
To find:
a) Write the rate law for the given reaction and the value of the rate constant at
b) Calculate the activation energy of the reaction from given data.
Answer to Problem 13.142QA
Solution:
a) The rate law for the given reaction is
b) The activation energy of the reaction is
Explanation of Solution
1) Concept:
We can write the rate law for the reaction as
We need to find the values of x, y to write complete rate law and then find the rate constant k of the reaction.
2) Given:
We are given the table for the values of initial concentrations and initial rates of
| Experiment | Initial Rate |
||
3) Calculations:
a) We need to first find the order of reaction with respect to
Using the general equation of rate law,
We can write rate equations for all the experiments as
Now by taking the ratio of equation (1) and (2), we can find value of x.
Now, to find value of y, we have to take ratio of equation (2) and equation (3) and put
Thus, we can write the rate law equation as
1. Using this rate law and the values of concentrations and initial rates, we can find the rate constant,
i) So from experiment 1, rate law is
ii) From experiment 2, rate law is
iii) From experiment 3, rate law is
The average value of rate constant
b) To find the activation energy, we have to plot the graph of
We have given table for the values of rate constants at different temperatures.
The plot of
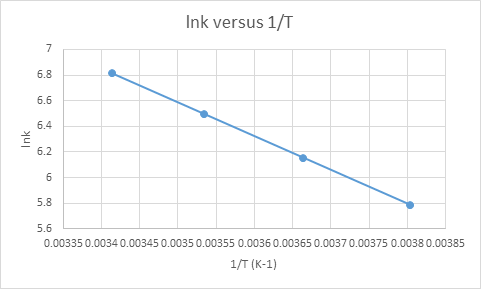
The activation energy would be
Conclusion:
a) The rate law for the given reaction is
b) The activation energy of the reaction is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Chemistry: An Atoms-Focused Approach (Second Edition)
- 10. The most important reason why Br- is a better nucleophile than Cl-is ___. A. polarizability; B. size; C. solvation; D. basicity; E. polarity. Please include all steps. Thanks!arrow_forwardPredicting the qualitative acid-base properties of salts Consider the following data on some weak acids and weak bases: base acid Ка K₁₁ name formula name formula nitrous acid HNO2 4.5×10 4 pyridine CHEN 1.7 × 10 9 4 hydrofluoric acid HF 6.8 × 10 methylamine CH3NH2 | 4.4 × 10¯ Use this data to rank the following solutions in order of increasing pH. In other words, select a '1' next to the solution that will have the lowest pH, a '2' next to the solution that will have the next lowest pH, and so on. solution 0.1 M NaNO2 0.1 M KF pH choose one v choose one v 0.1 M C5H5NHBr 0.1 M CH3NH3CI choose one v ✓ choose one 1 (lowest) 2 ☑ 3 4 (highest) 000 18 Ararrow_forward4. The major product from treatment of 2-propanol with the Jonesreagent is ___.A. acetone; B. none of the other answers is correct C. propene; D.propanoic acid; E carbon dioxide. Please include all steps! Thank you!arrow_forward
- 7. All of the following compounds that are at the same oxidation levelare ___.u. methyl epoxide, v. propyne, w. propanal, x. propene,y. 2,2-dihydroxypropane, z. isopropanol?A. u,v,w,y; B. u,v,w; C. v,w,y,z; D. v, z; E. x,y,z Please include all steps. Thank you!arrow_forward9. Which one of the following substituents is the worst leaving group inan SN2 reaction? A. -NH2; B. -OH; C. –F; D. NH3; E. H2O Please include all steps. Thanks!arrow_forwardUsing the general properties of equilibrium constants At a certain temperature, the equilibrium constant K for the following reaction is 2.5 × 105: CO(g) + H2O(g) CO2(g) + H2(g) Use this information to complete the following table. Suppose a 7.0 L reaction vessel is filled with 1.7 mol of CO and 1.7 mol of H2O. What can you say about the composition of the mixture in the vessel at equilibrium? What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. CO2(9)+H2(g) CO(g)+H₂O(g) What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. 3 CO(g)+3H2O(g) = 3 CO2(g)+3H2(g) There will be very little CO and H2O. x10 There will be very little CO2 and H2. 000 Neither of the above is true. K = ☐ K = ☐ 18 Ararrow_forward
- 8. When ethane thiol is treated with hydrogen peroxide the product is___.A. ethane disulfide; B. diethyl sulfide; C. ethane sulfoxide; D. ethanesulfate; E. ethyl mercaptan. Please include all steps. Thanks!arrow_forward5. The major product of the three step reaction that takes place when 1-propanol is treated with strong acid is?A. dipropyl ether; B. propene; C. propanal; D. isopropyl propyl ether;E. 1-hexanol Please include all steps. Thank you!arrow_forward6. The formula of the product of the addition of HCN to benzaldehydeis ___.A. C8H7NO; B. C8H6NO; C. C14H11NO; D. C9H9NO; E. C9H8NO Please include all steps. Thank you!arrow_forward
- Predicting the qualitative acid-base properties of salts Consider the following data on some weak acids and weak bases: base acid K K a name formula name formula nitrous acid HNO2 4.5×10 hydroxylamine HONH2 1.1 × 10 8 hypochlorous acid HCIO 8 3.0 × 10 methylamine CH3NH2 | 4.4 × 10¯ 4 Use this data to rank the following solutions in order of increasing pH. In other words, select a '1' next to the solution that will have the lowest pH, a '2' next to the solution that will have the next lowest pH, and so on. 0.1 M KCIO solution PH choose one 0.1 M NaNO2 0.1 M CH3NH3Br 0.1 M NaBr choose one ✓ choose one v ✓ choose one 1 (lowest) ☑ 2 3 4 (highest)arrow_forwardFor this Orgo problem, don't worry about question 3 below it. Please explain your thought process, all your steps, and also include how you would tackle a similar problem. Thank you!arrow_forwardUsing the general properties of equilibrium constants At a certain temperature, the equilibrium constant K for the following reaction is 0.84: H2(g) + 2(g) 2 HI(g) = Use this information to complete the following table. Suppose a 34. L reaction vessel is filled with 0.79 mol of HI. What can you say about the composition of the mixture in the vessel at equilibrium? There will be very little H2 and 12. ☐ x10 There will be very little HI. Neither of the above is true. What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. 2 HI(g) H₂(9)+12(9) K = What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. 2 H2(g)+212(9) 4 HI(g) K = ☐ ☑arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





