
Concept explainers
To explain: The following,
'a'If isomaltose is a mono-, di-, or polysaccharide?
Answer to Problem 13.55UTC
Solution:
'a'Isomaltose is a disaccharide.
Given: Structure of isomaltose in Haworth projection
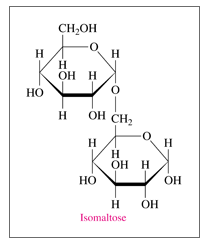
a.
Explanation of Solution
Isomaltose is a disaccharide as it contains two monosaccharides i.e.sugar units which are obtained after hydrolysis.
Therefore isomaltose is a disaccharide
b. The monosaccharides in isomaltose are two glucose units.
c. There is C1-C6 (a-a) O-glycosidic link in isomaltose.
Glycosidic link is the bond which connects two monosaccharides through anomeric carbon (a carbon which is coming from carbonyl group and attached with two oxygen atoms). In case of isomaltose, the anomeric carbon i.e. hemiacetal is linked with another sugar moiety through O atom. Thus this is a C1-C6 (a-a) O-glycosidic link.
Therefore, the monosaccharides in isomaltose are two glucose units and there is C1-C6 O-glycosidic link.
d. The given structure is an a-isomer of isomaltose.
As the OH group in the anomeric carbon is downward i.e. below the plane, so it is a-anomer (a-isomer of isomaltose).
Therefore the given structure is an a-isomer of isomaltose
e. Isomaltose is a reducing sugar
Isomaltose is a reducing sugar as it is capable of reducing Tollen’s reagent and Fehling solution. All the monosaccharides (aldoses) are reducing sugars along with some disaccharides. A disaccharide (as for example isomaltose) which has one anomeric carbon involved in glycosidic linkage but other anomeric carbon is free then it is able to reduce Tollen’s and Fehling solution.
Thus, isomaltose though a disaccharide is a reducing sugar.
- Isomaltose is a disaccharide.
- The monosaccharides in isomaltose are glucose units.
- The glycosidic link in isomaltose is C1-C6 (a-a) O-glycosidic link.
- The given structure is an a-isomer of isomaltose
- Isomaltose is a reducing sugar.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Study Guide And Selected Solutions Manual For Chemistry Format: Paperback
- V Biological Macromolecules Drawing the Haworth projection of an aldose from its Fischer projection Draw a Haworth projection of a common cyclic form of this monosaccharide: H C=O HO H HO H H OH CH₂OH Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Xarrow_forwardComplete the mechanismarrow_forwardComplete the mechanismarrow_forward
- 8 00 6 = 10 10 Decide whether each of the molecules in the table below is stable, in the exact form in which it is drawn, at pH = 11. If you decide at least one molecule is not stable, then redraw one of the unstable molecules in its stable form below the table. (If more than unstable, you can pick any of them to redraw.) Check OH stable HO stable Ounstable unstable O OH stable unstable OH 80 F6 F5 stable Ounstable X Save For Later Sub 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy C ཀྭ་ A F7 매 F8 F9 4 F10arrow_forwardJust try completing it and it should be straightforward according to the professor and TAs.arrow_forwardThe grading is not on correctness, so if you can just get to the correct answers without perfectionism that would be great. They care about the steps and reasoning and that you did something. I asked for an extension, but was denied the extension.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





