
Concept explainers
In Problem 18 the data show large and consistent differences between subjects. For example, subject A has the largest score in every treatment and subject D always has the smallest score. In the second stage of the ANOVA. the large individual differences get subtracted out of the denominator of the F-ratio. which results in a larger value for F.
The following data were created by using the same numbers that appeared in Problem 18. I1oever. we eliminated the consistent individual differences by scrambling the scores within each treatment.
| Treatment | |||||
| Subject | I | II | III | P | |
| A | 6 | 2 | 3 | 11 | |
| B | 5 | 1 | 5 | 11 | |
| C | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | |
| D | 1 | 8 | 2 | 11 | |
a. Use a repeated-measures ANOVA with
b. The data in problem 18 showed consistent differences between subjects and produced significant treatment effects. Explain how eliminating the consistent individual differences affected the results of this analysis compared with the results from Problem 18.
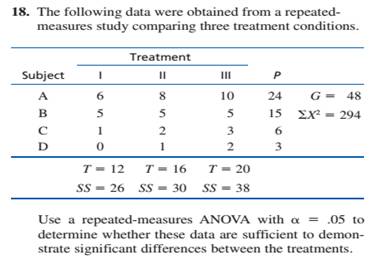
The following data were obtained from a repeated- measures study comparing three treatment conditions.
| Treatment | |||||
| Subject | I | II | III | P | |
| A | 6 | 8 | 10 | 24 | |
| B | 5 | 5 | 5 | 15 | |
| C | 1 | 2 | 3 | 6 | |
| D | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
Use a repeated-measures ANOVA with
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
Stats For Behav. Science W/mindtap
- I need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Statistics: Engineering Probabilities)arrow_forward310015 K Question 9, 5.2.28-T Part 1 of 4 HW Score: 85.96%, 49 of 57 points Points: 1 Save of 6 Based on a poll, among adults who regret getting tattoos, 28% say that they were too young when they got their tattoos. Assume that six adults who regret getting tattoos are randomly selected, and find the indicated probability. Complete parts (a) through (d) below. a. Find the probability that none of the selected adults say that they were too young to get tattoos. 0.0520 (Round to four decimal places as needed.) Clear all Final check Feb 7 12:47 US Oarrow_forwardhow could the bar graph have been organized differently to make it easier to compare opinion changes within political partiesarrow_forward
- 30. An individual who has automobile insurance from a certain company is randomly selected. Let Y be the num- ber of moving violations for which the individual was cited during the last 3 years. The pmf of Y isy | 1 2 4 8 16p(y) | .05 .10 .35 .40 .10 a.Compute E(Y).b. Suppose an individual with Y violations incurs a surcharge of $100Y^2. Calculate the expected amount of the surcharge.arrow_forward24. An insurance company offers its policyholders a num- ber of different premium payment options. For a ran- domly selected policyholder, let X = the number of months between successive payments. The cdf of X is as follows: F(x)=0.00 : x < 10.30 : 1≤x<30.40 : 3≤ x < 40.45 : 4≤ x <60.60 : 6≤ x < 121.00 : 12≤ x a. What is the pmf of X?b. Using just the cdf, compute P(3≤ X ≤6) and P(4≤ X).arrow_forward59. At a certain gas station, 40% of the customers use regular gas (A1), 35% use plus gas (A2), and 25% use premium (A3). Of those customers using regular gas, only 30% fill their tanks (event B). Of those customers using plus, 60% fill their tanks, whereas of those using premium, 50% fill their tanks.a. What is the probability that the next customer will request plus gas and fill the tank (A2 B)?b. What is the probability that the next customer fills the tank?c. If the next customer fills the tank, what is the probability that regular gas is requested? Plus? Premium?arrow_forward
- 38. Possible values of X, the number of components in a system submitted for repair that must be replaced, are 1, 2, 3, and 4 with corresponding probabilities .15, .35, .35, and .15, respectively. a. Calculate E(X) and then E(5 - X).b. Would the repair facility be better off charging a flat fee of $75 or else the amount $[150/(5 - X)]? [Note: It is not generally true that E(c/Y) = c/E(Y).]arrow_forward74. The proportions of blood phenotypes in the U.S. popula- tion are as follows:A B AB O .40 .11 .04 .45 Assuming that the phenotypes of two randomly selected individuals are independent of one another, what is the probability that both phenotypes are O? What is the probability that the phenotypes of two randomly selected individuals match?arrow_forward53. A certain shop repairs both audio and video compo- nents. Let A denote the event that the next component brought in for repair is an audio component, and let B be the event that the next component is a compact disc player (so the event B is contained in A). Suppose that P(A) = .6 and P(B) = .05. What is P(BA)?arrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt

