
Concept explainers
Project Evaluation This is a comprehensive project evaluation problem bringing together much of what you have learned in this and previous chapters. Suppose you have been hired as a financial consultant to Defense Electronics, Inc. (DEI), a large, publicly traded firm that is the market share leader in radar detection systems (RDSs). The company is looking at setting up a manufacturing plant overseas 10 produce a new tine of RDSs. This will be a five-year project. The company bought some land three years ago for $7 5 million in anticipation of using it as a toxic dump site for waste chemicals, but it built a piping system to safely discard the chemicals instead. The land was appraised last week for $7.1 million. In five years, the aftertax value of the land will be $7.4 million, but the company expects to keep the land for a future project. The company wants to build its new manufacturing plant on this land; the plant and equipment will cost $40 million 10 build. The following market data on DEI’s securities is current:
| Debt: | 260,000 6.8 percent coupon bonds outstanding, 25 years to maturity, selling for 103 percent of par; the bonds have a$1,000 par value each and make semiannual payments. |
| Common stock: | 9,500,000 shares outstanding, selling for $67 per share; the beta is 1.25. |
| 450,000 shares of 5.25 percent preferred stock outstanding, selling for $84 per share and having a par value of $100. | |
| Market: | 7 percent expected market risk premium; 3.6 percent risk-free rate. |
DEI use G.M. Wharton as its lead underwriter. Wharton charges DEI spreads of 6.5 percent on new common stock issues, 4.5 percent on new preferred stock issues, and 3 percent on new debit issues. Wharton has included all direct and indirect issuance costs (along with its profit) in setting these spreads. Wharton has recommended to DEI that it raise the funds needed to build the plant by issuing new shares of common stock. DEI’s tax rate is 35 percent. The project requires $1,400,000 in initial net working capital investment to get operational. Assume Wharton raises all equity for new projects externally.
- a. Calculate the project's initial Time 0 cash now, taking into account all side effects.
- b. The new RDS project is somewhat riskier than a typical project for DEI, primarily because the plant i~ being located overseas. Management has told you to use an adjustment factor of + 2 percent to account for this increased riskiness. Calculate the appropriate discount rate to use when evaluating DEI’s project.
- c. The manufacturing plant has an eight-year tax life, and DEI uses straight-line
depreciation. At the end of the project (i.e., the end of Year 5), the plant and equipment can be scrapped for $8.5 million. What is the aftertax salvage value of this plant and equipment? - d. The company will incur $7,900,000 in annual fixed costs. The plan is to manufacture 18,000 RDSs per year and sell them at $10,900 per machine; the variable production costs are $9,450 per RDS. What is the annual operating cash now (OCF) from this project?
- e. DEI’s comptroller is primarily interested in the impact of DEI’s investments on the bottom line of reported accounting Statement. What will you tell her is the accounting break-even quantity of ROSs sold for this project?
- f. Finally, DEI’s president wants you to throw all your calculations, assumptions, and everything else into the report for the chief financial officer all he want he to know is what the RDS project’s
internal rate of return (IRR) andnet present value (NPV) are. What will you report?
a.
To determine: The Initial Time 0 Cash Flow.
Introduction:
The cost of equity is the yield than an investor anticipates from the security as returns for the risk they accept by spend in the specific security. Additionally it is the return an investor needs before they prefer for an alternative investment which pays higher than the correct.
The cost of debt is the effective interest rate of cost which a business earns on their current debts. Debt involves in the formation of capital structure. As the debt is considered as an deduction expenditure, the cost of debt is usually determined as after-tax cost in order to formulate similar to the cost of equity.
Answer to Problem 24QP
The Initial Time 0 Cash Flow is -$50,794,407.64
Explanation of Solution
Determine the Value of Debt
Therefore the Value of Debt is $267,800,000
Determine the Value of Common Stock
Therefore the Value of Common Stock is $636,500,000
Determine the Value of Preferred Stock
Therefore the Value of Preferred Stock is $37,800,000
Determine the Total Market Value
Therefore the Total Market Value is $942,100,000
Determine the Weight of Debt
Therefore the Weight of Debt is 28.43%
Determine the Weight of Common Stock
Therefore the Weight of Common Stock is 67.56%
Determine the Weight of Preferred Stock
Therefore the Weight of Preferred Stock is 4.01%
Determine the Weighted Average Floatation Costs
Therefore the Weighted Average Floatation Costs is 5.42%
Determine the Amount Raised
Therefore the Amount Raised is $42,294,407.64
Determine the Initial Time 0 Cash Flow
Therefore the Initial Time 0 Cash Flow is -$50,794,407.64
b.
To determine: The Discount Rate of the Project.
Answer to Problem 24QP
The Discount Rate of the Project is 11.81%
Explanation of Solution
Determine the Cost of Equity using CAPM
Therefore the Cost of Equity is 12.35%
Determine the After-tax Cost of Debt
Using excel function =rate we find the pre-tax and after-tax cost of debt as,
Excel Spreadsheet:
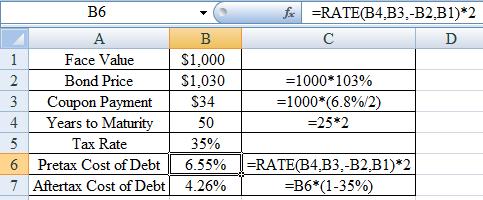
Therefore the After-tax Cost of Debt is 4.26%
Determine the Cost of Preferred Stock
Therefore the Cost of Preferred Stock is 6.25%
Determine the WACC
Therefore the WACC is 9.81%
Determine the Discount Rate of Project
Therefore the Discount Rate of Project is 11.81%
c.
To determine: The After-Tax Salvage Value.
Answer to Problem 24QP
The After-Tax Salvage Value is $10,775,000
Explanation of Solution
Determine the Annual Depreciation
Therefore the Annual Depreciation is $5,000,000
Determine the Book Value at the end of Year 5
Therefore Book Value at the end of Year 5 is $15,000,000
Determine the After-Tax Salvage Value
Therefore After-Tax Salvage Value is $10,775,000
d.
To determine: The Annual Operating Cash Flows.
Answer to Problem 24QP
The Annual Operating Cash Flows is $13,580,000
Explanation of Solution
Determine the Annual Operating Cash Flows
Therefore the Annual Operating Cash Flows is $13,580,000
e.
To determine: The Accounting Break-Even Sales Figure.
Answer to Problem 24QP
The Accounting Break-Even Sales Figure is 8,897 units
Explanation of Solution
Determine the Accounting Break Even Sales Figure
Therefore the Accounting Break Even Sales Figure is 8,897 units
f.
To determine: The Net Present Value (NPV) and Internal Rate of Return (IRR).
Answer to Problem 24QP
The Net Present Value (NPV) is $9,591,825.14 and Internal Rate of Return (IRR) is 18.17%
Explanation of Solution
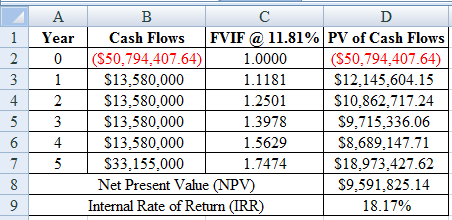
Determine the Net Present Value (NPV) and Internal Rate of Return
Using excel spreadsheet we calculate the Net Present Value (NPV) and Internal Rate of Return as,
Excel Spreadsheet:
Excel Workings:
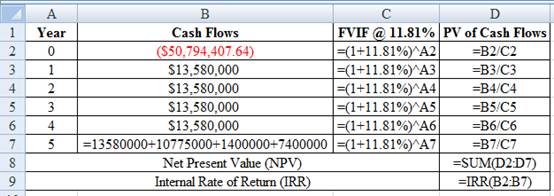
Therefore the Net Present Value (NPV) is $9,591,825.14 and Internal Rate of Return (IRR) is 18.17%
Since the net present value (NPV) is positive the project should be accepted.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
EBK CORPORATE FINANCE
- Sales are $2.90 million, cost of goods sold is $590,000, depreciation expense is $148,000, other operating expenses are $298,000, addition to retained earnings is $1,126,625, dividends per share are $1, tax rate is 21 percent, and number of shares of common stock outstanding is 88,000. LaTonya's Flop Shops has no preferred stock outstanding. Use the above information to calculate the times interest earned ratio for LaTonya's Flop Shops, Incorporated. Note: Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Interest earned timesarrow_forwardTwo building owners - Alice and Bob - each own a building worth $1,000,000. They are considering forming a mutual insurance pool. Based on historical data, there are three possible fire damage scenarios for each building in a given year: No damage: 85% probability Partial damage: 12% probability, with repair costs of $200,000 Total loss: 3% probability, with a cost of $1,000,000 Calculate the standard deviationarrow_forwardWhat is the role of the researcher, population and sampling, and data collection, could you help explain each one of them? How to start working on the population structures essential to research? What are the structured ways in which to present key research elements?arrow_forward
- Could you please help explain the Qualitative Research Data Analysis? What is the Coding, and Interrater Reliability? How do they work and when we use them?What are the description of populations and Samples, please help to explain them.arrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardAll computations must be done and shown manually. Kindly no spreadsheetcomputations. So that I am able to follow and understand clearly please.arrow_forward
- Don't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardOne year ago, the Jenkins Family Fun Center deposited $3,700 into an investment account for the purpose of buying new equipment four years from today. Today, they are adding another $5,500 to this account. They plan on making a final deposit of $7,700 to the account next year. How much will be available when they are ready to buy the equipment, assuming they earn a rate of return of 9 percent?arrow_forwardIt is anticipated that Pinnaclewalk will next pay an annual dividend of $2.2 per share in one year. The firm's cost of equity is 19.2% and its anticipated growth rate is 3.1%. There are 420000 outstanding. Use the Gordon Growth Model to price Pinnaclewalk's shares. {Express your answer in dollars and cents} What is Pinnaclewalk's market capitalization? {Express your answer in millions of dollars rounded to two decimal places}arrow_forward
- Thumbtack's capital structure is shown in table below. If taxes are paid annually and Thumbtack's combined tax rate is 36 percent, determine the weighted average cost of capital Loans Bonds 12%/yr/semi $3,000,000 8%/yr/qtr $4,500,000 Common Stock $72/share price; $2,000,000 $8/shr/yr dividend; Retained Earnings (Answer should be in %) 1%/yr share price growth $1,500,000arrow_forwardYou have an investment worth $61,345 that is expected to make regular monthly payments of $1,590 for 20 months and a special payment of $X in 3 months. The expected return for the investment is 0.92 percent per month and the first regular payment will be made in 1 month. What is X? Note: X is a positive number.arrow_forwardA bond with a par value of $1,000 and a maturity of 8 years is selling for $925. If the annual coupon rate is 7%, what’s the yield on the bond? What would be the yield if the bond had semiannual payments?arrow_forward
- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

