
Concept explainers
Draw the enol tautomers for each of the following compounds. If the compound has more than one enol tautomer, indicate which one is more stable.
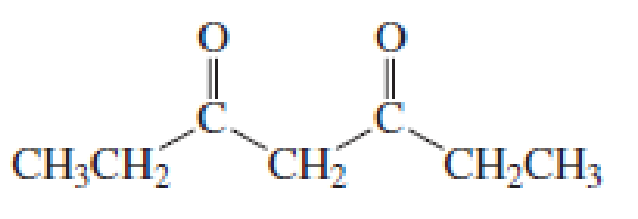
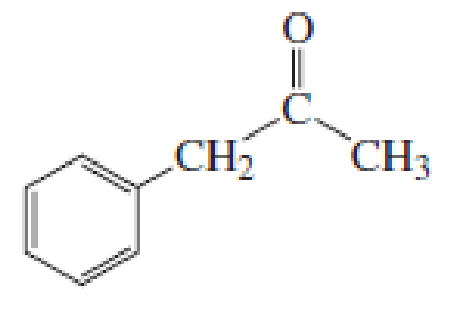
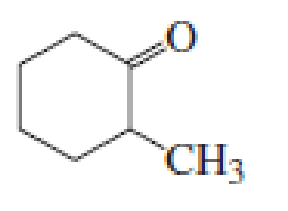
(a)
Interpretation:
The enol tautomer of the given compound has to be drawn and more stable structure has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Tautomerism is the ability of a molecule to exist in more than one chemical form.
Tautomers are formed by the migration of a hydrogen atom, accompanied by the switching of a single and neighboring double bond.
The only difference in keto-enol tautomers is the location of hydrogen and double bond.
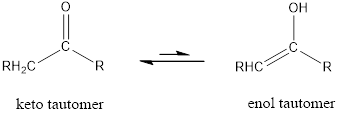
Enol tautomer is much less stable than the keto tautomer.
Enol tautomer is more stable when enol tautomer is aromatic or when the double bonds are conjugated.
Resonance is an electron displacement effect for stabilizing a molecule through delocalization of bonding electrons in the pi orbital.
Delocalized electrons stabilize a compound. The extra stability gains from having delocalized electrons are called resonance stabilization or resonance energy.
Explanation of Solution
Given keto tautomer is,
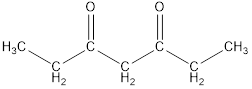
The only difference in keto-enol tautomer is the location of hydrogen and double bond.
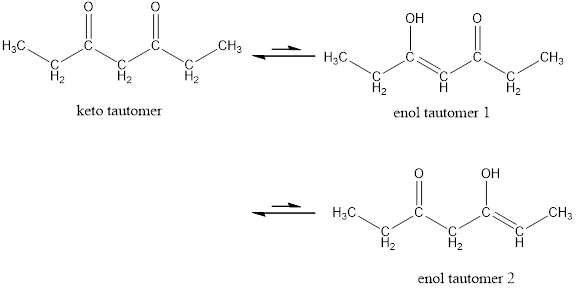
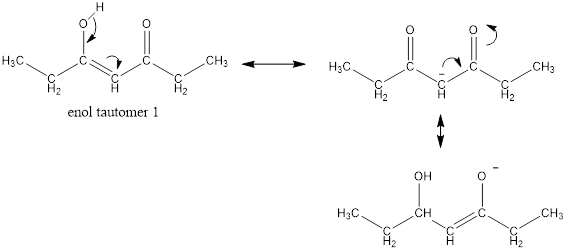
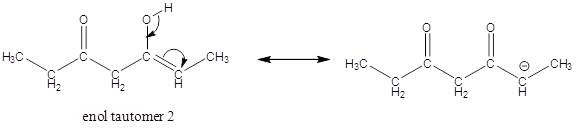
Enol tautomer 1 is more stable than enol tautomer 2.
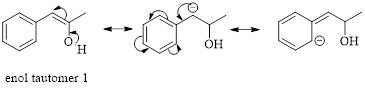
Enol tautomer 1 can undergo delocalization and are more stable.
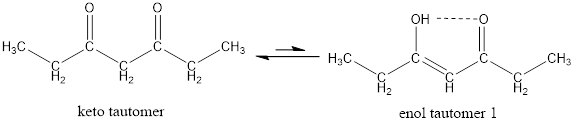
Thus enol tautomer 1 is more stable since it has more resonance structures and also possess intramolecular hydrogen bonding.
(b)
Interpretation:
The enol tautomer of the given compound has to be drawn and more stable structure has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Tautomerism is the ability of a molecule to exist in more than one chemical form.
Tautomers are formed by the migration of a hydrogen atom, accompanied by the switching of a single and neighboring double bond.
The only difference in keto-enol tautomers is the location of hydrogen and double bond.

Enol tautomer is much less stable than the keto tautomer.
Enol tautomer is more stable when enol tautomer is aromatic or when the double bonds are conjugated.
Resonance is an electron displacement effect for stabilizing a molecule through delocalization of bonding electrons in the pi orbital.
Delocalized electrons stabilize a compound. The extra stability gains from having delocalized electrons are called resonance stabilization or resonance energy.
Explanation of Solution
Given keto tautomer is,
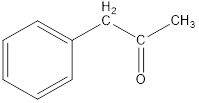
The only difference in keto-enol tautomers is the location of hydrogen and double bond.
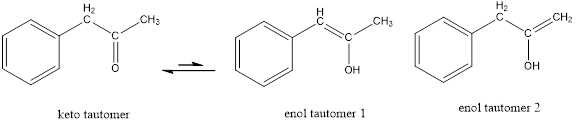
These tautomers undergo resonance and are shown below,
Enol tautomer 1 can undergo delocalization. Enol tautomer 1 is more stable than enol tautomer 2.
The enol tautomer 1 is more stable because there is a conjugation between the double bond and benzene ring. No such conjugation is possible in the enol tautomer 2.
(c)
Interpretation:
The enol tautomer of the given compound has to be drawn and more stable structure has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Tautomerism is the ability of a molecule to exist in more than one chemical form.
Tautomers are formed by the migration of a hydrogen atom, accompanied by the switching of a single and neighboring double bond.
The only difference in keto-enol tautomers is the location of hydrogen and double bond.

Enol tautomer is much less stable than the keto tautomer.
Enol tautomer is more stable when enol tautomer is aromatic or when the double bonds are conjugated.
Explanation of Solution
Given keto tautomer is,
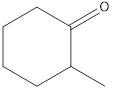
The only difference in keto-enol tautomers is the location of hydrogen and double bond.
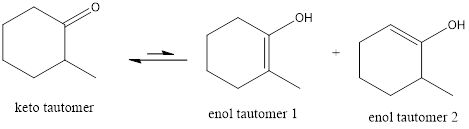

The alkene double bond formed by tautomer 1 is tetra-substituted which is stable than tautomer 2.
Hence, enol tautomer 1 is more stable.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry Study Guide & Solution Manual, Books a la Carte Edition
- Please correct answer and don't use hand ratingarrow_forwardNonearrow_forward%Reflectance 95 90- 85 22 00 89 60 55 50 70 65 75 80 50- 45 40 WA 35 30- 25 20- 4000 3500 Date: Thu Feb 06 17:21:21 2025 (GMT-05:0(UnknownD Scans: 8 Resolution: 2.000 3000 2500 Wavenumbers (cm-1) 100- 2981.77 1734.25 2000 1500 1000 1372.09 1108.01 2359.09 1469.82 1181.94 1145.20 1017.01 958.45 886.97 820.49 668.25 630.05 611.37arrow_forward
- Nonearrow_forwardCH3 CH H3C CH3 H OH H3C- -OCH2CH3 H3C H -OCH3 For each of the above compounds, do the following: 1. List the wave numbers of all the IR bands in the 1350-4000 cm-1 region. For each one, state what bond or group it represents. 2. Label equivalent sets of protons with lower-case letters. Then, for each 1H NMR signal, give the 8 value, the type of splitting (singlet, doublet etc.), and the number protons it represents. of letter δ value splitting # of protons 3. Redraw the compound and label equivalent sets of carbons with lower-case letters. Then for each set of carbons give the 5 value and # of carbons it represents. letter δ value # of carbonsarrow_forwardDraw the correct ionic form(s) of arginine at the pKa and PI in your titration curve. Use your titration curve to help you determine which form(s) to draw out.arrow_forward
- Carbohydrates- Draw out the Hawthorne structure for a sugar from the list given in class. Make sure to write out all atoms except for carbons within the ring. Make sure that groups off the carbons in the ring are in the correct orientation above or below the plane. Make sure that bonds are in the correct orientation. Include the full name of the sugar. You can draw out your curve within the text box or upload a drawing below.arrow_forwardHow many milliliters of 97.5(±0.5) wt% H2SO4 with a density of 1.84(±0.01) g/mL will you need to prepare 2.000 L of 0.110 M H2SO4? If the uncertainty in delivering H2SO4 is ±0.01 mL, calculate the absolute uncertainty in the molarity (0.110 M). Assume there is negligible uncertainty in the formula mass of H2SO4 and in the final volume (2.000 L) and assume random error.arrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
