1 Introduction, Measurement, Estimating 2 Describing Motion: Kinematics In One Dimension 3 Kinematics In Two Or Three Dimensions; Vectors 4 Dynamics: Newton's Laws Of Motion 5 Using Newton's Laws: Friction, Circular Motion, Drag Forces 6 Gravitation And Newton's Synthesis 7 Work And Energy 8 Conservation Of Energy 9 Linear Momentum 10 Rotationalmotion 11 Angular Momentum; General Rotation 12 Static Equilibrium; Elasticity And Fracture 13 Fluids 14 Oscillations 15 Wave Motion 16 Sound 17 Temperature, Thermal Expansion And The Ideal Gas Law 18 Kinetic Theory Of Gases 19 Heat And The First Law Of Thermodynamics 20 Second Law Of Thermodynamics 21 Electric Charge And Electric Field 22 Gauss's Law 23 Electric Potential 24 Capacitance, Dielectrics, Electric Energy Storage 25 Electric Currents And Resistance 26 Dc Circuits 27 Magnetism 28 Sources Of Magnetic Field 29 Electromagnetic Induction And Faraday's Law 30 Inductance, Electromagnetic Oscillations, And Ac Circuits 31 Maxwell's Equation And Electromagnetic Waves 32 Light: Reflection And Refraction 33 Lenses And Optical Instruments 34 The Wave Nature Of Light: Interference 35 Diffraction And Polarization 36 Special Theory Of Relativity 37 Early Quantum Theory And Models Of The Atom 38 Quantum Mechanics 39 Quantum Mechanics Of Atoms 40 Molecules And Solids 41 Nuclear Physics And Radioactivity 42 Nuclear Energy; Effects And Uses Of Radiation 43 Elementary Particles 44 Astrophysics And Cosmology expand_more
13.1 Phases Of Matter 340 13.2 Density And Specific Gravity 13.3 Pressure In Fluids 13.4 Atmospheric Pressure And Gauge Pressure 13.5 Pascal’s Principle 13.6 Measurement Of Pressure; Gauges And The Barometer 13.7 Buoyancy And Archimedes’ Principle 13.8 Fluids In Motion; Flow Rate And The Equation Of Continuity 13.9 Bernoulli’s Equation 13.10 Applications Of Bernoulli’s Principle: Torricelli, Airplanes, Baseballs, Tia 13.11 Viscosity 13.12 Flow In Tubes: Poiseuille’s Equation, Blood Flow 13.13 Surface Tension And Capillarity 13.14 Pumps, And The Heart Chapter Questions expand_more
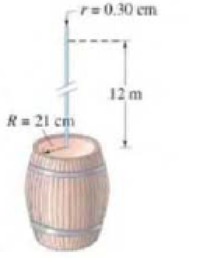
Problem 1Q: If one material has a higher density than another, must the molecules of the first be heavier than... Problem 2Q: Airplane travelers sometimes note that their cosmetics bottles and other containers have leaked... Problem 3Q: The three containers in Fig. 1343 are filled with water to the same height and have the same surface... Problem 4Q: Consider what happens when you push both a pin and theblunt end of a pen against your skin with the... Problem 5Q: A small amount of water is boiled in a 1-gallon metal can.The can is removed from the heat and the... Problem 6Q Problem 7Q: An ice cube floats in a glass of water filled to the brim.What can you say about the density of ice?... Problem 8Q: Will an ice cube float in a glass of alcohol? Why or why not? Problem 9Q: A submerged can of Coke will sink, but a can of Diet Coke will float. (Try it!) Explain. Problem 10Q: Why dont ships made of iron sink? Problem 11Q: Explain how the tube in Fig. 1344, known as a siphon, can transfer liquid from one container to a... Problem 12Q: A barge filled high with sand approaches a low bridge overthe river and cannot quite pass under it.... Problem 13Q: Explain why helium weather balloons, which are used tomeasure atmospheric conditions at high... Problem 14Q: A row boat floats in a swimming pool, and the levelof the water at the edge of the pool is marked.... Problem 15Q: Will an empty balloon have precisely the same apparentweight on a scale as a balloon filled with... Problem 16Q: Why do you float higher in salt water than in fresh water? Problem 17Q: If you dangle two pieces of paper vertically, a few inchesapart (Fig. 1345), and blow between them,... Problem 18Q: Why does the stream of water from a faucet becomenarrower as it falls (Fig. 1346)? FIGURE 13-46... Problem 19Q Problem 20Q: A tall Styrofoam cup is filled with water. Two holes arepunched in the cup near the bottom, and... Problem 21Q: Why do airplanes normally lake off into the wind? Problem 22Q: Two ships moving in parallel paths close to one another riskcolliding. Why? Problem 23Q Problem 24Q Problem 1P: (I) The approximate volume of the granite monolith known as E1 Capitan in Yosemite National Park... Problem 2P: (I) What is the approximate mass of air in a living room5.6 m 3.8 m 2.8 m? Problem 3P: (I) If you tried to smuggle gold bricks by filling your backpack, whose dimensions are 56 cm 28 cm ... Problem 4P: (I) State your mass and then estimate your volume. [Hint:Because you can swim on or just under the... Problem 5P: (II) A bottle has a mass of 35.00g when empty and 98.44gwhen filled with water. When filled with... Problem 6P: (II) If 5.0L of antifreeze solution (specific gravity = 0.80)is added to 4.0 L of water to make a... Problem 7P Problem 8P: (I) Estimate the pressure needed to raise a column of waterto the same height as a 35-m-tall oak... Problem 9P: (I) Estimate the pressure exerted on a floor by (a) one pointedchair leg (66 kg on all four legs) of... Problem 10P: (I) What is the difference in blood pressure (mm-Hg)between the top of the head and bottom of the... Problem 11P: (II) How high would the level be in an alcohol barometer atnormal atmospheric pressure? Problem 12P: (II) In a movie, Tarzan evades his captors by hiding underwater for many minutes while breathing... Problem 13P: (II) The maximum gauge pressure in a hydraulic lift is17.0 atm. What is the largest-size vehicle... Problem 14P: (II) The gauge pressure in each of the four tires of an automobile is 240 kPa. If each tire has a... Problem 15P: (II) (a) Determine the total force and the absolute pressureon the bottom of a swimming pool 28.0 m... Problem 16P: (II) A house at the bottom of a hill is fed by a full tank ofwater 5.0 m deep and connected to the... Problem 17P: (II) Water anti then oil (which dont mix) are poured into a U-shaped tube, open at both ends. They... Problem 18P: (II) In working out his principle, Pascal showed dramaticallyhow force can be multiplied with fluid... Problem 19P: (II) What is the normal pressure of the atmosphere at thesummit of Mt. Everest, 8850 m above sea... Problem 20P: (II) A hydraulic press for compacting powdered samples hasa large cylinder which is 10.0 cm in... Problem 21P: (II) An open-tube mercury manometer is used to measure the pressure in an oxygen tank. When the... Problem 22P: (III) A beaker of liquid accelerates from rest, on a horizontal surface, with acceleration a to the... Problem 23P: (III) Water stands at a height h behind a vertical dam of uniform width b. (a) Use integration to... Problem 24P: (III) Estimate the density of the water 5.4 km deep in the sea. (See Table 121 and Section 124... Problem 25P: (III) A cylindrical bucket of liquid (density ) is rotated about its symmetry axis, which is... Problem 26P: (I) What fraction of a piece of iron will he submerged when be floats in mercury? Problem 27P: (I) A geologist finds that a Moon rock whose mass is 9.28 kg has an apparent mass of 6.18 kg when... Problem 28P: (II) A crane lifts the 16,000-kg steel hull of a sunken ship out of the water. Determine (a) the... Problem 29P: (II) A spherical balloon has a radius of 7.35 m and is filled with helium. How large a cargo can it... Problem 30P: (II) A 74-kg person has an apparent mass of 54 kg (because of buoyancy) when standing in water that... Problem 31P: (II) What is the likely identity of a metal (see Table 131) if a sample has a mass of 63.5 g when... Problem 32P: (II) Calculate the true mass (in vacuum) of a piece of aluminum whose apparent mass is 3.0000 kg... Problem 33P Problem 34P: (II) A scuba diver and her gear displace a volume of 65.0 L and have a total mass of 68.0 kg. (a)... Problem 35P: (II) The specific gravity of ice is 0.917, whereas that of seawater is 1.025. What percent of an... Problem 36P: (II) Archimedes principle can be used not only to determine the specific gravity of a solid using a... Problem 37P: (II) (a) Show that the buoyant force FB on a partially submerged object such as a ship acts at the... Problem 38P: (II) A cube of side length 10.0 cm and made of unknown material floats at the surface between water... Problem 39P: (II) How many helium-filled balloons would it take to lift a person? Assume the person has a mass of... Problem 40P Problem 41P: (III) If an object floats in water, its density can be determined by tying a sinker to it so that... Problem 42P: (III) A 3.25-kg piece of wood (SG = 0.50) floats on water. What minimum mass of lead, hung from the... Problem 43P: (I) A 15-cm-radius air duct is used to replenish the air of aroom 8.2 m 5.0 m 3.5 m every 12 min.... Problem 44P Problem 45P: (I) How fast does water flow from a hole at the bottom of a very wide, 5.3-m-deep storage tank... Problem 46P: (II) A fish tank has dimensions 36 cm wide by 1.0 m long by0.60 m high. If the filter should process... Problem 47P: (II) What gauge pressure in the water mains is necessary if afirehose is to spray water to a height... Problem 48P Problem 49P: (II) A 180-km/h wind blowing over the flat roof of a housecauses the roof to lift off the house. If... Problem 50P: (II) A 6.0-cm-diameter horizontal pipe gradually narrows to4.5 cm. When water flows through this... Problem 51P: (II) Estimate the air pressure inside a category 5 hurricane,where the wind speed is 300 km/h (Fig.... Problem 52P: (II) What is the lift (in newtons) due to Bernoullis principle ona wing of area 88 m2 if the air... Problem 53P: (II) Show that the power needed to drive a fluid through apipe with uniform cross-section is equal... Problem 54P: (II) Water at a gauge pressure of 3.8 atm at street level flows into an office building at a speed... Problem 55P: (II) In Fig. 1355, take into account the speed of the top surface of the tank and show that the... Problem 56P: (II) Suppose the top surface of the vessel in Fig. 1355 is subjected to an external gauge pressure... Problem 57P: (II) You are watering your lawn with a hose when you put your finger over the hose opening to... Problem 58P: (III) Suppose the opening in the tank of Fig. 1355 is a height h1 above the base and the liquid... Problem 59P Problem 60P: (III) (a) Show that the flow speed measured by a venturi meter (see Fig. 1332) is given by the... Problem 61P Problem 62P: (III) A fire hose exerts a force on the person holding it. This is because the water accelerates as... Problem 63P: (II) A viscometer consists of two concentric cylinders. 10.20 cm and 10.60 cm in diameter. A liquid... Problem 64P Problem 65P: (I) Engine oil (assume SAE 10, Table 133) passes througha fine 1.80-mm-diameler tube that is 8.6 cm... Problem 66P Problem 67P: (II) What diameter must a 15.5-m-long air duct have if the ventilation and heating system is to... Problem 68P: (II) What must be the pressure difference between the two ends of a 1.9-km section of pipe, 29 cm in... Problem 69P: (II) Poiseuilles equation does not hold if the flow velocity is high enough that turbulence sets in.... Problem 70P Problem 71P: (III) A patient is to be given a blood transfusion. The blood is to flow through a tube from a... Problem 72P: (I) If the force F needed to move the wire in Fig. 1335 is 3.4 103 , calculate the surface tension ... Problem 73P: (I) Calculate the force needed to move the wire in Fig. 1335 if it is immersed in a soapy solution... Problem 74P: (II) The surface tension of a liquid can be determined by measuring the force F needed to just lift... Problem 75P: (III) Estimate the diameter of a steel needle that can just float on water due to surface tension. Problem 76P: (III) Show that inside a soap bubble, there must be a pressure P in excess of that outside equal to... Problem 77P: (III) A common effect of surface tension is the ability of a liquid to rise up a narrow tube due to... Problem 78GP: A 2.8-N force is applied to the plunger of a hypodermic needle. If the diameter of the plunger is... Problem 79GP: Intravenous infusions are often made under gravity, as shown in Fig. 1356. Assuming the fluid has a... Problem 80GP: A beaker of water rests on an electronic balance that reads 998.0 g. A 2.6-cm-diameter solid copper... Problem 81GP: Estimate the difference in air pressure between the top and the bottom of the Empire State building... Problem 82GP: A hydraulic lift is used to jack a 920-kg car 42 cm off the floor. The diameter of the output piston... Problem 83GP: When you ascend or descend a great deal when driving in a car, your ears pop, which means that the... Problem 84GP: Giraffes are a wonder of cardiovascular engineering. Calculate the difference in pressure (in... Problem 85GP: Suppose a person can reduce the pressure in his lungs to 75 mm-Hg gauge pressure. How high can water... Problem 86GP: Airlines are allowed to maintain a minimum air pressurewithin the passenger cabin equivalent to that... Problem 87GP: A simple model (Fig. 13-57) considers a continent as ablock (density 2800 kg/m3) floating in the... Problem 88GP: A ship, carrying fresh water to a desert island in theCaribbean, has a horizontal cross-sectional... Problem 89GP: During ascent, and especially during descent, volume changesof trapped air in the middle ear can... Problem 90GP: A raft is made of 12 logs lashed together. Each is 45 cm indiameter and has a length of 6.1 m. How... Problem 91GP: Estimate the total mass of the Earths atmosphere, usingthe known value of atmospheric pressure at... Problem 92GP Problem 93GP: Four lawn sprinkler heads are fed by a 1.9-cm-diameterpipe. The water comes out of the heads at an... Problem 94GP: A bucket of water is accelerated upward at 1.8 g. What isthe buoyant force on a 3.0-kg granite rock... Problem 95GP: The stream of water from a faucet decreases in diameter as itfalls (Fig. 13-58). Derive an equation... Problem 96GP: You need to siphon water from a clogged sink. The sink has an area of 0.38 m2 and is filled to a... Problem 97GP: An airplane has a mass of 1.7 106 kg, and the air flows past the lower surface of the wings at 95... Problem 98GP: A drinking fountain shoots water about 14 cm up in the air from a nozzle of diameter 0.60 cm. The... Problem 99GP: A hurricane-force wind of 200 km/h blows across the face of a storefront window. Estimate the force... Problem 100GP: Blood from an animal is placed in a bottle 1.30 m above a 3.8-cm-long needle, of inside diameter... Problem 101GP Problem 102GP Problem 103GP: A two-component model used to determine percent body fat in a human body assumes that a fraction f(... Problem 104GP: (III) Air pressure decreases with altitude. The following data show the air pressure at different... format_list_bulleted


 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning




