
Concept explainers
Find the amount of coal (in kg) required for generating for each year.
Answer to Problem 17P
The amount of coal (in kg) required for generating electricity for each year are calculated and tabulated in Table 1.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Refer to problem 13-17 accompanying table in the textbook, the average efficiency of the power plants is 35%.
The heating value of the coal is
Formula used:
Formula to calculate the power plant efficiency is,
Rearrange the equation,
Convert kWh to MJ,
Formula to calculate the amount of coal required for generating one year is,
Calculation:
Find the energy input from the fuel in each year:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Now convert all the values from kWh to MJ:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
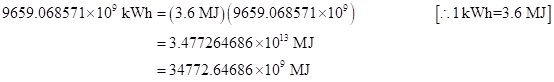
Now find the amount of coal required in every year:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the energy input for all years for Coal, in kWh and MJ along with coal required to produce 35% of efficiency is shown in Table 1 (with approximately rounded values).
Table 1
| Energy Produced (10^9 kWh) | Energy(considering efficiency) 109 kWh | Energy (considering efficiency) 109 MJ | Amount of coal needed in kg |
| 1161.562 | 3318.748571 | 11947.49486 | 1.59E+12 |
| 1594.011 | 4554.317143 | 16395.54171 | 2.19E+12 |
| 1966.265 | 5617.9 | 20224.44 | 2.70E+12 |
| 2040.913 | 5831.18 | 20992.248 | 2.80E+12 |
| 2217.555 | 6335.871429 | 22809.13714 | 3.04E+12 |
| 2504.786 | 7156.531429 | 25763.51314 | 3.44E+12 |
| 3380.674 | 9569.068571 | 34772.64686 | 4.64E+12 |
Conclusion:
Hence, the amount of coal (in kg) required for generating electricity for each year has been calculated.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Engineering Fundamentals: An Introduction to Engineering
- Using a relevant image such as a 3D architectural rendering of a warehouse landscape in Edmond.arrow_forwardA simple beam has a span of 10 m and supports a total uniformly distributed load of 12 kN/m. Properties of W 480×86: Property Value A = 10800 mm² bf = 180 mm tf = 15 mm Ix = 383.13 × 10⁶ mm⁴ tw = 12 mm d = 480 mm Questions: Calculate the maximum shear in the beam in kN. Calculate the average shear stress in the beam in MPa. Calculate the maximum shear stress in the beam in MPa. Given the properties of the wide flange: Property Value d = 530 mm bf = 210 mm tw = 18 mm tf = 16 mm Question: Compute the value of rₜ, defined as the radius of gyration of the compression flange plus 1/3 of the compression web area about the y-axis.arrow_forwardGiven an existing two-story steel structure with interior columns spaced as shown in Fig.2. The columns are spaced at 18 ft in the North-South direction and at 30 ft in the East-West direction. An interior lower-story column is to be removed by adding newsteel girder as shown in Fig. 4. The floor dead loads and the roof dead loads are 70 psfand 18 psf respectively. The floor live loads and the roof live loads are 50 psf and20 psf respectively. All existing steel materials are ASTM A36 steel (Fy=36 ksi). Newgirder is ASTM A992 steel (Fy= 50 ksi). All columns are W8x31. Use the LRFD Method.Assumptions:1- The loads given include column and beam self weights.2- Existing beam and new girder are simply supported at both ends.3- New girder top flange is laterally braced at mid span and at girder ends only.4- Columns are continuous from foundation to roof and are prevented from sway atfloor level and at roof level in both directions.5- Columns are pin supported at foundation, at floor level,…arrow_forward
- Determine the bending moment at support A for the beam shown using the slope-deflection method. Use the sign convention defined in the chapter. a. 232.9 k-ft b. -182.1 k-ft c. 182.1 k-ft d. -232.9 k-ftarrow_forwardWhat is the shear and normal stresses of Point J and Point K?arrow_forwardWhat are the states of stress (magnitude and tension/compression of the normal stresses and shear stress) at Point J and Point K?arrow_forward
- Consider, M people (aka pax) who want to travel by car from O to D. They all start working at D at Q (e.g., Q-8am). If a person departs at time t, assume the time needed to go from O to D is given by c(t)=A+Bx(t), where x(t) is the flow of people departing at time t [car/unit of time]. In addition, a is the penalty for being early at work (E(t) is how early the person arrived when departing at time t), and ẞ is the penalty for being late at work (L(t) is how late the person arrived when departing at time t). Assume 0 < a < 1 < ß. Further assume the departure time choice problem under the equilibrium conditions. Prove that the arrival time of people who depart when most of the M people start their trips is equal to Q.arrow_forwarda. A b. A 3. Sketch normal depth, critical depth and the water surface profile. Assume at A and B the water is flowing at normal depth. Label and Identify all curves (i.e., M1, S2, etc.) Yn > Ye Уп Ye Уп> Ус yarrow_forward2. Design a trapezoidal ditch to carry Q = 1000 cfs. The ditch will be a lined channel, gravel bottom with sides shown below on a slope of S = 0.009. The side slopes of the 20-ft wide ditch will be 1 vertical to 3 horizontal. a) Determine the normal depth of flow (yn) using the Normal value for Manning's n. b) If freeboard requirements are 25% of the normal depth, how deep should the ditch be constructed? c) Classify the slope. T b Уп Z 1 Yn + FBarrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Engineering Fundamentals: An Introduction to Engi...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305084766Author:Saeed MoaveniPublisher:Cengage Learning
Engineering Fundamentals: An Introduction to Engi...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305084766Author:Saeed MoaveniPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Sustainable EnergyCivil EngineeringISBN:9781133108689Author:Richard A. DunlapPublisher:Cengage Learning
Sustainable EnergyCivil EngineeringISBN:9781133108689Author:Richard A. DunlapPublisher:Cengage Learning


