
Concept explainers
(a)
To find: The pooled estimate of the standard deviation with degree of freedom.
(a)
Answer to Problem 39E
Solution: The pooled estimate of the standard deviation is 38.14 with degree of freedom 105.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation: The pooled variance can be calculated as
where
The degrees of freedom can be calculated as
(b)
To test: Whether it is appropriate to use a pooled standard deviation for the provided analysis.
(b)
Answer to Problem 39E
Solution: Yes, it is appropriate to use a pooled standard deviation for the provided analysis.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation: If the largest standard deviation of a group is less than the twice of the smallest standard deviation, then one can use the pooled standard deviation for the analysis. That is,
Conclusion: The largest pooled standard deviation for the provided analysis is 42.4, which is less than twice the smallest pooled standard deviation of the provided analysis. Therefore, it is appropriate to use a pooled standard deviation for the provided analysis.
(c)
To find: The marginal means.
(c)
Answer to Problem 39E
Solution: The marginal means of sender individual is 70.9, for sender group is 48.85, for responder individual is 59.75, and for responder group is 60.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation: Marginal
The marginal means of sender group can be calculated as
The marginal means of responder individual can be calculated as
The marginal means of responder group can be calculated as
Therefore, the marginal means of sender individual is 70.9, for sender group is 48.85, for responder individual is 59.75, and for responder group is 60.
(d)
To graph: The means.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Calculation: To plot the means, use Minitab and follow the steps below:
Step 1: Open the Minitab worksheet.
Step 2: Go to ANOVA > Interaction plot.
Step 3: Select “Mean” in the column for “Responses” and select “Respondent and Sender” in the column for “Factors.”.
The plot for means is obtained as
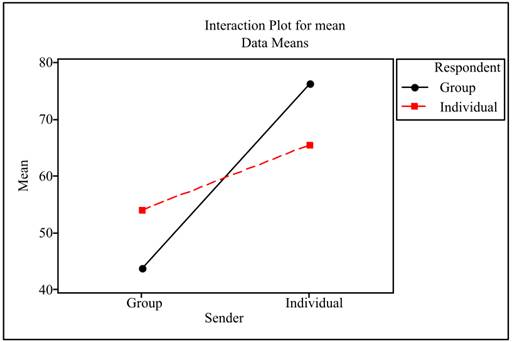
Interpretation: The patterns are not parallel. It can be seen from the plot that there is an interaction among sender and responder. So, there is an interaction among group A and group B. This interaction is significant as two lines are not parallel to each other.
(e)
To find: P-values and its interpretation for the F-statistics.
(e)
Answer to Problem 39E
Solution: The sender effect is significant as P-value is less than 0.05 significance level. The responder effect is not significant as P- value is greater than 0.05. The interaction effect is not significant as P- value is greater than 0.05.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation: The degree of freedom for sender is calculated by
The degree of freedom for responder is calculated by
The degree of freedom for interaction is calculated by
The degree of freedom for error term is calculated by
The P-value for sender group can be calculated by using the formula
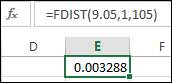
The P-value for responder group can be calculated by using the formula
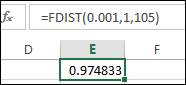
The P-value for interaction can be calculated by using the formula
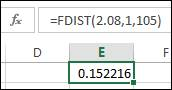
Interpretation: Therefore only the sender effect is significant as P-value is less than 0.05 significance level. The responder effect is not significant as P- value is greater than 0.05. The interaction effect is not significant as P- value is greater than 0.05.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
- The following ordered data list shows the data speeds for cell phones used by a telephone company at an airport: A. Calculate the Measures of Central Tendency using the table in point B. B. Are there differences in the measurements obtained in A and C? Why (give at least one justified reason)? 0.8 1.4 1.8 1.9 3.2 3.6 4.5 4.5 4.6 6.2 6.5 7.7 7.9 9.9 10.2 10.3 10.9 11.1 11.1 11.6 11.8 12.0 13.1 13.5 13.7 14.1 14.2 14.7 15.0 15.1 15.5 15.8 16.0 17.5 18.2 20.2 21.1 21.5 22.2 22.4 23.1 24.5 25.7 28.5 34.6 38.5 43.0 55.6 71.3 77.8arrow_forwardIn a company with 80 employees, 60 earn $10.00 per hour and 20 earn $13.00 per hour. a) Determine the average hourly wage. b) In part a), is the same answer obtained if the 60 employees have an average wage of $10.00 per hour? Prove your answer.arrow_forwardThe following ordered data list shows the data speeds for cell phones used by a telephone company at an airport: A. Calculate the Measures of Central Tendency from the ungrouped data list. B. Group the data in an appropriate frequency table. 0.8 1.4 1.8 1.9 3.2 3.6 4.5 4.5 4.6 6.2 6.5 7.7 7.9 9.9 10.2 10.3 10.9 11.1 11.1 11.6 11.8 12.0 13.1 13.5 13.7 14.1 14.2 14.7 15.0 15.1 15.5 15.8 16.0 17.5 18.2 20.2 21.1 21.5 22.2 22.4 23.1 24.5 25.7 28.5 34.6 38.5 43.0 55.6 71.3 77.8arrow_forward
- Businessarrow_forwardhttps://www.hawkeslearning.com/Statistics/dbs2/datasets.htmlarrow_forwardNC Current Students - North Ce X | NC Canvas Login Links - North ( X Final Exam Comprehensive x Cengage Learning x WASTAT - Final Exam - STAT → C webassign.net/web/Student/Assignment-Responses/submit?dep=36055360&tags=autosave#question3659890_9 Part (b) Draw a scatter plot of the ordered pairs. N Life Expectancy Life Expectancy 80 70 600 50 40 30 20 10 Year of 1950 1970 1990 2010 Birth O Life Expectancy Part (c) 800 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 1950 1970 1990 W ALT 林 $ # 4 R J7 Year of 2010 Birth F6 4+ 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 Year of 1950 1970 1990 2010 Birth Life Expectancy Ox 800 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 Year of 1950 1970 1990 2010 Birth hp P.B. KA & 7 80 % 5 H A B F10 711 N M K 744 PRT SC ALT CTRLarrow_forward
- Harvard University California Institute of Technology Massachusetts Institute of Technology Stanford University Princeton University University of Cambridge University of Oxford University of California, Berkeley Imperial College London Yale University University of California, Los Angeles University of Chicago Johns Hopkins University Cornell University ETH Zurich University of Michigan University of Toronto Columbia University University of Pennsylvania Carnegie Mellon University University of Hong Kong University College London University of Washington Duke University Northwestern University University of Tokyo Georgia Institute of Technology Pohang University of Science and Technology University of California, Santa Barbara University of British Columbia University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill University of California, San Diego University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign National University of Singapore McGill…arrow_forwardName Harvard University California Institute of Technology Massachusetts Institute of Technology Stanford University Princeton University University of Cambridge University of Oxford University of California, Berkeley Imperial College London Yale University University of California, Los Angeles University of Chicago Johns Hopkins University Cornell University ETH Zurich University of Michigan University of Toronto Columbia University University of Pennsylvania Carnegie Mellon University University of Hong Kong University College London University of Washington Duke University Northwestern University University of Tokyo Georgia Institute of Technology Pohang University of Science and Technology University of California, Santa Barbara University of British Columbia University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill University of California, San Diego University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign National University of Singapore…arrow_forwardA company found that the daily sales revenue of its flagship product follows a normal distribution with a mean of $4500 and a standard deviation of $450. The company defines a "high-sales day" that is, any day with sales exceeding $4800. please provide a step by step on how to get the answers in excel Q: What percentage of days can the company expect to have "high-sales days" or sales greater than $4800? Q: What is the sales revenue threshold for the bottom 10% of days? (please note that 10% refers to the probability/area under bell curve towards the lower tail of bell curve) Provide answers in the yellow cellsarrow_forward
- Find the critical value for a left-tailed test using the F distribution with a 0.025, degrees of freedom in the numerator=12, and degrees of freedom in the denominator = 50. A portion of the table of critical values of the F-distribution is provided. Click the icon to view the partial table of critical values of the F-distribution. What is the critical value? (Round to two decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardA retail store manager claims that the average daily sales of the store are $1,500. You aim to test whether the actual average daily sales differ significantly from this claimed value. You can provide your answer by inserting a text box and the answer must include: Null hypothesis, Alternative hypothesis, Show answer (output table/summary table), and Conclusion based on the P value. Showing the calculation is a must. If calculation is missing,so please provide a step by step on the answers Numerical answers in the yellow cellsarrow_forwardShow all workarrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





