
To label:
To label the diagram of the antibody.
Introduction:
The structure of the antibody resembles the alphabet Y and consists of 4 proteins (2 light chains and 2 heavy chains).
Pictorial representation:
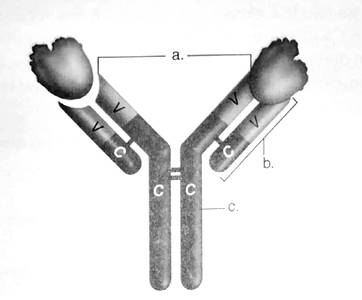
Figure: The structure of an antibody molecule.
The correct answers are:
- Antigen binding sites
- Light chain
- Heavy chain
V stands for the variable region
C stands for the constant region
Explanation for the answers:
- Antigen binding site − These are the sites on the amino-terminal end of both light and heavy chain. It provides a site of attachment for the antigen.
- Light chain − There is 2 identical light chains consisting of polypeptides. They are bound to the heavy chain via disulfide bonds and non-covalent interactions.
- Heavy chain − There are 5 types of heavy chains (accordingly antibodies are named) and attached to each other via the disulfide bonds.
V stands for variable region. The amino-terminal end of both heavy and light chain of about 100-110 amino acids vary considerably among antibodies and hence are called as variable region.
C stands for the constant region. The carboxy-terminalend of both light and heavy chain shows similarity among antibodies and hence is considered as constant regions.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
CUSTOMIZED LAB MANUAL FOR BIOLOGY 1407
- Don't copy the other answerarrow_forward4. Aerobic respiration of 5 mM acetate solution. Assume no other carbon source and that acetate is equivalent to acetyl-CoA. NADH FADH2 OP ATP SLP ATP Total ATP Show your work using dimensional analysis here: 5. Aerobic respiration of 2 mM alpha-ketoglutaric acid solution. Assume no other carbon source. NADH FADH2 OP ATP Show your work using dimensional analysis here: SLP ATP Total ATParrow_forwardBiology You’re going to analyze 5 ul of your PCR product(out of 50 ul) on the gel. How much of 6X DNAloading buffer (dye) are you going to mix with yourPCR product to make final 1X concentration ofloading buffer in the PCR product-loading buffermixture?arrow_forward
- Write the assignment on the title "GYMNOSPERMS" focus on the explanation of its important families, characters and reproduction.arrow_forwardAwnser these Discussion Questions Answer these discussion questions and submit them as part of your lab report. Part A: The Effect of Temperature on Enzyme Activity Graph the volume of oxygen produced against the temperature of the solution. How is the oxygen production in 30 seconds related to the rate of the reaction? At what temperature is the rate of reaction the highest? Lowest? Explain. Why might the enzyme activity decrease at very high temperatures? Why might a high fever be dangerous to humans? What is the optimal temperature for enzymes in the human body? Part B: The Effect of pH on Enzyme Activity Graph the volume of oxygen produced against the pH of the solution. At what pH is the rate of reaction the highest? Lowest? Explain. Why does changing the pH affect the enzyme activity? Research the enzyme catalase. What is its function in the human body? What is the optimal pH for the following enzymes found in the human body? Explain. (catalase, lipase (in your stomach),…arrow_forwardAnwser these Discussion Questions: Part One Why were the plants kept in the dark prior to the experiment? Why is this important? Why is it important to boil the leaf? Explain why it was necessary to use boiling alcohol? What is the purpose of the iodine? Part Two What was the purpose of keeping the leaf in the dark and then covering it with a cardboard cut-out? What conclusions can you draw from this part of the lab? Part Three 7. In this experiment what was the purpose of adding the soda lime? 8. Why was a sealed bag placed around each plant? 9. What happened in the control plants? 10. What was the result on photosynthesis? Part Four 11. Why was a variegated leaf used in this experiment? !2. What conclusions can you draw about starch production in a variegated leaf?arrow_forward
- How did the color differences between the two bacterial species you used in this experiment help you determine if the streak plate method you performed was successful?arrow_forwardseries of two-point crosses were carried out among six loci (a, b, c, d, e and f), producing the following recombination frequencies. According to the data below, the genes can be placed into how many different linkage groups? Loci a and b Percent Recombination 50 a and c 14 a and d 10 a and e 50 a and f 50 b and c 50 b and d 50 b and e 35 b and f 20 c and d 5 c and e 50 c and f 50 d and e 50 d and f 50 18 e and f Selected Answer: n6 Draw genetic maps for the linkage groups for the data in question #5. Please use the format given below to indicate the genetic distances. Z e.g. Linkage group 1=P____5 mu__Q____12 mu R 38 mu 5 Linkage group 2-X_____3 mu__Y_4 mu sanightarrow_forwardWhat settings would being able to isolate individual bacteria colonies from a mixed bacterial culture be useful?arrow_forward
- Can I get a handwritten answer please. I'm having a hard time understanding this process. Thanksarrow_forwardSay you get AATTGGCAATTGGCAATTGGCAATTGGCAATTGGCAATTGGCAATTGGC 3ʹ and it is cleaved with Mspl restriction enzyme - how do I find how many fragments?arrow_forwardWhat is amplification bias?arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





