
Concept explainers
Hurst Company’s beginning inventory and purchases during the fiscal year ended December 31, 20-2, were as follows:
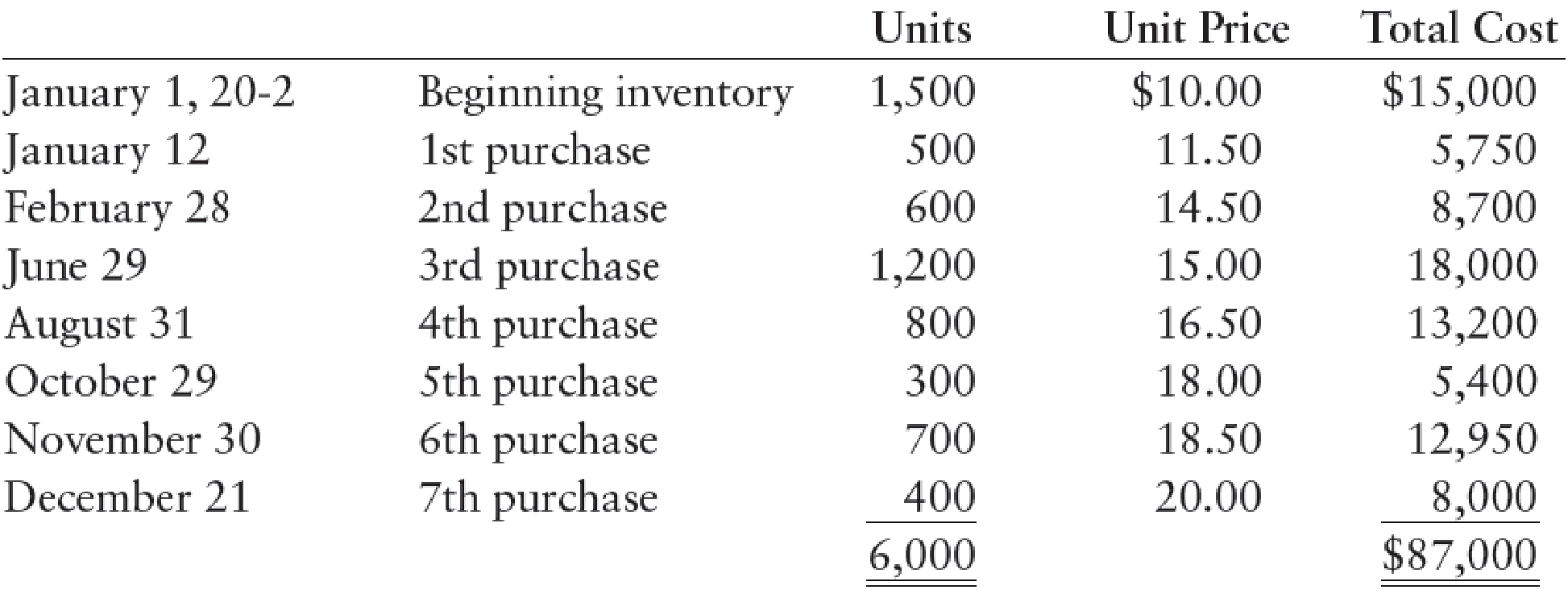
There are 1,200 units of inventory on hand on December 31, 20-2.
REQUIRED
- 1. Calculate the total amount to be assigned to the cost of goods sold for 20-2 and ending inventory on December 31 under each of the following periodic inventory methods:
- (a) FIFO
- (b) LIFO
- (c) Weighted-average (round calculations to two decimal places)
- 2. Assume that the market price per unit (cost to replace) of Hurst’s inventory on December 31 was $18. Calculate the total amount to be assigned to the ending inventory on December 31 under each of the following methods:
- (a) FIFO lower-of-cost-or-market
- (b) Weighted-average lower-of-cost-or-market
- 3. In addition to taking a physical inventory on December 31, Hurst decides to estimate the ending inventory and cost of goods sold. During the fiscal year ended December 31, 20-2, net sales of $100,000 were made at a normal gross profit rate of 35%. Use the gross profit method to estimate the cost of goods sold for the fiscal year ended December 31 and the inventory on December 31.
1.
(a)
Calculate the total amount of cost of goods sold and cost of ending inventory on December 31, under FIFO method (Periodic inventory system).
Explanation of Solution
First-in-First-Out (FIFO): In First-in-First-Out method, the first purchased items are sold first. The value of the ending inventory consists of the recently purchased items.
Calculate the total amount of cost of goods sold and cost of ending inventory on December 31, under FIFO method (Periodic inventory system):
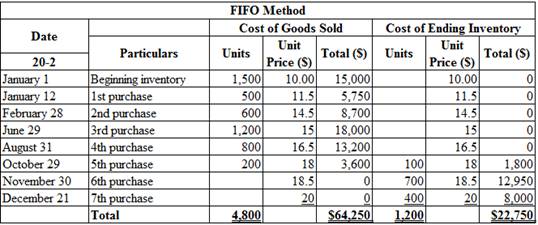
Table (1)
Therefore, the cost of sold and cost of ending inventory under FIFO (Periodic inventory system) is $64,250 and $22,750.
2.
(b)
Calculate the total amount of cost of goods sold and cost of ending inventory on December 31, under LIFO method (Periodic inventory system).
Explanation of Solution
Last-in-First-Out (LIFO): In Last-in-First-Out method, the last purchased items are sold first. The value of the closing stock consists of the initially purchased items.
Calculate the total amount of cost of goods sold and cost of ending inventory on December 31, under LIFO method (Periodic inventory system):
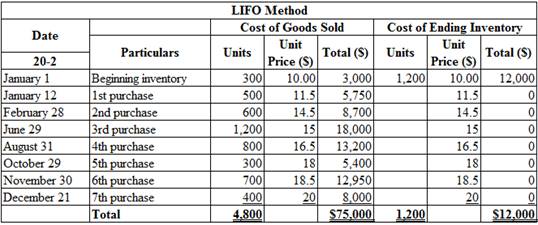
Table (2)
Therefore, the cost of sold and cost of ending inventory under LIFO (Periodic inventory system) is $75,000 and $12,000.
3.
(c)
Calculate the total amount of cost of goods sold and cost of ending inventory on December 31, 20-2 under weighted average cost method.
Explanation of Solution
Weighted-average cost method: Under average cost method inventories are priced at the average of all available inventories. Average cost is the quotient of total cost of goods available for sale and total units available for sale.
Calculate the total amount of cost of goods sold and cost of ending inventory on December 31 under weighted average cost method:
Step 1: Calculate the weighted-average cost.
Step 2: Calculate the amount of ending inventory.
Step 3: Calculate the amount of cost of goods sold.
Therefore, the cost of sold and cost of ending inventory under weighted average cost method (Periodic inventory system) is $69,600 and $17,400.
2.
(a)
Calculate the cost of ending inventory on December 31 under FIFO method (Lower of cost or market).
Explanation of Solution
Lower-of-cost-or-market: The lower-of-cost-or-market (LCM) is a method which requires the reporting of the ending merchandise inventory in the financial statement of a company, at its current market value or at is historical cost price, whichever is less.
First-in-First-Out (FIFO): In First-in-First-Out method, the first purchased items are sold first. The value of the ending inventory consists of the recently purchased items.
Calculate the cost of ending inventory under FIFO (Lower of cost or market):
|
Particulars |
FIFO Cost (A) |
Market Cost (B) |
LCM Valuation (C = A or B ) Whichever is lesser |
| Ending inventory under FIFO | $22,750 | $21,600 | $21,600 |
Table (3)
Working note:
Calculate the market cost.
Therefore, the cost of ending inventory on December 31 under FIFO method (Lower of cost or market) is $21,600.
2.
(b)
Calculate the cost of ending inventory on December 31 under weighted average cost method (Lower of cost or market).
Explanation of Solution
Weighted-average cost method: Under average cost method inventories are priced at the average of all available inventories. Average cost is the quotient of total cost of goods available for sale and total units available for sale.
Calculate the cost of ending inventory under weighted average cost (Lower of cost or market):
|
Particulars |
Weighted Average Cost (A) |
Market Cost (B) |
LCM Valuation (C = A or B ) Whichever is lesser |
| Ending inventory under weighted average cost | $17,400 | $21,600 | $17,400 |
Table (4)
Working note:
Calculate the market cost.
Therefore, the cost of ending inventory on December 31 under weighted average cost method (Lower of cost or market) is $17,400.
3.
Estimate the cost of goods sold and ending inventory for the year December 31 uing the gross profit methods.
Explanation of Solution
Gross profit method:
- Gross profit method is used to determine the amount of estimated inventory lost or destroyed by theft, fire, or other hazards.
- The gross profit for the period is calculated from the preceding year, which is adjusted for any current period changes in the sales and cost price of the inventory.
- It estimates the value of inventory and cost of goods sold by avoiding the expenses occurred on physical count of inventory.
Estimate the cost of goods sold and ending inventory for the year December 31 uing the gross profit methods:
| Gross profit Method | ||
| Details | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Beginning inventory, January 1, 20-2 | 15,000 | |
| Add: Net cost of purchases, January 1, 20-2 – December 31, 20-2 | 72,000 | |
| Cost of goods available for sale | 87,000 | |
| Less: Estimated cost of goods sold. | ||
| Net sales | 100,000 | |
| Less: Estimated gross profit of 35% | (35,000) | |
| Estimated cost of goods sold | (65,000) | |
| Estimated cost of inventory at December 31, 20-2 | $22,000 | |
Table (5)
Working note:
Calculate the estimated gross profit.
The estimated gross profit is 35% of the net sales.
Therefore, the estimated cost of goods sold and ending inventory for the year December 31 uing the gross profit methods is $65,000 and $22,000.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Bundle: College Accounting, Chapters 1-15, Loose-Leaf Version, 22nd + LMS Integrated for CengageNOWv2, 1 term Printed Access Card
- Check my work The finance director for the City of Green Falls printed the General Fund Revenues and Appropriations Ledgers shown below for the year just ended. REVENUES LEDGER Ref. Account Description Est. Revenues Dr(Cr) Revenues Balance Cr(Dr) Dr(Cr) Estimated Revenues-Taxes-Real Property 102 Budget Authorization 6,452,400 6,452,400 103 Accrued Revenue 104 Previous Deferral 109 Deferral 6,455,000 345,000 (308,000) (2,600) (347,600) (39,600) 110 Budget Amendment 111 Closing entry 40,000 (6,492,400) 400 (6,492,000) 112 Closing entry (6,492,000) Estimated Revenues-Taxes-Sales 102 Budget Authorization. 103 Received in Cash 110 Budget Amendment 111 Closing Entry 112 Closing Entry 736,250 (25,000) (711,250) 710,600 736,250 25,650 650 (710,600) (710,600) e Q Search ་ PRE a 1 < 2/arrow_forwardPrecision Tools Inc. has the following information related to its direct materials usage: Standard Quantity: 120,000 units Actual Quantity: 140,000 units Standard Price: $2.50 per unit Actual Price: $2.80 per unit A. Calculate the materials price variance and state whether it is favorable or unfavorable. B. Calculate the materials usage variance and state whether it is favorable or unfavorable.arrow_forwardJob Costing: The warehouse supervisor at Alpha Electronics implements a strict cycle counting process where system accuracy must stay above 99%. Daily variances between 1-2% require immediate recount, while those exceeding 2% trigger supervisor review and investigation. During today's audit of electronic components, the system showed 2,400 items, but physical count revealed only 2,356 items present in the warehouse. The supervisor needs to determine the variance percentage before deciding on next steps.??arrow_forward
 College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning





