
Find the Rankine active force
Answer to Problem 13.18P
The Rankine active force
The location
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The height (H) of the retaining wall is 8.0 m.
The depth
The unit weight
The sand friction angle
The saturated sand friction angle
The cohesion
The surcharge pressure (q) is
The depth
The saturated unit weight
The cohesion
Calculation:
Determine the active earth pressure coefficient
Substitute
Determine the total stress
Substitute
Determine the pore water pressure at 0 m depth using the relation.
Here,
Take the unit weight of the water as
Substitute
Determine the effective active earth pressure
Substitute
Determine the total stress
Substitute
Determine the pore water pressure at 3.0 m depth using the relation.
Substitute
Determine the effective active earth pressure
Substitute
Determine the total stress
Substitute
Determine the pore water pressure at 8 m depth using the relation.
Substitute
Determine the effective active earth pressure
Substitute
Show the variation of effective active earth pressure and pore water pressure for the respective depth as in Figure 1.
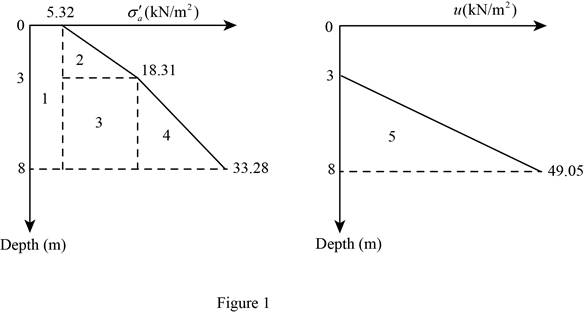
Refer Figure 1.
Determine the active earth pressure per unit length for area 1 using the relation.
Here, b is the width and h is the depth.
Substitute
Determine the active earth pressure per unit length for area 2 using the relation.
Substitute
Determine the active earth pressure per unit length for area 3 using the relation.
Substitute 5.0 m for b and
Determine the active earth pressure per unit length for area 4 using the relation.
Substitute 5.0 m for b and
Determine the active earth pressure per unit length for area 5 using the relation.
Substitute 5.0 m for b and
Determine the Rankine active force
Substitute
Thus, the Rankine active force
Determine the location
Substitute
Thus, the location of the resultant force is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
PRINCIPLES OF GEOTECH.ENGINEERING >LL+M
- Problem 2 (Using force method) Determine the force in each member of the truss. E = 29000 ksi 3 k 1.5 in² 4 ft 1.5 in² 1.5 in² 2 in² 6 k D 1.5 in² 3 ft 2 in² Barrow_forwardThe single degree of freedom (SDOF) system that you studied under free vibration in Assignment #3 - Laboratory Component has been subjected to a strong ground motion. The acceleration at the base (excitation) and the acceleration at the roof (response) of the SDOF system was recorded with sampling rate 50 Hz (50 samples per second, or dt= 0.02 seconds). The file ElCentro.txt includes the two columns of acceleration data. The first column lists the acceleration at the base of the SDOF system. The second column lists the acceleration at the roof of the SDOF system. (a) Plot the time histories of the recorded accelerations at the base and at the roof of the SDOF system. (b) Compute the acceleration, velocity and displacement time histories of the roof of the SDOF system subjected to the recorded base acceleration using the Central Difference method. Plot the accel- eration, velocity and displacement time histories. Plot the restoring force, the damping force, and the inertia force time…arrow_forwardPlease explain step by step and show formulaarrow_forward
- Please explain step by step and show formulaarrow_forwardFor an reinforced concrete two-way slab shown in figure under the load (P). (the slab continuous over all edges - all sides are fixed), Determine (By using yield line theory): A- Draw the Yield line Pattern B- Determine the moment m 3BAT C- Find The required flexural steel to resist the loads causing the slab to collapse if P = 200 KN, fc = 28 MPa, fy = 420 MPa d = 120 mm. Use 10 mm bars. (Pmin = 0.002) 6m 8m >2m->) 3marrow_forward3BAT For an reinforced concrete two-way slab shown in figure under the load (P). (the slab continuous over all edges - all sides are fixed), Determine (By using yield line theory): A- Draw the Yield line Pattern B- Determine the moment m KN, fc Please don't solve in Al anco if P = 200 6m 8m 2m-)) 3marrow_forward
- Please explain step by step and show formulaarrow_forwardPlease explain step by step and show formulaarrow_forward4-You are making a bookshelf (shown below) to carry books that range from 8½" to 11" in height and would take up 29" of space along the length. The material is wood having a Young's Modulus of 3.66 ksi, thickness of 3/8", and width of 12". You want to find the maximum vertical deflection of the bookshelf. The vertical deflection of the shelf is given by: -0.67665 x10 8x4 -0.26689x105 x3 +0.12748x10³ x² -0.018057=0 x Bookshelf Booksarrow_forward
- The difference in water surface levels in two tanks, which are connected by three pipes in series of lengths 300 m, 170 m, and 210 m, having diameters 300 mm, 200 mm, and 400 mm, respectively, is 12 m. Determine the rate of flow of water if coefficients of friction are 0.005, 0.0052, and 0.0048, respectively. Determine the discharge and velocity in each pipe, considering the minor losses and neglecting minor losses.arrow_forward3 BAT For an reinforced concrete two-way slab shown in figure under the load (P). (the slab continuous over all edges - all sides are fixed), Determine (By using yield line theory): A- Draw the Yield line Pattern B- Determine the moment m C- Find The required flexural steel to resist the loads causing the slab to collapse if P = 200 KN, f=28 MPa, fy = 420 MPa d = 120 mm. Use 10 mm bars. (Pmin = 0.002) 6m 8m >2m-)) 3marrow_forwardREINFORCED CONCRETE DESIGNANALYSIS OF SINGLY REINFORCED BEAMS (STRENGTH DESIGN METHOD)Direction:Solution must be completeUse ballpen/inkpenAnswer in two decimal placesBox your final answerarrow_forward
 Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning



