
Concept explainers
At what approximate positions might the following compounds show IR absorptions?
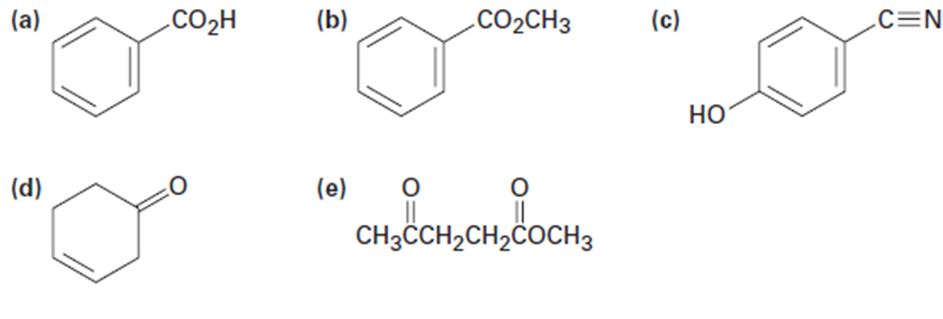
a)
Interpretation:
The approximate absorption frequency has to be given for compound.
Concept introduction:
Spectroscopy: It is study of the interaction of matter and electromagnetic radiation, a continuum of different types of electromagnetic radiation each associated with a particular energy range makes up the electromagnetic spectrum.
IR frequency (cm-1): It is the number of wave crests that pass by a given point in one second frequency has units of hertz (Hz).
Stretch vibrations: It is a vibration occurring along the line of the bond a stretching vibration changes the bond length.
Bending vibrations: It is a vibration that does not occur along the line of the bond, bending vibration changes the bond angle.
Answer to Problem 33AP
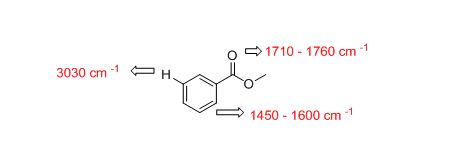
The IR absorptions values at 1450-1600 cm-1 is for carbon double bond carbon stretching frequency, 3030 cm-1 is for aromatic carbon hydrogen stretching frequency, 1710-1760 cm-1 is for acid carbonyl frequency and 2500-3100 cm-1 is for acid hydroxyl frequency.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The approximate absorption frequency for the given compound,
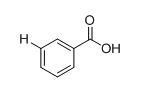
The IR absorptions values at 1450-1600 cm-1 is for carbon double bond carbon stretching frequency, 3030 cm-1 is for aromatic carbon hydrogen stretching frequency, 1710-1760 cm-1 is for acid carbonyl frequency and 2500-3100 cm-1 is for acid hydroxyl frequency.
Therefore, the approximate absorption frequency for the given compound is shown below,
The approximate absorption frequency is given for compound.
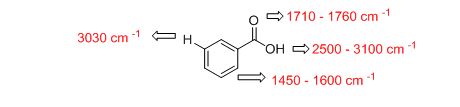
b)
Interpretation:
The approximate absorption frequency has to be given for compound.
Concept introduction:
Spectroscopy: It is study of the interaction of matter and electromagnetic radiation, a continuum of different types of electromagnetic radiation each associated with a particular energy range makes up the electromagnetic spectrum.
IR frequency (cm-1): It is the number of wave crests that pass by a given point in one second frequency has units of hertz (Hz).
Stretch vibrations: It is a vibration occurring along the line of the bond a stretching vibration changes the bond length.
Bending vibrations: It is a vibration that does not occur along the line of the bond, bending vibration changes the bond angle.
Answer to Problem 33AP
The IR absorptions values at 1450-1600 cm-1 is for carbon double bond carbon stretching frequency, 3030 cm-1 is for aromatic carbon hydrogen stretching frequency, 1710-1760 cm-1 is for acid carbonyl frequency and 2500-3100 cm-1 is for acid hydroxyl frequency.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The approximate absorption frequency for the given compound,
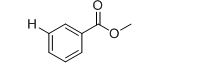
The IR absorptions values at 1450-1600 cm-1 is for carbon double bond carbon stretching frequency, 3030 cm-1 is for aromatic carbon hydrogen stretching frequency, 1710-1760 cm-1 is for acid carbonyl frequency and 2500-3100 cm-1 is for acid hydroxyl frequency.
Therefore, the approximate absorption frequency for the given compound is shown below,
The difference between given pairs of isomers is explained by using infrared spectroscopy.
c)
Interpretation:
The difference between given pairs of isomer has to be explained by using infrared spectroscopy.
Concept introduction:
Spectroscopy: It is study of the interaction of matter and electromagnetic radiation, a continuum of different types of electromagnetic radiation each associated with a particular energy range makes up the electromagnetic spectrum.
IR frequency (cm-1): It is the number of wave crests that pass by a given point in one second frequency has units of hertz (Hz).
Stretch vibrations: It is a vibration occurring along the line of the bond a stretching vibration changes the bond length.
Bending vibrations: It is a vibration that does not occur along the line of the bond, bending vibration changes the bond angle.
Answer to Problem 33AP
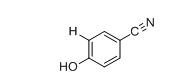
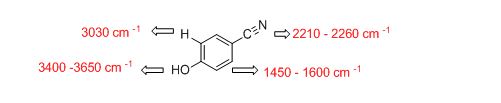
The IR absorptions values at 1450-1600 cm-1 is for carbon double bond carbon stretching frequency, 3030 cm-1 is for aromatic carbon hydrogen stretching frequency, 2210-2260 cm-1 is for acid carbonyl frequency and 3400-3650 cm-1 is for acid hydroxyl frequency.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The approximate absorption frequency for the given compound,
The IR absorptions values at 1450-1600 cm-1 is for carbon double bond carbon stretching frequency, 3030 cm-1 is for aromatic carbon hydrogen stretching frequency, 2210-2260 cm-1 is for acid carbonyl frequency and 3400-3650 cm-1 is for acid hydroxyl frequency.
Therefore, the approximate absorption frequency for the given compound is shown below,
The difference between given pairs of isomers is explained by using infrared spectroscopy.
d)
Interpretation:
The difference between given pairs of isomer has to be explained by using infrared spectroscopy.
Concept introduction:
Spectroscopy: It is study of the interaction of matter and electromagnetic radiation, a continuum of different types of electromagnetic radiation each associated with a particular energy range makes up the electromagnetic spectrum.
IR frequency (cm-1): It is the number of wave crests that pass by a given point in one second frequency has units of hertz (Hz).
Stretch vibrations: It is a vibration occurring along the line of the bond a stretching vibration changes the bond length.
Bending vibrations: It is a vibration that does not occur along the line of the bond, bending vibration changes the bond angle.
Answer to Problem 33AP
The IR absorptions values at 1640-1680 cm-1 is for carbon double bond carbon stretching frequency, 3020-3100 cm-1 is for vinylic carbon hydrogen stretching frequency and 1715 cm-1 is for acid hydroxyl frequency.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The approximate absorption frequency for the given compound,
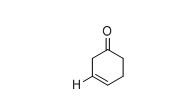
The IR absorptions values at 1640-1680 cm-1 is for carbon double bond carbon stretching frequency, 3020-3100 cm-1 is for vinylic carbon hydrogen stretching frequency and 1715 cm-1 is for acid hydroxyl frequency.
Therefore, the approximate absorption frequency for the given compound is shown below,
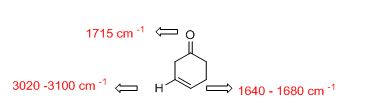
The difference between given pairs of isomers is explained by using infrared spectroscopy.
e)
Interpretation:
The difference between given pairs of isomer has to be explained by using infrared spectroscopy.
Concept introduction:
Spectroscopy: It is study of the interaction of matter and electromagnetic radiation, a continuum of different types of electromagnetic radiation each associated with a particular energy range makes up the electromagnetic spectrum.
IR frequency (cm-1): It is the number of wave crests that pass by a given point in one second frequency has units of hertz (Hz).
Stretch vibrations: It is a vibration occurring along the line of the bond a stretching vibration changes the bond length.
Bending vibrations: It is a vibration that does not occur along the line of the bond, bending vibration changes the bond angle.
Answer to Problem 33AP
The IR absorptions values at 1715 cm-1 is for carbonyl (ketone) stretching frequency and 1735 cm-1 is for carbonyl ester frequency.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The approximate absorption frequency for the given compound,
The IR absorptions values at 1715 cm-1 is for carbonyl (ketone) stretching frequency and 1735 cm-1 is for carbonyl ester frequency.
Therefore, the approximate absorption frequency for the given compound is shown below,
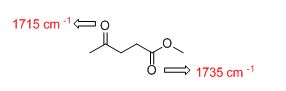
The difference between given pairs of isomers is explained by using infrared spectroscopy.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual eBook, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card for McMurry's Organic Chemistry, 9th
- For each of the substituted benzene molecules below, determine the inductive and resonance effects the substituent will have on the benzene ring, as well as the overall electron-density of the ring compared to unsubstituted benzene. Molecule Inductive Effects O donating O withdrawing O no inductive effects Resonance Effects Overall Electron-Density ○ donating ○ withdrawing O no resonance effects O electron-rich O electron-deficient O similar to benzene Cl O donating O withdrawing ○ donating ○ withdrawing O no inductive effects O no resonance effects O Explanation Check O electron-rich O electron-deficient similar to benzene X © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessarrow_forwardIdentifying electron-donating and For each of the substituted benzene molecules below, determine the inductive and resonance effects the substituent will have on the benzene ring, as well as the overall electron-density of the ring compared to unsubstituted benzene. Molecule Inductive Effects NH2 ○ donating NO2 Explanation Check withdrawing no inductive effects Resonance Effects Overall Electron-Density ○ donating O withdrawing O no resonance effects O donating O withdrawing O donating withdrawing O no inductive effects Ono resonance effects O electron-rich electron-deficient O similar to benzene O electron-rich O electron-deficient O similar to benzene olo 18 Ar 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forwardRank each of the following substituted benzene molecules in order of which will react fastest (1) to slowest (4) by electrophilic aromatic substitution. Explanation Check Х (Choose one) OH (Choose one) OCH3 (Choose one) OH (Choose one) © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centerarrow_forward
- Assign R or S to all the chiral centers in each compound drawn below porat bg 9 Br Brarrow_forwarddescrive the energy levels of an atom and howan electron moces between themarrow_forwardRank each set of substituents using the Cahn-Ingold-Perlog sequence rules (priority) by numbering the highest priority substituent 1.arrow_forward

 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


