
Concept explainers
Selected stock transactions
The following selected accounts appear in the ledger of Parks Construction Inc. at the beginning of the current year:
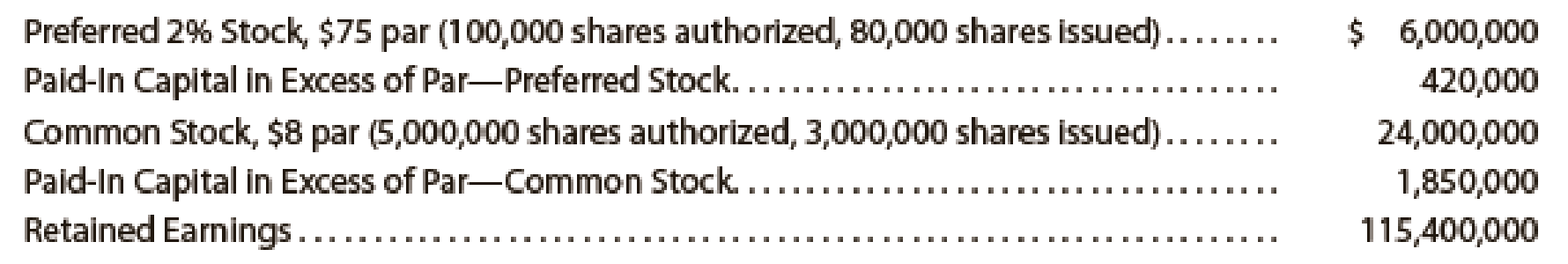
During the year, the corporation completed a number of transactions affecting the stockholders’ equity. They are summarized as follows:
- a. Issued 400,000 shares of common stock at $11, receiving cash.
- b. Issued 5,000 shares of preferred 2% stock at $90.
- c. Purchased 150,000 shares of treasury common for $10 per share.
- d. Sold 80,000 shares of treasury common for $13 per share.
- e. Sold 20,000 shares of treasury common for $9 per share.
- f. Declared cash dividends of $1.50 per share on
preferred stock and $0.06 per share on common stock. - g. Paid the cash dividends.
Instructions
Journalize the entries to record the transactions.
Explanation of Solution
Common stock: These are the ordinary shares that a corporation issues to the investors in order to raise funds. In return, the investors receive a share of profit from the profits earned by the corporation in the form of dividend.
Preferred stock: The stock that provides a fixed amount of return (dividend) to its stockholder before paying dividends to common stockholders is referred as preferred stock.
Cash dividends: The amount of cash provided by a corporation out of its distributable profits to its shareholders as a return for the amount invested by them is referred as cash dividends.
Treasury Stock: It refers to the shares that are reacquired by the corporation that are already issued to the stockholders, but reacquisition does not signify retirement.
a.
Record the issuance of common stock.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash | 4,400,000 | ||
| Common Stock | 3,200,000 | ||
|
Paid-in Capital in Excess of Par value – Common Stock | 1,200,000 | ||
| (To record issuance of 9,000 shares in excess of par) |
Table (1)
Description:
- Cash is an asset account. The amount is increased, because cash is received upon stock issued. Therefore, debit Cash account with the amount of cash received.
- Common Stock is a stockholders’ equity account and the amount is increased due to issuance of common stock. Therefore, credit Common Stock account with the value of common stock.
- Paid-in Capital in Excess of Par Value – Common stock is a stockholders’ equity account and the amount is increased due to increase in capital. Therefore, credit Paid-in Capital in Excess of Par Value account with the excess amount of cash received over the Common Stock value.
b.
Record the issuance of par value preferred stock.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash | 450,000 | ||
| Preferred Stock | 375,000 | ||
|
Paid-in Capital in Excess of Par value – Preferred Stock | 75,000 | ||
| (To record issuance of 5,000 preferred shares in excess of par) |
Table (2)
Description:
- Cash is an asset account. The amount is increased, because cash is received upon stock issued. Therefore, debit Cash account with the amount of cash received.
- Preferred Stock is a stockholders’ equity account and the amount is increased due to issuance of common stock. Therefore, credit Common Stock account with the value of common stock.
- Paid-in Capital in Excess of Par Value is a stockholders’ equity account and the amount is increased due to increase in capital. Therefore, credit Paid-in Capital in Excess of Par Value account with the excess amount of cash received over the Preferred Stock value.
c.
Record the purchase of 150,000 shares of treasury common stock at $10 per share.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Treasury Stock | 1,500,000 | ||
| Cash | 1,500,000 | ||
| (To record the purchase of 150,000 treasury stock) |
Table (3)
Description:
Incorporation P has repurchased 150,000 of its own treasury stock for $1,500,000.
- Treasury stock is contra-stockholders’ equity account with a normal debit balance. Thus, when treasury stocks are purchased, it decreases the stockholders’ equity account. In this case, it reduces the stockholders’ equity by $1,500,000. Therefore, treasury stock account is debited with $1,500,000.
- Cash is an asset. It is decreased as cash is paid for the purchase of treasury stock. Therefore, the cash account is credited with $1,500,000.
d.
Record the resale of 80,000 shares of treasury stock for cash at $13 per share.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash | 1,040,000 | ||
|
Treasury stock | 800,000 | ||
|
Paid-in capital from treasury stock | 240,000 | ||
| (To record sale of treasury stock for above the cost price) |
Table (4)
Description:
- Cash is an asset. It is increased as cash is received from the sale of treasury stock. Therefore, the cash account is credited with $1,040,000.
- Treasury stock is contra-stockholders’ equity account with a normal debit balance. Thus, when treasury stocks are sold at its cost price, then cash would be debited and treasury stock would be credited. But, when treasury stocks are sold for higher than its cost price, then cash would be debited and treasury stock would be credited for cost price, and paid-in capital from treasury stock would be credited for excess selling price.
e.
Record the resale of 20,000 shares of treasury stock for cash at $9 per share.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash | 180,000 | ||
|
Paid-in capital from treasury stock | 20,000 | ||
|
Treasury stock | 200,000 | ||
| (To record sale of treasury stock for below the cost price) |
Table (5)
Description:
- Cash is an asset. It is increased as cash is received from the sale of treasury stock. Therefore, the cash account is credited with $180,000.
- Treasury stock is contra-stockholders’ equity account with a normal debit balance. Thus, when treasury stocks are sold at its cost price, then cash would be debited and treasury stock would be credited. But, when treasury stocks are sold for lesser than its cost price, then cash would be debited and treasury stock would be credited for cost price, and paid-in capital from treasury stock would be debited for deficit selling price.
f.
Calculate the amount of cash dividend declared and paid.
| Particulars | Outstanding number of preferred shares | Outstanding number of common shares |
| Beginning of year | 80,000 | 3,000,000 |
| Transaction A increase common shares | 400,000 | |
| Transaction B increases preferred shares | 5,000 | |
| Transaction C decreases common shares | -150,000 | |
| Transaction D increase common shares | 80,000 | |
| Transaction E increase common shares | 20,000 | |
| Total outstanding shares at the end of the year | 85,000 | 3,350,000 |
| Multiply: Cash dividends per share | ||
| Cash Dividends in total | $127,500 | $201,000 |
Table (6)
Record the declaration of cash dividend on preferred stock and common stock.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| Cash Dividends | 328,500 | ||||
| Cash Dividends Payable | 328,500 | ||||
| (To record declaration of dividends on common stock and preferred stock) | |||||
Table (7)
Description:
Declaration date: The date on which the board of directors of a corporation announces officially to distribute the dividends to its shareholders is referred as declaration date.
- Cash Dividends is a temporary stockholders’ equity account. The account is debited as the cash dividends are declared and eventually be transferred to Retained Earnings account. Therefore, Cash Dividends account is debited
- Cash Dividends Payable is a liability account and the amount owed to the stockholders is increased. Therefore, Cash Dividends Payable account is credited.
g.
Record the payment of cash dividend declared in (F).
Record the journal entry for the payment of cash dividends.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| Cash Dividends Payable | 328,500 | ||||
| Cash | 328,500 | ||||
| (To record payment of dividends) | |||||
Table (8)
Description:
Payment date: The date on which the company makes payments to its shareholders for the declared cash dividends is referred as payment date.
- Dividends Payable is a liability account and the amount is decreased because the dividends owed are paid off. Therefore, debit Dividends Payable with $328,500.
- Cash is an asset account and the amount is decreased because cash is paid. Therefore, credit Cash account with $328,500.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Financial Accounting
- Please explain the correct approach for solving this financial accounting question.arrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting problem with appropriate steps and explanations?arrow_forwardPlease provide the correct answer to this financial accounting problem using accurate calculations.arrow_forward
- I need assistance with this general accounting question using appropriate principles.arrow_forwardCan you explain this financial accounting question using accurate calculation methods?arrow_forwardCan you help me solve this financial accounting question using valid financial accounting techniques?arrow_forward
- Please provide the accurate answer to this financial accounting problem using appropriate methods.arrow_forwardPlease provide the solution to this general accounting question using proper accounting principles.arrow_forwardI need help finding the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with valid methods.arrow_forward
 Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning- Century 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage
 Corporate Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305653535Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Corporate Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305653535Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning





