
Concept explainers
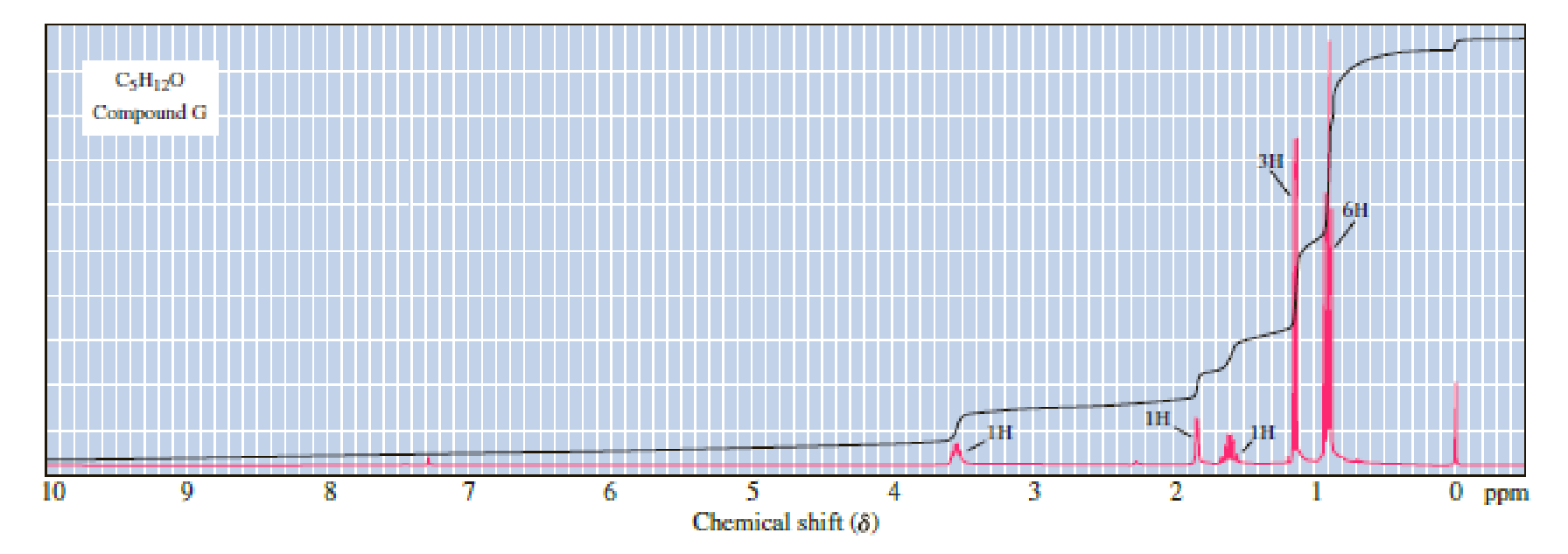
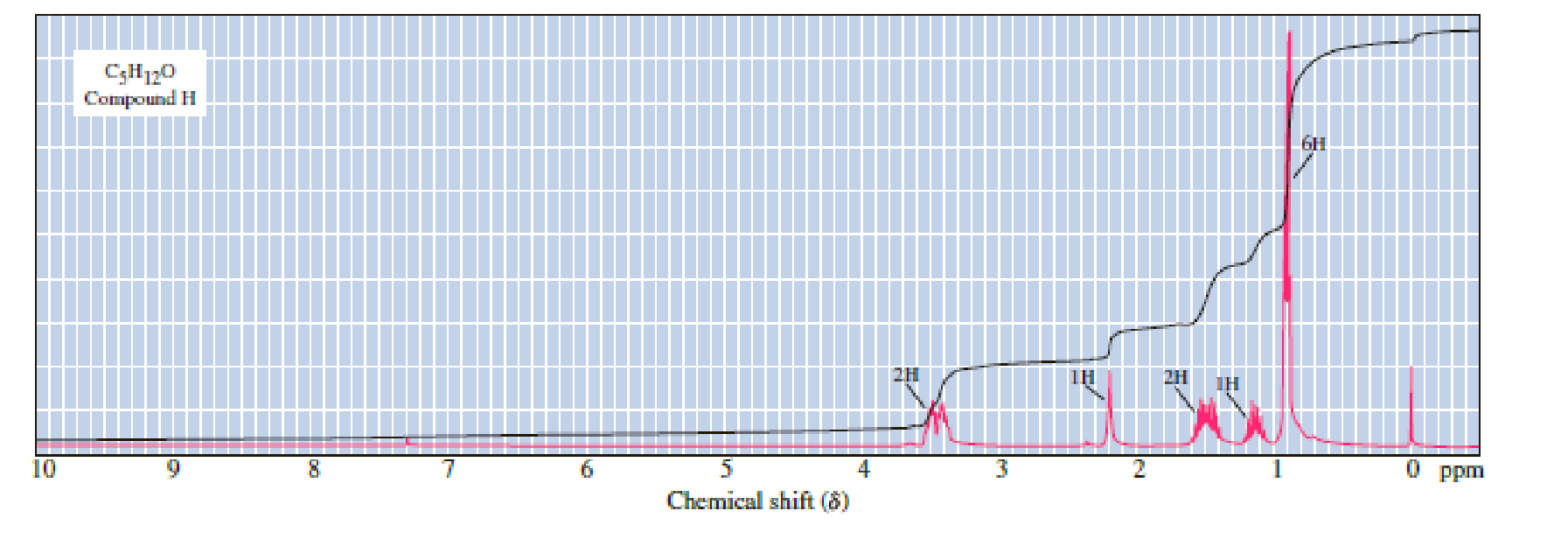
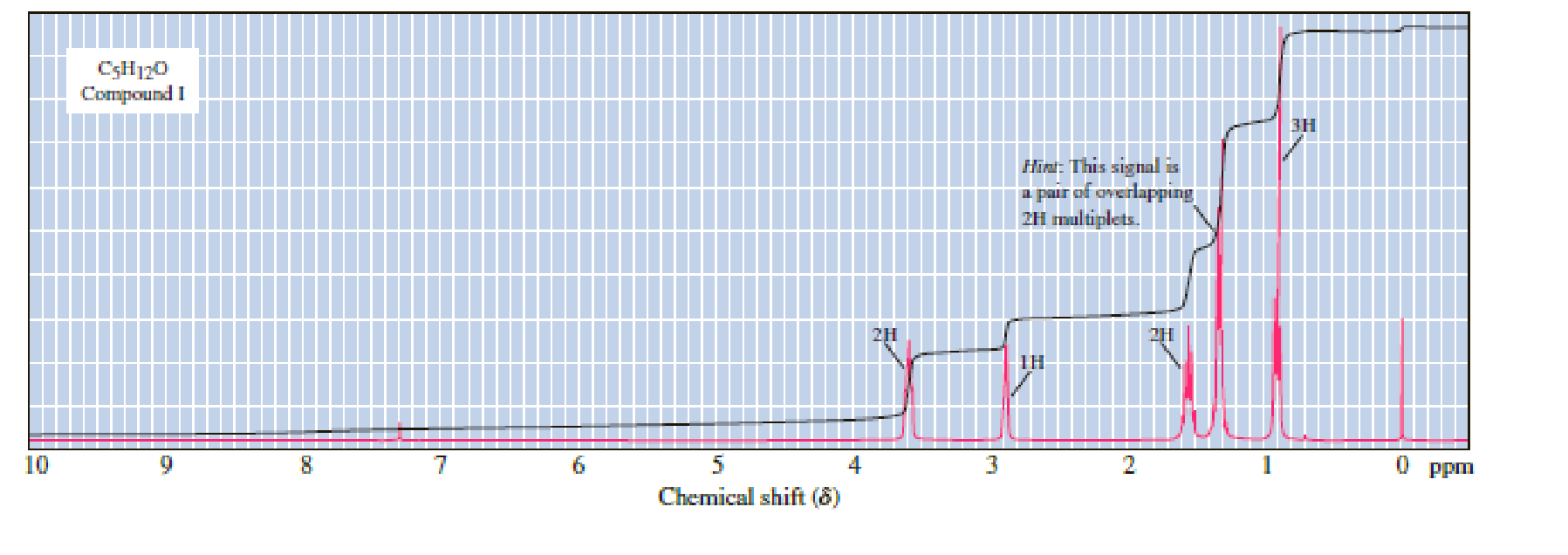
Following are 1H-NMR spectra for compounds G, H, and I, each with the molecular formula C5H12O. Each is a liquid at room temperature, is slightly soluble in water, and reacts with sodium metal with the evolution of a gas.
(a) Propose structural formulas of compounds G, H, and I.
(b) Explain why there are four lines between δ 0.86 and 0.90 for compound G.
(c) Explain why the 2H multiplets at δ 1.5 and 3.5 for compound H are so complex.
(a)
Interpretation:
Following compounds G,H and I stractural formula has to be proposed with the help of given molecular formula
Concept introduction:
The
Chemical shift: The NMR spectrum of any compound is taken with reference to a standard compound called reference compound. Generally, tetramethylsilane (TMS) is taken as the reference compound. The methyl protons of TMS are equivalent and produces only one sharp peak at the rightmost end of the scale.
The distance between the TMS signal and the signals produced by the compound is called the chemical shift. Chemical shift basically measures the shift in the signal position of the compound with respect to the reference signal.
Chemical shift in delta scale is given as,
Explanation of Solution
Index of Hydrogen Deficiency (IHD) calculation,
Given molecular formula is
We calculate the
From the molecular formula, there is an index of hydrogen deficiency is zero for these molecules, so there are no rings (or) double bonds.
The fact that the compounds are slightly soluble in water and react with sodium metal indicates that each molecule has an hydroxyl
The
There are 5 peaks observed in the given
A multiplet is observed for 1 hydrogen at around
The one doublet is observed for 1 hydrogen at around
Another one multiplet is observed for one hydrogen at around
One doublet is observed for 3 hydrogens at around
The one doublet is observed for 6 hydrogens at around
Based on the above
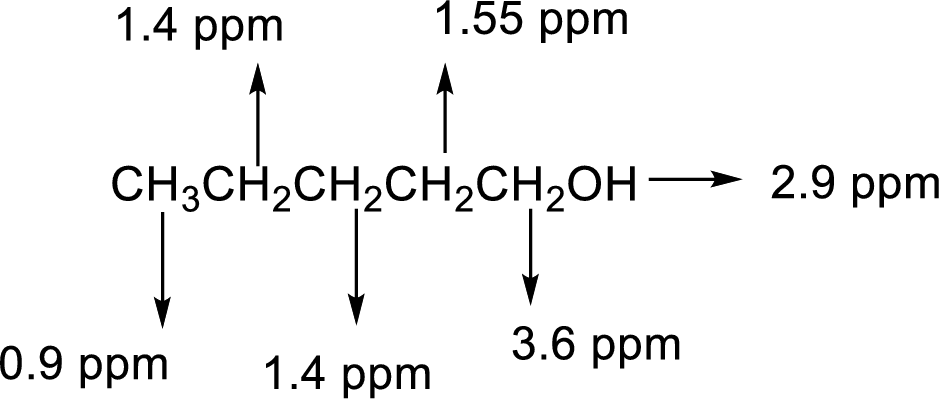
The
There are 5 peaks observed in the given
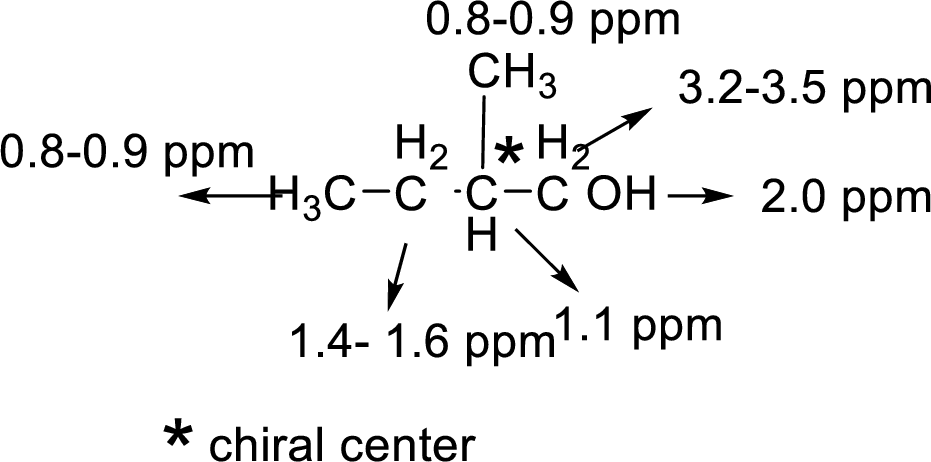
The
There are 5 peaks observed in the given
Based on the above
(b)
Interpretation:
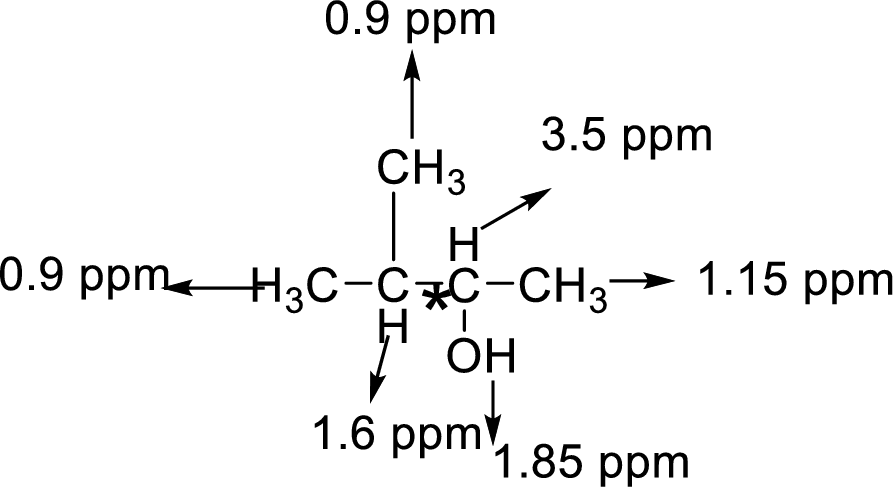
The following compound-G has four lines observed in the range of
Concept introduction:
The
Diastereotopic: If the protons are not interchangeable by either of the symmetry operations, then the protons are Diastereotopic; the protons are not chemically equivalent if a chiral center present in the molecule.
Explanation of Solution
Let us consider the given compound-G:

Above the molecule, the carbon atom 2 attached with hydroxyl
That is makes the two methyl groups are diastereotopic, so they have different chemical shifts, the four lines are actually two doublets.
(c)
Interpretation:
The Following compound-H is two hydrogens appread at multiplet, this compound is complex or not, the behaind reason should be explained.
Concept introduction:
The
Chemical shift: The NMR spectrum of any compound is taken with reference to a standard compound called reference compound. Generally, tetramethylsilane (TMS) is taken as the reference compound. The methyl protons of TMS are equivalent and produces only one sharp peak at the rightmost end of the scale.
The distance between the TMS signal and the signals produced by the compound is called the chemical shift. Chemical shift basically measures the shift in the signal position of the compound with respect to the reference signal.
Chemical shift in delta scale is given as,
Diastereotopic: If the protons are not interchangeable by either of the symmetry operations, then the protons are Diastereotopic; the protons are not chemically equivalent if a chiral center present in the molecule.
Explanation of Solution
Let us consider the given compound-H:
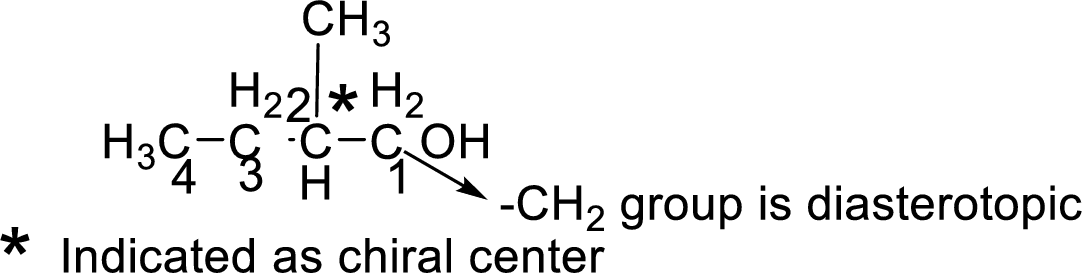
Above the molecule, the carbon atom 2 attached with hydroxyl
This chiral center makes the adjacent
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Physical Universe
Physical Science
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology (12th Edition)
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
- 9. Write Me product as well as the reaction Mechanism For each of the Following Vanctions +H₂504 4.50+ T C. +212 Fellz 237 b. Praw the potential energy Diagrams For each OF Mese Rauctions and account For any differences that appear in the two potential Puergy Diagrams which of here two reactions 19 Found to be Reversable, Rationalice your answer based upon the venation mechanisms and the potential energy diagrams.arrow_forward9. Write Me product as well as the reaction Mechanism For each of the Following Veritious +H2504 4.50+ + 1/₂ Felly ◎+ 7 b. Praw he potential energy Diagrams For each OF Mese Ronctions and account for any differences that appeak in the two potential Puergy Diagramsarrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Incorrect, 3 attempts remaining 1. excess Br2, NaOH 2. neutralizing workup Qarrow_forward
- Given the electrode Pt | Ag | Ag+ (aq), describe it.arrow_forwardAt 25°C, the reaction Zn2+ + 2e ⇄ Zn has a normal equilibrium potential versus the saturated calomel electrode of -1.0048 V. Determine the normal equilibrium potential of Zn versus the hydrogen electrode.Data: The calomel electrode potential is E° = 0.2420 V versus the normal hydrogen electrode.arrow_forwardElectrochemistry. State the difference between E and E0.arrow_forward
- In an electrolytic cell, the positive pole is always assumed to be on the right side of the battery notation. Is that correct?arrow_forwardIn an electrolytic cell, the positive pole is always assumed to be on the right side of the battery. Is that correct?arrow_forwardCalculate the free energy of formation of 1 mol of Cu in cells where the electrolyte is 1 mol dm-3 Cu2+ in sulfate solution, pH 0. E° for the Cu2+/Cu pair in this medium is +142 mV versus ENH.Assume the anodic reaction is oxygen evolution.Data: EH2 = -0.059 pH (V) and EO2 = 1.230 - 0.059 pH (V); 2.3RT/F = 0.059 Varrow_forward
- If the normal potential for the Fe(III)/Fe(II) pair in acid at zero pH is 524 mV Hg/Hg2Cl2 . The potential of the saturated calomel reference electrode is +246 mV versus the NHE. Calculate E0 vs NHE.arrow_forwardGiven the galvanic cell whose scheme is: (-) Zn/Zn2+ ⋮⋮ Ag+/Ag (+). If we know the normal potentials E°(Zn2+/Zn) = -0.76V and E°(Ag+/Ag) = 0.799 V. Indicate the electrodes that are the anode and the cathode and calculate the E0battery.arrow_forwardIndicate the functions that salt bridges have in batteries.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
