
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The complete reaction between
Concept introduction:
A
Answer to Problem 13.52E
The completed reaction between
Explanation of Solution
The incomplete reaction is shown below.
The thiols react with heavy metal ions such as
Therefore, the completed reaction between
The completed reaction between
(b)
Interpretation:
The complete reaction between
Concept introduction:
A chemical reaction is a process in which rearrangement of atoms or ions takes place between two reacting species. A balanced chemical equation represents an equation in which all the reactants and products are written with their stoichiometric coefficients. The number of atoms of an element on both sides of the equation is equal.
Answer to Problem 13.52E
The completed reaction between
Explanation of Solution
The incomplete reaction is shown below.
Two molecules of thiol undergo an oxidation reaction with a nascent oxygen atom. The thiol molecules react with nascent oxygen atom to form a disulfide compound. Therefore, the completed reaction between
The completed reaction between
(c)
Interpretation:
The complete reaction between given disulfide and nascent hydrogen atoms is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
A chemical reaction is a process in which rearrangement of atoms or ions takes place between two reacting species. A balanced chemical equation represents an equation in which all the reactants and products are written with their stoichiometric coefficients. The number of atoms of an element on both sides of the equation is equal.
Answer to Problem 13.52E
The complete reaction between given disulfide and nascent hydrogen atoms is shown below.
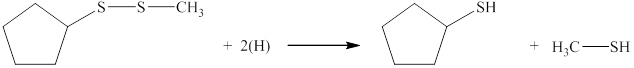
Explanation of Solution
The incomplete reaction is shown below.
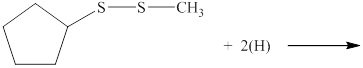
Figure 1
A disulfide compound undergoes reduction reaction with nascent hydrogen atoms to form two thiol molecules.
Therefore, the complete reaction between given disulfide and nascent hydrogen atom is shown below.
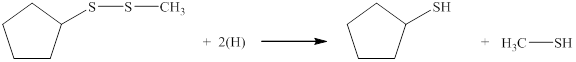
Figure 2
The complete reaction between given disulfide and nascent hydrogen atom is shown in Figure 2.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Bundle: Chemistry For Today: General, Organic, And Biochemistry, 9th + Owlv2 With Mindtap Reader, 1 Term (6 Months) Printed Access Card
- Synthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- If possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forwardSynthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forward
- We mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardQuestion 3 (4 points), Draw a full arrow-pushing mechanism for the following reaction Please draw all structures clearly. Note that this intramolecular cyclization is analogous to the mechanism for halohydrin formation. COH Br + HBr Brarrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if 2,2-dimethylpropanal and acetaldehyde are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning  Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning





