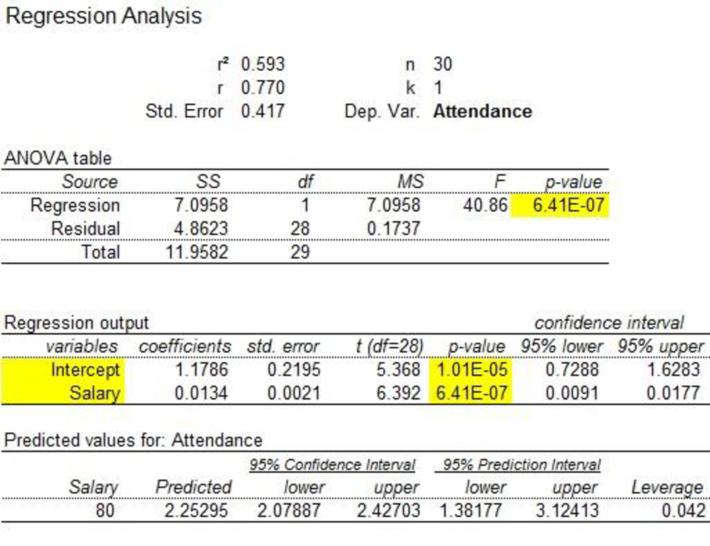
From the above output, the regression equation is as follows:
The expected attendance for a team with a salary of $80.0 million is 2.25295.
c.
Find the number of people expected to attend if the owners pay an additional amount of $30 million.
Answer to Problem 63DE
The mean number of people expected to attend if the owners pay an additional amount of $30 million is 0.4000 million.
Explanation of Solution
From Part (b), the regression equation is as follows:
The expected number of people who attend is as follows:
The expected number of people who attend if the owners pay an additional amount of $30million is the difference between the expected attendance with a salary of 110 and the expected attendance with a salary of 80 million.
That is,
Thus, the mean number of people expected to attend when the owners pay an additional amount of $30 million is 0.4000 million.
d.
Check whether the slope of the regression line is positive or not.
Answer to Problem 63DE
There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the slope of the regression line is positive at the 5% level of significance.
Explanation of Solution
Define
Null hypothesis:
That is, the slope of the regression line is less than or equal to zero.
Alternate hypothesis:
That is, the slope of the regression line is greater than zero.
Consider the level of significance as 0.05.
From Part (b), the standard error of
The test statistic is calculated as follows:
Thus, the test statistic value is 6.38.
Here, the sample size is
Critical value:
Step-by-step software procedure to obtain the critical value
· Open an EXCEL file.
· In cell A1, enter the formula “=T.INV(0.95,28)”.
Output obtained using the EXCEL is given as follows:
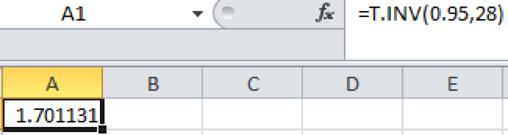
From the EXCEL output, the critical value is 1.701.
Decision rule based on critical value:
Reject the null hypothesis if
Conclusion:
The t-calculated value is 6.38 and the critical value is 1.701.
That is,
Thus, the null hypothesis is rejected.
Hence, there is sufficient evidence to conclude that the slope of the regression line is positive at the 5% level of significance.
e.
Find the coefficient of determination and interpret it.
Answer to Problem 63DE
There is 59.30% of variation in attendance, which can be explained by the salary.
Explanation of Solution
From Part (b), the coefficient of determination is 0.593.
Thus, there is 59.30% variation in attendance, which can be explained by the salary.
f.
Find the correlation between attendance and team batting average.
Find the correlation between attendance and team ERA.
Conduct a hypothesis test for the variables’ attendance and team’s batting average.
Conduct a hypothesis test for attendance and team ERA.
Answer to Problem 63DE
The correlation between attendance and team batting average is 0.630.
The correlation between attendance and team ERA is –0.055.
There is a positive association between attendance and team’s batting average at the 0.05 significance level.
There is no association between attendance and team’s ERA at the 0.05 significance level.
Explanation of Solution
Correlation between attendance and team’s batting average is as follows:
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the correlation between attendance and team’s batting average using Excel Mega stat software:
- Choose MegaStat > Correlation/Regression > Correlation Matrix.
- In Input ranges, Select the data values.
- Click OK.
The output obtained using Mega stat is as follows:
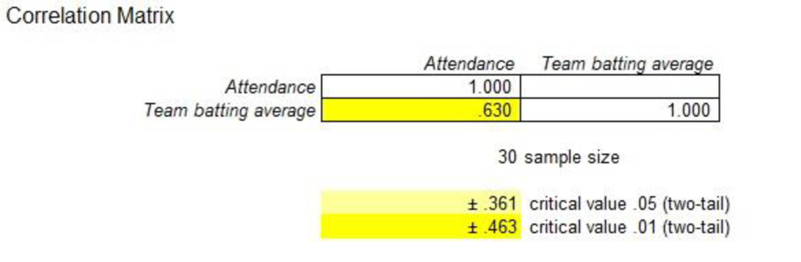
From the above output, the correlation between attendance and team’s batting average is 0.630.
Correlation between attendance and team’s ERA is as follows:
Follow the above procedure to obtain the correlation between attendance and team’s ERA as follows:
The output obtained using Mega stat is as follows:
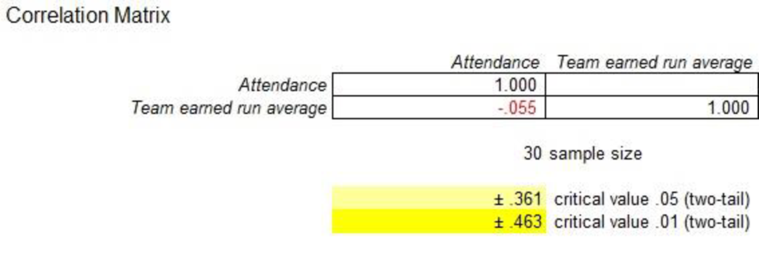
From the above output, the correlation between attendance and team’s ERA is –0.055.
The correlation between attendance and team’s batting average is positively correlated, and the correlation between attendance and team’s ERA is negatively associated.
Therefore, it is noticed that the correlation between attendance and team’s batting average is stronger than the correlation between attendance and team’s ERA.
Hypothesis test for attendance and team’s batting average:
The null and alternative hypotheses are stated below:
Null hypothesis:
That is, the correlation between attendance and team’s batting average is less than or equal to zero.
Alternative hypothesis:
That is, the correlation between “attendance and team batting average” is greater than zero.
Here, the sample size is 30 and the correlation coefficient between “attendance and team batting average is 0.630.
The test statistic is as follows:
Thus, the test statistic value is 4.29.
The degrees of freedom is as follows:
The level of significance is 0.05. Therefore,
Critical value:
Step-by-step software procedure to obtain the critical value using the EXCEL software:
- Open an EXCEL file.
- In cell A1, enter the formula “=T.INV (0.95, 28)”.
Output obtained using EXCEL is given as follows:
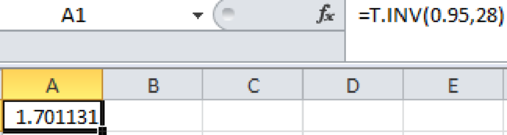
From the above output, the critical value is 1.701.
Decision rule:
Reject the null hypothesis H0, if
Conclusion:
The value of test statistic is 4.29 and the critical value is 1.701.
Here,
By the rejection rule, reject the null hypothesis.
Thus, it can be concluded that there is a positive association between attendance and team’s batting average.
Hypothesis test for attendance and team’s ERA:
The hypotheses are given below:
Null hypothesis:
That is, the correlation between attendance and team’s ERA is greater than or equal to zero.
Alternative hypothesis:
That is, the correlation between “attendance and team ERA” is less than zero.
Here, the sample size is 30 and the correlation between attendance and team’s ERA is –0.055.
The test statistic is as follows:
Thus, the t-test statistic value is –0.29.
Critical value:
Step-by-step software procedure to obtain the critical value using the EXCEL software:
- Open an EXCEL file.
- In cell A1, enter the formula “=T.INV (0.95, 28)”.
Output obtained using EXCEL is given as follows:
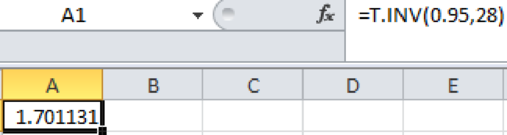
From the above output, the critical vale is –1.7011.
Conclusion:
The value of test statistic is –0.29 and the critical value is –1.7011.
Here,
By the rejection rule, fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Thus, it can be concluded that there is no association between “attendance and team ERA”.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
STATISTICAL TECHNIQUES-ACCESS ONLY
- Examine the Variables: Carefully review and note the names of all variables in the dataset. Examples of these variables include: Mileage (mpg) Number of Cylinders (cyl) Displacement (disp) Horsepower (hp) Research: Google to understand these variables. Statistical Analysis: Select mpg variable, and perform the following statistical tests. Once you are done with these tests using mpg variable, repeat the same with hp Mean Median First Quartile (Q1) Second Quartile (Q2) Third Quartile (Q3) Fourth Quartile (Q4) 10th Percentile 70th Percentile Skewness Kurtosis Document Your Results: In RStudio: Before running each statistical test, provide a heading in the format shown at the bottom. “# Mean of mileage – Your name’s command” In Microsoft Word: Once you've completed all tests, take a screenshot of your results in RStudio and paste it into a Microsoft Word document. Make sure that snapshots are very clear. You will need multiple snapshots. Also transfer these results to the…arrow_forward2 (VaR and ES) Suppose X1 are independent. Prove that ~ Unif[-0.5, 0.5] and X2 VaRa (X1X2) < VaRa(X1) + VaRa (X2). ~ Unif[-0.5, 0.5]arrow_forward8 (Correlation and Diversification) Assume we have two stocks, A and B, show that a particular combination of the two stocks produce a risk-free portfolio when the correlation between the return of A and B is -1.arrow_forward
- 9 (Portfolio allocation) Suppose R₁ and R2 are returns of 2 assets and with expected return and variance respectively r₁ and 72 and variance-covariance σ2, 0%½ and σ12. Find −∞ ≤ w ≤ ∞ such that the portfolio wR₁ + (1 - w) R₂ has the smallest risk.arrow_forward7 (Multivariate random variable) Suppose X, €1, €2, €3 are IID N(0, 1) and Y2 Y₁ = 0.2 0.8X + €1, Y₂ = 0.3 +0.7X+ €2, Y3 = 0.2 + 0.9X + €3. = (In models like this, X is called the common factors of Y₁, Y₂, Y3.) Y = (Y1, Y2, Y3). (a) Find E(Y) and cov(Y). (b) What can you observe from cov(Y). Writearrow_forward1 (VaR and ES) Suppose X ~ f(x) with 1+x, if 0> x > −1 f(x) = 1−x if 1 x > 0 Find VaRo.05 (X) and ES0.05 (X).arrow_forward
- Joy is making Christmas gifts. She has 6 1/12 feet of yarn and will need 4 1/4 to complete our project. How much yarn will she have left over compute this solution in two different ways arrow_forwardSolve for X. Explain each step. 2^2x • 2^-4=8arrow_forwardOne hundred people were surveyed, and one question pertained to their educational background. The results of this question and their genders are given in the following table. Female (F) Male (F′) Total College degree (D) 30 20 50 No college degree (D′) 30 20 50 Total 60 40 100 If a person is selected at random from those surveyed, find the probability of each of the following events.1. The person is female or has a college degree. Answer: equation editor Equation Editor 2. The person is male or does not have a college degree. Answer: equation editor Equation Editor 3. The person is female or does not have a college degree.arrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL



