
Concept explainers
In Fig. 13-21, a central particle of mass M is surrounded by a square array of other particles, separated by either distance d or distance d/2 along the perimeter of the square. What are the magnitude and direction of the net gravitational force on the central particle due to the other particles?
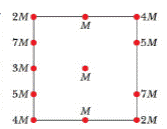
Figure 13-21 Question 1.
To find:
The magnitude and direction of the net gravitational force acting on the central particle due to the other particles
Answer to Problem 1Q
Solution:
The net gravitational force acting on the central particle due to the other particles is
and is directed towards left.
Explanation of Solution
1) Concept:
Observing the figure, we can cancel out the equal and opposite forces. The sum of the remaining forces will be the net force acting on the central particle M.
2) Given:
Thefigure of system of particles is given.
3) Formulae:
The Gravitational force of attraction between two bodies of masses M and m separated by distance R is,
4) Calculations:
From the given figure, we can infer that the gravitation force due to each particle on one of the sides of the square is cancelled by the gravitational force due to one of the particles on the opposite side of the square with the same mass except particle 3M. Particle 3M would exert force on M, but there is no force on the opposite side which can cancel this force.
So, the net force acting on the central particle M is due to the particle 3M which is
As we know the gravitational force is an attractive force, the force on particle M by particle 3M is pointing towards the left.
Conclusion:
Using the formula for gravitational force, we can find the net force acting on the particle due to the system of particles.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Fundamentals Of Physics - Volume 1 Only
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
- pls help on all asked questions kindlyarrow_forward19. Mount Everest, Earth's highest mountain above sea level, has a peak of 8849 m above sea level. Assume that sea level defines the height of Earth's surface. (re = 6.38 × 106 m, ME = 5.98 × 1024 kg, G = 6.67 × 10 -11 Nm²/kg²) a. Calculate the strength of Earth's gravitational field at a point at the peak of Mount Everest. b. What is the ratio of the strength of Earth's gravitational field at a point 644416m below the surface of the Earth to a point at the top of Mount Everest? C. A tourist watching the sunrise on top of Mount Everest observes a satellite orbiting Earth at an altitude 3580 km above his position. Determine the speed of the satellite.arrow_forwardpls help on allarrow_forward
- pls help on allarrow_forward6. As the distance between two charges decreases, the magnitude of the electric potential energy of the two-charge system: a) Always increases b) Always decreases c) Increases if the charges have the same sign, decreases if they have the opposite signs d) Increases if the charges have the opposite sign, decreases if they have the same sign 7. To analyze the motion of an elastic collision between two charged particles we use conservation of & a) Energy, Velocity b) Momentum, Force c) Mass, Momentum d) Energy, Momentum e) Kinetic Energy, Potential Energyarrow_forwardpls help on all asked questions kindlyarrow_forward
- pls help on all asked questions kindlyarrow_forward17. Two charges, one of charge +2.5 × 10-5 C and the other of charge +3.7 × 10-6 C, are 25.0 cm apart. The +2.5 × 10−5 C charge is to the left of the +3.7 × 10−6 C charge. a. Draw a diagram showing the point charges and label a point Y that is 20.0 cm to the left of the +3.7 × 10-6 C charge, on the line connecting the charges. (Field lines do not need to be drawn.) b. Calculate the net electric field at point Y.arrow_forward3arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





