
Principles Of Macroeconomics V 8.0
18th Edition
ISBN: 9781453378717
Author: Taylor
Publisher: BOSTON ACADEMIC (DBA FLAT WORLD)
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 13, Problem 21P
Use Table 26.3 to answer the following questions.
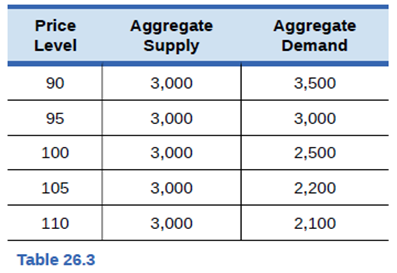
- Sketch an aggregate supply and aggregate demand diagram.
- What is the equilibrium output and
price level? - If aggregate demand shifts right, what is equilibrium output?
- If aggregate demand shifts left, what is equilibrium output?
- In this scenario, would you suggest using aggregate demand to alter the level of output or to control any inflationary increases in the price level?
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
17. The South African government's distributive stance is clear given its prioritisation of social
spending, which includes grants and subsidised goods. Discuss the advantages and
disadvantages of an in-kind subsidy versus a cash grant. Use a graphical illustration to
support your arguments.
[15]
18. Redistributive expenditure can take the form of direct cash transfers (grants) and/or in-kind
subsidies. With references to the graphs below, discuss the merits of these two transfer
types in the presence and absence of a positive externality.
[14]
19. Expenditure on education and healthcare have, by far, the biggest redistributive effect in
South Africa' by one estimate dropping the Gini-coefficient by 10 percentage points.
Discuss the South African government's performance in health and education provision by
evaluating both the outputs and outcomes in these areas of service delivery. [15]
20. Define the following concepts and provide an example in each case: tax rate structure,
general…
Summarise the case for government intervention in the education market
Should Maureen question the family about the history of the home? Can Maureen access public records for proof of repairs?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Principles Of Macroeconomics V 8.0
Ch. 13 - Do rational expectations tend to look back at past...Ch. 13 - Legislation proposes that the government should...Ch. 13 - Would it make sense to argue that rational...Ch. 13 - Summarize the Keynesian and Neoclassical models.Ch. 13 - Does neoclassical economics focus on the long term...Ch. 13 - Does neoclassical economics view prices and wages...Ch. 13 - What shape is the long-nm aggregate supply curve?...Ch. 13 - What is the difference between rational...Ch. 13 - A neoclassical economist and a Keynesian economist...Ch. 13 - Do neoclassical economists tend to focus more on...
Ch. 13 - Do neoclassical economists tend to focus more on...Ch. 13 - Do neoclassical economists see a value in...Ch. 13 - If aggregate supply is vertical, what role does...Ch. 13 - What is the shape of the neoclassical long-run...Ch. 13 - When the economy is experiencing a recession, why...Ch. 13 - If the economy is suffering through a rampant...Ch. 13 - If most people have rational expectations, how...Ch. 13 - Explain why the neoclassical economists believe...Ch. 13 - Economists from all theoretical persuasions...Ch. 13 - Is it a logical contradiction to be a neoclassical...Ch. 13 - Use Table 26.3 to answer the following questions....
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
What is an action plan? Why are action plans such an important part of market planning? Why is it so important ...
MARKETING:REAL PEOPLE,REAL CHOICES
Quick ratio and current ratio (Learning Objective 7) 1520 min. Consider the following data COMPANY A B C D Cash...
Financial Accounting, Student Value Edition (5th Edition)
E2-13 Identifying increases and decreases in accounts and normal balances
Learning Objective 2
Insert the mis...
Horngren's Accounting (12th Edition)
11-9. Identify a company with a product that interests you. Consider ways the company could use customer relati...
Business Essentials (12th Edition) (What's New in Intro to Business)
1.10 Brown’s, a local bakery, is worried about increased costs—particularly energy. Last year’s records can pro...
Operations Management
S6-2 Determining inventory costing methods
Ward Hard ware does not expect costs to change dramatically and want...
Horngren's Financial & Managerial Accounting, The Financial Chapters (Book & Access Card)
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 3. Distinguish between a direct democracy and a representative democracy. Use appropriate examples to support your answers. [4] 4. Explain the distinction between outputs and outcomes in social service delivery [2] 5. A R1000 tax payable by all adults could be viewed as both a proportional tax and a regressive tax. Do you agree? Explain. [4] 6. Briefly explain the displacement effect in Peacock and Wiseman's model of government expenditure growth and provide a relevant example of it in the South African context. [5] 7. Explain how unbalanced productivity growth may affect government expenditure and briefly comment on its relevance to South Africa. [5] 8. South Africa has recently proposed an increase in its value-added tax rate to 15%, sparking much controversy. Why is it argued that value-added tax is inequitable and what can be done to correct the inequity? [5] 9. Briefly explain the difference between access to education and the quality of education, and why we should care about the…arrow_forward20. Factors 01 pro B. the technological innovations available to companies. A. the laws that regulate manufacturers. C. the resources used to create output D. the waste left over after goods are produced. 21. Table 1.1 shows the tradeoff between different combinations of missile production and home construction, ceteris paribus. Complete the table by calculating the required opportunity costs for both missiles and houses. Then answer the indicated question(s). Combination Number of houses Opportunity cost of houses in Number of missiles terms of missiles J 0 4 K 10,000 3 L 17,000 2 1 M 21,000 0 N 23,000 Opportunity cost of missiles in terms of houses Tutorials-Principles of Economics m health carearrow_forwardIn a small open economy with a floating exchange rate, the supply of real money balances is fixed and a rise in government spending ______ Group of answer choices Raises the interest rate so that net exports must fall to maintain equilibrium in the goods market. Cannot change the interest rate so that net exports must fall to maintain equilibrium in the goods market. Cannot change the interest rate so income must rise to maintain equilibrium in the money market Raises the interest rate, so that income must rise to maintain equilibrium in the money market.arrow_forward
- Suppose a country with a fixed exchange rate decides to implement a devaluation of its currency and commits to maintaining the new fixed parity. This implies (A) ______________ in the demand for its goods and a monetary (B) _______________. Group of answer choices (A) expansion ; (B) contraction (A) contraction ; (B) expansion (A) expansion ; (B) expansion (A) contraction ; (B) contractionarrow_forwardAssume a small open country under fixed exchanges rate and full capital mobility. Prices are fixed in the short run and equilibrium is given initially at point A. An exogenous increase in public spending shifts the IS curve to IS'. Which of the following statements is true? Group of answer choices A new equilibrium is reached at point B. The TR curve will shift down until it passes through point B. A new equilibrium is reached at point C. Point B can only be reached in the absence of capital mobility.arrow_forwardA decrease in money demand causes the real interest rate to _____ and output to _____ in the short run, before prices adjust to restore equilibrium. Group of answer choices rise; rise fall; fall fall; rise rise; fallarrow_forward
- If a country's policy makers were to continously use expansionary monetary policy in an attempt to hold unemployment below the natural rate , the long urn result would be? Group of answer choices a decrease in the unemployment rate an increase in the level of output All of these an increase in the rate of inflationarrow_forwardA shift in the Aggregate Supply curve to the right will result in a move to a point that is southwest of where the economy is currently at. Group of answer choices True Falsearrow_forwardAn oil shock can cause stagflation, a period of higher inflation and higher unemployment. When this happens, the economy moves to a point to the northeast of where it currently is. After the economy has moved to the northeast, the Federal Reserve can reduce that inflation without having to worry about causing more unemployment. Group of answer choices True Falsearrow_forward
- The long-run Phillips Curve is vertical which indicates Group of answer choices that in the long-run, there is no tradeoff between inflation and unemployment. that in the long-run, there is no tradeoff between inflation and the price level. None of these that in the long-run, the economy returns to a 4 percent level of inflation.arrow_forwardSuppose the exchange rate between the British pound and the U.S. dollar is £1 = $2.00. The U.S. government implementsU.S. government implements a contractionary fiscal policya contractionary fiscal policy. Illustrate the impact of this change in the market for pounds. 1.) Using the line drawing tool, draw and label a new demand line. 2.) Using the line drawing tool, draw and label a new supply line. Note: Carefully follow the instructions above and only draw the required objects.arrow_forwardJust Part D please, this is for environmental economicsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning





Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781337617383
Author:Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:Cengage Learning



