
Interpretation: The experimental procedure to test the hypothesis that solute blocking of solvent vaporization is not the reason that solutions have lower vapor pressures than the pure solvents is to be determined.
Concept introduction: According to Raoult’s law, the vapor pressure of a solution is equal to the product of the mole fraction and the vapor pressure of the pure solvent.
The expression of Raoult’s law is,
Answer to Problem 1DE
Solution: The interaction between solute and solvent and the number of solute particles are responsible for the lower vapor pressures of the solution than the pure solvents.
Explanation of Solution
According to Raoult’s law, the vapor pressure of a solution is equal to the product of the mole fraction and the vapor pressure of the pure solvent.
The expression of Raoult’s law is,
When a solute is added to a solution, the vapor pressure of the solution decreases because on addition of solute, the gap between the solvent molecules gets filled. Hence, on the surface of solution, the number of solvent molecule is less as compared to the pure solvent. This indicates that the number of solvent molecule enter into the gas phase is less and due to this there is a decrease in vapor pressure.
Using the Raoult’s law, the lowering of vapor pressure can be explained.
Assume two sealed containers, one is for pure solvent and other is for solution. The equilibrium stage arises when the number of molecules striking on the surface of the molecule becomes equal to the number of molecules going to the gas phase. On addition of solute, half of the surface of the solution is occupied by the solute and half of the surface is occupied by solvent molecules.
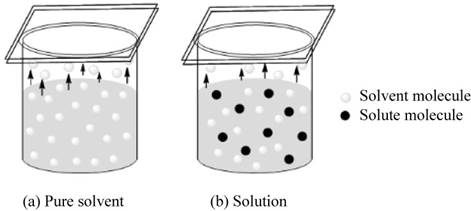
Figure 1
The vapor pressure of the solution depends upon the number of solvent molecule present on the surface of the solution. As the number of solute molecule increases, the number of solvent molecule present on the surface of solution decreases, now lesser number of solvent molecules is present to go in gas phase. Hence, the vapor pressure of the solution decreases.
The attraction between molecules of solvent with solute also plays an important role in lowering the vapor pressure. If there is a strong attraction between the solute and solvent, than the solvent molecule try to remain in the solution rather than escaping from it. Due to this, lowering of vapor pressure occurs because now there are less number of solvent molecule in vapor phase.
Another important factor is that, number of molecules present in the solution is not important rather than this number of solute particles present in the solution is important.
More the number of solute particles, low will be the vapor pressure.
The interaction between solute and solvent and the number of solute particles are responsible for the lower vapor pressures of the solution than the pure solvents.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
MAST F/ CHEM: THE CENTRAL SCI CODE ALON
- Predict the major products of this organic reaction: H OH 1. LiAlH4 2. H₂O ? Note: be sure you use dash and wedge bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. G C टेarrow_forwardFor each reaction below, decide if the first stable organic product that forms in solution will create a new C-C bond, and check the appropriate box. Next, for each reaction to which you answered "Yes" to in the table, draw this product in the drawing area below. Note for advanced students: for this problem, don't worry if you think this product will continue to react under the current conditions - just focus on the first stable product you expect to form in solution. NH2 CI MgCl ? Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? Yes No MgBr ? Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? Yes No G टेarrow_forwardFor each reaction below, decide if the first stable organic product that forms in solution will create a new CC bond, and check the appropriate box. Next, for each reaction to which you answered "Yes" to in the table, draw this product in the drawing area below. Note for advanced students: for this problem, don't worry if you think this product will continue to react under the current conditions - just focus on the first stable product you expect to form in solution. དྲ。 ✗MgBr ? O CI Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new C-C bond? Yes No • ? Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? Yes No × : ☐ Xarrow_forward
- Predict the major products of this organic reaction: OH NaBH4 H ? CH3OH Note: be sure you use dash and wedge bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ☐ : Sarrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction: 1. LIAIHA 2. H₂O ? Note: be sure you use dash and wedge bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X : ☐arrow_forwardFor each reaction below, decide if the first stable organic product that forms in solution will create a new C - C bond, and check the appropriate box. Next, for each reaction to which you answered "Yes" to in the table, draw this product in the drawing area below. Note for advanced students: for this problem, don't worry if you think this product will continue to react under the current conditions - just focus on the first stable product you expect to form in solution. NH2 tu ? ? OH Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? Yes No Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? Yes No C $ ©arrow_forward
- As the lead product manager at OrganometALEKS Industries, you are trying to decide if the following reaction will make a molecule with a new C-C bond as its major product: 1. MgCl ? 2. H₂O* If this reaction will work, draw the major organic product or products you would expect in the drawing area below. If there's more than one major product, you can draw them in any arrangement you like. Be sure you use wedge and dash bonds if necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. If the major products of this reaction won't have a new CC bond, just check the box under the drawing area and leave it blank. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. This reaction will not make a product with a new CC bond. G marrow_forwardIncluding activity coefficients, find [Hg22+] in saturated Hg2Br2 in 0.00100 M NH4 Ksp Hg2Br2 = 5.6×10-23.arrow_forwardgive example for the following(by equation) a. Converting a water insoluble compound to a soluble one. b. Diazotization reaction form diazonium salt c. coupling reaction of a diazonium salt d. indacator properties of MO e. Diazotization ( diazonium salt of bromobenzene)arrow_forward
- 2-Propanone and ethyllithium are mixed and subsequently acid hydrolyzed. Draw and name the structures of the products.arrow_forward(Methanesulfinyl)methane is reacted with NaH, and then with acetophenone. Draw and name the structures of the products.arrow_forward3-Oxo-butanenitrile and (E)-2-butenal are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol. Draw and name the structures of the products.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





