
Concept explainers
Prepare Budgeted Financial Statements
HomeSuites is a chain of all-suite, extended-stay hotel properties. The chain has 15 properties with an average of 200 rooms in each property. In year 1, the occupancy rate (the number of rooms filled divided by the number of rooms available) was 70 percent, based on a 365-day year. The average room rate was $180 for a night. The basic unit of operation is the “night,” which is one room occupied for one night.
The operating income for year 1 is as follows:
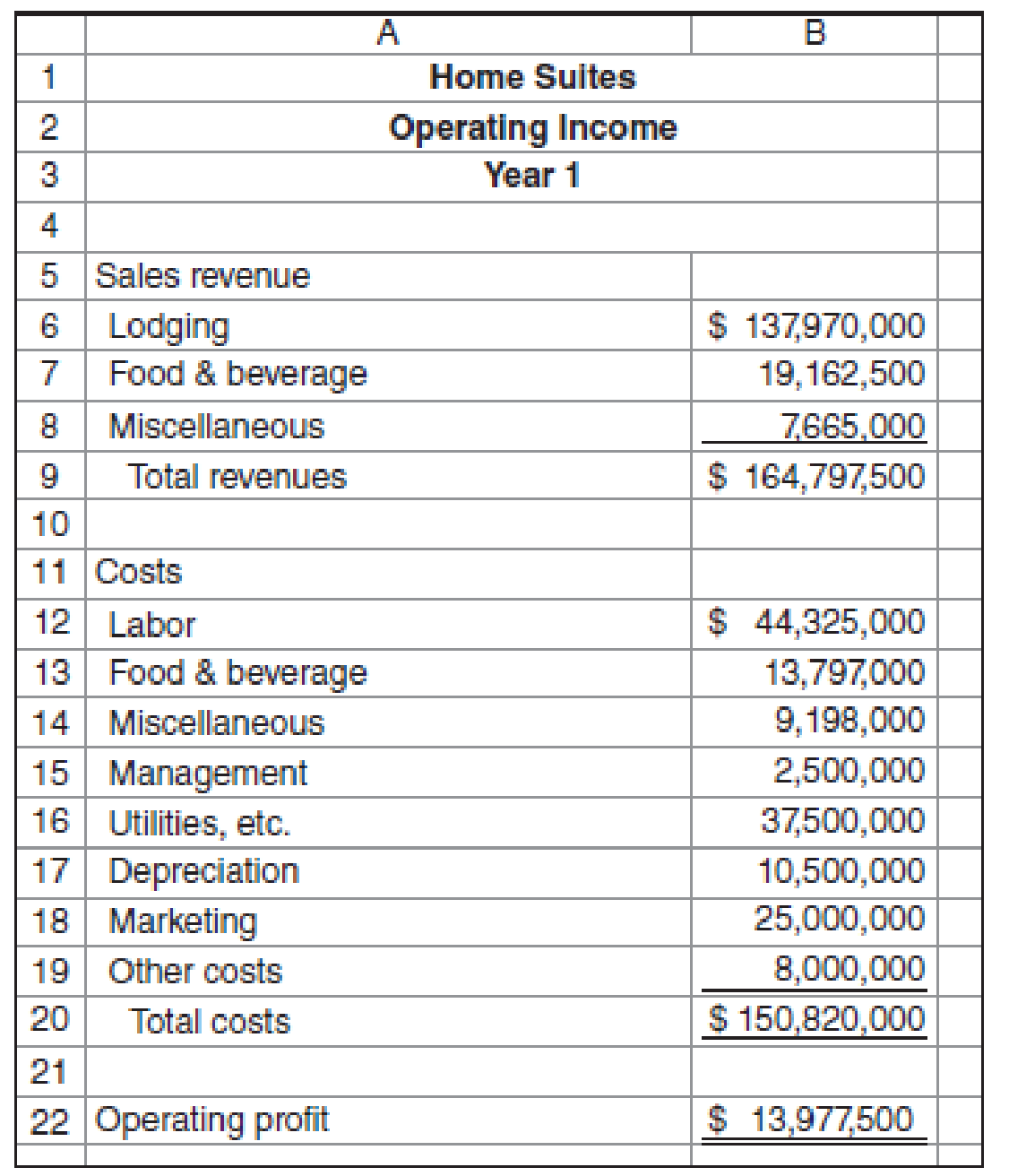
In year 1, the average fixed labor cost was $400,000 per property. The remaining labor cost was variable with respect to the number of nights. Food and beverage cost and miscellaneous cost are all variable with respect to the number of nights. Utilities and
At the beginning of year 2, HomeSuites will open three new properties with no change in the average number of rooms per property. The occupancy rate is expected to remain at 70 percent. Management has made the following additional assumptions for year 2:
- The average room rate will increase by 5 percent.
- Food and beverage revenues per night are expected to decline by 20 percent with no change in the cost.
- The labor cost (both the fixed per property and variable portion) is not expected to change.
- The miscellaneous cost for the room is expected to increase by 25 percent, with no change in the miscellaneous revenues per room.
- Utilities and depreciation costs (per property) are
forecast to remain unchanged. - Management costs will increase by 8 percent, and marketing costs will increase by 10 percent.
- Other costs are not expected to change.
Required
Prepare a
Prepare a budgeted income statement for year 2.
Explanation of Solution
Budgeted income statement:
The budgeted income statement shows the overall profit and loss of the business in the budgeted period. It includes the sales revenue and direct and indirect cost of the production to calculate the operating profit of the budgeted period.
Prepare a budgeted income statement:
|
Company H Budgeted Income Statement For year 2 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Total amount |
| Sales revenue (1): | ||
| Lodging | 173,842,200 | |
| Food & beverage | 18,396,000 | |
| Miscellaneous | 9,198,000 | |
| Total revenue | 201,436,200 | |
| Operating costs: | ||
| Labor (4) | 53,190,000 | |
| Food & beverage (1) | 16,556,400 | |
| Miscellaneous (1) | 13,797,000 | |
| Management (2) | 2,700,000 | |
| Utilities (3) | 45,000,000 | |
| Depreciation (3) | 12,600,000 | |
| Marketing (2) | 27,500,000 | |
| Other costs | 8,000,000 | |
| Total operating cost | 179,343,400 | |
| Operating profit | 22,092,800 | |
Table: (1)
Thus, the operating profit is $22,092,800 for company H for year 2.
Working note 1:
Calculate the revenue and costs for year 2:
| Particulars |
Total nights in a year 2 (8) (a) |
Cost per night (5) (b) |
% change (c) |
Total amount |
| Sales revenue: | ||||
| Lodging | 919,800 | 180 | 1.05 | $173,842,200 |
| Food & beverage | 919,800 | $25 | 0.8 | $18,396,000 |
| Miscellaneous | 919,800 | $10 | - | $9,198,000 |
| Costs: | ||||
| food & beverage | 919,800 | $18 | - | $16,556,400 |
| Miscellaneous | 919,800 | $12 | 1.25 | $13,797,000 |
Table: (2)
Working note 2:
Calculate the management and marketing costs:
| Particulars |
Amount (a) |
% change (b) |
Total amount |
| Costs: | |||
| Management | 2,500,000 | 1.08 | 2,700,000 |
| Marketing | 2,500,000 | 1.1 | 2,750.000 |
Table: (3)
Working note 3:
Calculate the utilities and depreciation:
| Particulars |
Amount (a) |
Number of property in year 1 (b) |
Cost per property |
Number of property in year 2 (d) |
Total cost in year 2 |
| Costs: | |||||
| Utilities | $3,750,000 | 15 | $250,000 | 18 | $4,500,000 |
| Depreciation | $1,050,000 | 15 | $70,000 | 18 | $1,260,000 |
Table: (4)
Working note 4:
Calculate the labor cost:
| Particulars |
Cost per property (a) |
Number of property (b) |
Total nights in a year 2 |
Variable labor cost per night (d) |
Total variable cost |
Total cost |
| Labor cost | $400,000 | 18 | $7,200,000 | 919,800 | $45,990,000 | $53,190,000 |
Table: (5)
Working note 5:
| Particulars |
Amount (a) |
Total nights in a year (7) (b) |
Cost per night |
| Revenue: | |||
| Food & beverage | $19,162,500 | 766,500 | $25 |
| Miscellaneous | $7,665,000 | 766,500 | $10 |
| Costs: | |||
| Food & beverage | $13,797,000 | 766,500 | $18 |
| Miscellaneous | $9,198,000 | 766,500 | $12 |
Table: (6)
Working note 6:
Calculate average variable cost per unit:
| Particulars |
Total fixed labor cost (a) |
Labor cost for year 1 (b) |
Net labor cost |
Total nights in a year (d) |
Cost per night |
| Labor cost | $6,000,000 | $44,325,000 | $38,325,000 | $766,500 | $50 |
Table: (7)
The fixed labor cost per property is $400,000, and there are 15 properties so the total fixed labor cost will be $6,000,000
Working note 7:
Calculate the number of nights for year 1:
|
Number of properties (a) |
Number of rooms in each property (b) |
Days in a year (c) |
Occupancy rate (d) |
Total nights in a year |
| 15 | 200 | 365 | 70% | 766,500 |
Table: (8)
Working note 8:
Calculate the number of nights for year 2:
|
Number of properties (a) |
Number of rooms in each property (b) |
Days in a year (c) |
Occupancy rate (d) |
Total nights in a year |
| 18 | 200 | 365 | 70% | 919,800 |
Table: (9)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
FUNDAMENTALS OF COST ACCOUNTING
- How much income should be recognized?arrow_forwardAt the end of the current year, the owners' equity in Durante Co. is now $385,000. During the year, the assets of the business had increased by $79,000 and the liabilities had increased by $138,000. What must Owners' equity at the beginning of the year have been?arrow_forwardNot use ai solution given correct answer general accounting questionarrow_forward
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,



