
Concept explainers
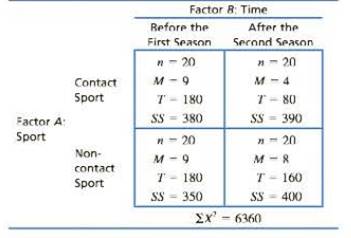
Most sports injuries are immediate and obvious, like a broken leg. However, some can be more subtle, like the neurological damage that may occur when soccer players repeatedly head a soccer ball. To examine effects of repeated heading. McAllister et al. (2013) examined a group of football and ice hockey players and a group of athletes in noncontact sports before and shortly after the season. The dependent variable was performance on a conceptual thinking task. Following are hypothetical data from an independent-measures study similar to the one by McAllister et al. The researchers measured conceptual thinking for contact and noncontact athletes at the beginning of their first season and for separate groups of athletes at the end of their second season.
- a. Use a two-factor ANOVA with α = .05 to evaluate the main effects and interactions.
- b. Calculate the effects size (η2) for the main effects and the interaction.
- c. Briefly describe the outcome of the study.
a.
Answer to Problem 23P
Both the main effects and interaction are significant.
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
Following data is given:
| Factor B: Time | |||
|
Before the first season |
After the second season | ||
|
Factor A: Sport |
Contact sport |
|
|
| Non contact support |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Calculation:
Let, k represent total numbers of treatment conditions.
Let N represent total numbers of observations. Then
Let G represent grand total. Then,
Evaluation of the main effect for factor A is:
The hypotheses are given below:
Null hypothesis: There is no difference between the two levels of factor A that is main effect for factor A is not significant.
Alternate hypothesis: There is significant difference between the two levels of factor A that is main effect for factor A is significant.
Degrees of freedom corresponding to
Degrees of freedom corresponding to:
Variability between treatments is given as:
Degrees of freedom corresponding to
F ratio is given as:
From the table in appendix B.4, the critical value corresponding to degrees of freedom
Since, F-ratio is greater than critical value, so reject the null hypothesis and conclude that there are significant differences between levels of factor A.
Evaluation of the main effect for factor B is:
The hypotheses are given below:
Null hypothesis: There is no difference between the two levels of factor B that is main effect for factor B is not significant.
Alternate hypothesis: There is significant difference between the two levels of factor B that is main effect for factor B is significant.
F ratio is given as:
From the table in appendix B.4, the critical value corresponding to degrees of freedom
Since, F-ratio is greater than critical value, so reject the null hypothesis and conclude that there are significant differences between levels of factor B that is main effect for factor B is significant.
Evaluation of the interaction is:
The hypotheses are given below:
Null hypothesis: There is no interaction between the two factors A and B.
Alternate hypothesis: There is no interaction between the two factors A and B.
F ratio is given as:
From the table in appendix B.4, the critical value corresponding to degrees of freedom
Since, F-ratio is greater than critical value, so reject the null hypothesis and conclude that there is significant interaction between factors A and B or interaction is significant.
Conclusion:
Both the main effects and interaction are significant.
b.
Answer to Problem 23P
The value of
The value of
The value of
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
From part a.
The value of
The value of
The value of
Conclusion:
The value of
The value of
The value of
c.
Answer to Problem 23P
For contact sport athletes, there is a significant decrease in scores that is scores after the second season are less than the scores after the first session. For non-contact sport athletes, there is small decrease or no significant difference in scores after the second season.
Explanation of Solution
From the given info, for the contact support, mean scores before the first season and after the second season are 9 and 4 respectively. Therefore, there is a significant decrease in time after the second season corresponding to the contact sport.
From the given info, for the non-contact support, mean scores before the first season and after the second season are 9 and 8 respectively. Therefore, there is little bit decrease in time after the second season corresponding to the non-contact sport.
Conclusion:
For contact sport athletes, there is a significant decrease in scores corresponding to the factor time that is scores after the second season are less than the scores after the first session. For non-contact sport athletes, there is small decrease or no decrease in scores after the second season.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Essentials of Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap Course List)
- 30% of all college students major in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math). If 48 college students are randomly selected, find the probability thata. Exactly 12 of them major in STEM. b. At most 17 of them major in STEM. c. At least 12 of them major in STEM. d. Between 9 and 13 (including 9 and 13) of them major in STEM.arrow_forward7% of all Americans live in poverty. If 40 Americans are randomly selected, find the probability thata. Exactly 4 of them live in poverty. b. At most 1 of them live in poverty. c. At least 1 of them live in poverty. d. Between 2 and 9 (including 2 and 9) of them live in poverty.arrow_forward48% of all violent felons in the prison system are repeat offenders. If 40 violent felons are randomly selected, find the probability that a. Exactly 18 of them are repeat offenders. b. At most 18 of them are repeat offenders. c. At least 18 of them are repeat offenders. d. Between 17 and 21 (including 17 and 21) of them are repeat offenders.arrow_forward
- Consider an MA(6) model with θ1 = 0.5, θ2 = −25, θ3 = 0.125, θ4 = −0.0625, θ5 = 0.03125, and θ6 = −0.015625. Find a much simpler model that has nearly the same ψ-weights.arrow_forwardLet {Yt} be an AR(2) process of the special form Yt = φ2Yt − 2 + et. Use first principles to find the range of values of φ2 for which the process is stationary.arrow_forwardDescribe the important characteristics of the autocorrelation function for the following models: (a) MA(1), (b) MA(2), (c) AR(1), (d) AR(2), and (e) ARMA(1,1).arrow_forward
- « CENGAGE MINDTAP Quiz: Chapter 38 Assignment: Quiz: Chapter 38 ips Questions ra1kw08h_ch38.15m 13. 14. 15. O Which sentence has modifiers in the correct place? O a. When called, she for a medical emergency responds quickly. b. Without giving away too much of the plot, Helena described the heroine's actions in the film. O c. Nearly the snakebite victim died before the proper antitoxin was injected. . O O 16 16. O 17. 18. O 19. O 20 20. 21 21. 22. 22 DS 23. 23 24. 25. O O Oarrow_forwardQuestions ra1kw08h_ch36.14m 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. Ӧ 17. 18. 19. OS 20. Two separate sentences need Oa. two separate subjects. Ob. two dependent clauses. c. one shared subject.arrow_forwardCustomers experiencing technical difficulty with their Internet cable service may call an 800 number for technical support. It takes the technician between 30 seconds and 11 minutes to resolve the problem. The distribution of this support time follows the uniform distribution. Required: a. What are the values for a and b in minutes? Note: Do not round your intermediate calculations. Round your answers to 1 decimal place. b-1. What is the mean time to resolve the problem? b-2. What is the standard deviation of the time? c. What percent of the problems take more than 5 minutes to resolve? d. Suppose we wish to find the middle 50% of the problem-solving times. What are the end points of these two times?arrow_forward
- Exercise 6-6 (Algo) (LO6-3) The director of admissions at Kinzua University in Nova Scotia estimated the distribution of student admissions for the fall semester on the basis of past experience. Admissions Probability 1,100 0.5 1,400 0.4 1,300 0.1 Click here for the Excel Data File Required: What is the expected number of admissions for the fall semester? Compute the variance and the standard deviation of the number of admissions. Note: Round your standard deviation to 2 decimal places.arrow_forward1. Find the mean of the x-values (x-bar) and the mean of the y-values (y-bar) and write/label each here: 2. Label the second row in the table using proper notation; then, complete the table. In the fifth and sixth columns, show the 'products' of what you're multiplying, as well as the answers. X y x minus x-bar y minus y-bar (x minus x-bar)(y minus y-bar) (x minus x-bar)^2 xy 16 20 34 4-2 5 2 3. Write the sums that represents Sxx and Sxy in the table, at the bottom of their respective columns. 4. Find the slope of the Regression line: bi = (simplify your answer) 5. Find the y-intercept of the Regression line, and then write the equation of the Regression line. Show your work. Then, BOX your final answer. Express your line as "y-hat equals...arrow_forwardApply STATA commands & submit the output for each question only when indicated below i. Generate the log of birthweight and family income of children. Name these new variables Ibwght & Ifaminc. Include the output of this code. ii. Apply the command sum with the detail option to the variable faminc. Note: you should find the 25th percentile value, the 50th percentile and the 75th percentile value of faminc from the output - you will need it to answer the next question Include the output of this code. iii. iv. Use the output from part ii of this question to Generate a variable called "high_faminc" that takes a value 1 if faminc is less than or equal to the 25th percentile, it takes the value 2 if faminc is greater than 25th percentile but less than or equal to the 50th percentile, it takes the value 3 if faminc is greater than 50th percentile but less than or equal to the 75th percentile, it takes the value 4 if faminc is greater than the 75th percentile. Include the outcome of this code…arrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL


